2547
MRI enhancement of TPP-TEMPOL during reduces kidney damage1School of Biomedical Engineering, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
In this study, we synthesis a mitochondria-targeted contrast agent named triphenylphosphine-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TPP-TEMPOL) to protect the kidney from the damage induced by rhabdomyolysis. At the same time, measured the T1 changes by MRI.
Introduction
Triphenylphosphine (PPh3) was supposed to mitochondria target in previous studies[1]. 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPOL) has been approved as a MRI contrast agent which can eliminate thereactive oxygen species (ROS) and decrease the damage of acute kidney injure (AKI)[2]. Here, we connect the triphenylphosphine with TEMPOL to constrcut mitochondria targeted TEMPOL (TPP-TEMPOL) for targeting the mitochondria, intervening the early damage of AKI induced by glycerol, and MR imaging.Method
Phantoms: TPP-TEMPOL were dissolved in phosphate buffer solution (PBS, pH=7.4), concentration was 0~120 mM.Animal: Animal studies have been approved by our Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. C57BL/6 mouse (8 weeks, n=24) were divided into four groups randomly, control + Saline, control+ TPP-TEMPOL, AKI + Saline and AKI + TPP-TEMPOL. AKI mouse were fasted water for 16 hours, and injected 50% glycerol (7 ml/kg, saline) in the mouse’s limb. 2h later, the saline or TPP-TEMPOL (6.25 mg/ml, 5ml/kg) was injected in tail vein, then MR imaging was conducted. 24h later, all mouse were sacrificed for HE stain and sera diagnosis.
MRI: All MRI studies were conducted on a 7 T animal MRI scanner (Bruker Biospec, Billerica, MA). Inversion recovery (IR) sequence with rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement (RARE) readout was used for T1 value measurement. Repetition time (TR) /echo time (TE)=8000/40 ms, inversion time= 10.5, 20, 30, 40, 50 100, 300, 500 800, 1000, 1500, 2000, 4000.
Pathology:Mouse’s blood were centrifuge for sera (3000 rpm, 15 min, 4℃), then, BUN concentration was measured by ELISA. Kidneys were collected, weighed, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The images were taken by an upright microscope (Olympus BX43) with a 100× oil objective (UPlanSApo, NA: 1.40).
Statistical Analysis: All data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA), shown as mean ± SD and analyzed by the unpaired, two‐tailed Student t‐test assuming equal variances. Differences were considered significant at P < 0.05.
Result
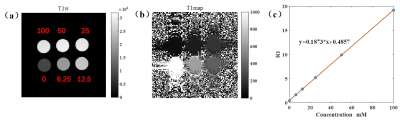
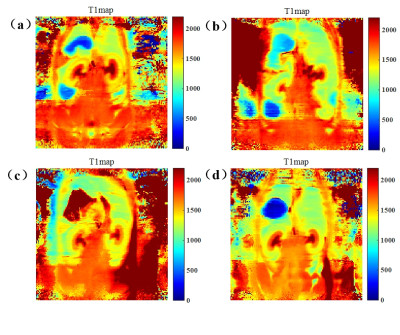
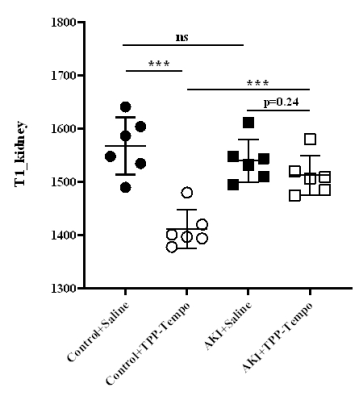
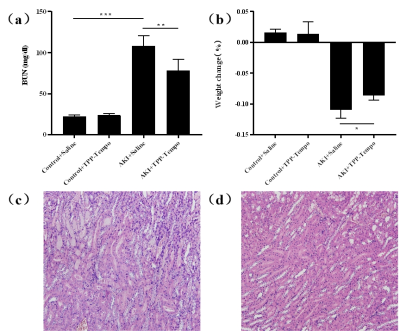
As shown in Figure 1, the longitudinal relaxivities (r1) was determined to 0.1873 mM-1/s-1. T1-map of kidney in different group were shown (Figure 2). After injection of TPP-TEMPOL, the T1 value of kidney in AKI group is different with that in control group. It seems that TPP-TEMPOL exhibits MRI enhancement in vivo. As shown in Figure 3, BUN of AKI group increased dramatically compare to that of AKI treated group. Weight loss in AKI group is smaller than that of control group. Figure 3c shown the H&E stain of AKI group, a large number of inflammatory cells infiltrated into the renal interstitial space and protein tubes appeared. However, in treated AKI group (Figure 3d), tubules were much more normal. These all confirmed that TPP-TEMPOL can mitigate damage from AKI.Discusion and Conclusion
In this study, we aimed to use mitochondria target contrast agents (TPP-TEMPOL) to alleviate the damage of AKI and monitor the T1 changes by MR scanner. The result confirmed that TPP-TEMPOL can protect from the injure induce by ROS. However, more reliable blood index should be investigated in future experiments.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Zhong X C, Shi M H, Liu H N, et al. Mitochondrial targeted doxorubicin derivatives delivered by ROS-responsive nanocarriers to breast tumor for overcoming of multidrug resistance[J]. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 2020: 1-9.
2. Aksu U, Ergin B, Bezemer R, et al. Scavenging reactive oxygen species using tempol in the acute phase of renal ischemia/reperfusion and its effects on kidney oxygenation and nitric oxide levels[J]. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental, 2015, 3(1): 1-10.
Figures