2527
Renal lipid content based on PDFF Imaging is a new potential biomarker for assessing early renal injury in patients with metabolic syndrome1Department of Medical Imaging, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China, 3Department of Nephrology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University (Academy of Orthopedics· Guangdong Province), Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
Renal fat content has been known as correlated with renal injury in type 2 diabetes. However, it is not clear the change of renal fat content in patients with metabolic syndrome (MS), which is a more popular disease threatened human health. In the present study, we assess the feasibility and reproducibility of renal fat fraction (FF) using PDFF imaging with MR mDixon-Quant sequence. And we aim to investigate the changes of renal FF in patients with MS, whose estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) grade were G1(normal or elevated) and G2(mild decline) described in KDIGO (Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes). In addition, we evaluate the correlation of renal FF and eGFR and the major factors of eGFR. The results show that with eGFR decreasing, renal FF in patients with MS-G2 group increased significantly compared with control and MS-G1 group. And the renal FF is an important affection factor of eGFR with a significant negative correlation. The noninvasive quantitative Dixon-based MRI may be a new biomarker for the evaluation of early renal impairment.
Background/Introduction
Metabolic syndrome(MS), as an important risk fator for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular, is a serious threat to human health. At present, it is also considered as an independent risk factor for chronic kidney disease(CKD). During obesity for MS patients, surplus energy will be deposited in various tissues and organs in the form of adipose and contributes to their damage through toxic processes named lipotoxici [1, 2]. Therefore, accurate measurement of renal fat content in patients with MS is of great significance for the evaluation of renal function changes and the detection of early renal injury. MR PDFF imaging is an invaluable tool for evaluation of fat content in kidney [3, 4]. In this study, we explored the value of renal lipid content based on PDFF imaging for the assessment of early renal injury in patients with metabolic syndrome, and investigate the relationship between renal FF and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).Methods
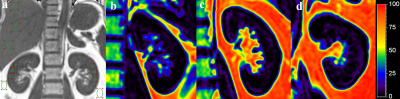
24 MS patients (G1, eGFR≥90ml, n=10; G2, 60≤ eGFR<90ml, n=14)and 23 non-MS volunteers were included. All participants received 3D multiecho Dixon gradient-recalled echo sequence (mDixon-Quant) using a 3.0-T magnetic resonance scanner (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands). The FF of renal, hepatic, perirenal adipose were measured(Fig.1a). And triglyceride(TG), high density lipoprotein(HDL), low density lipoprotein(LDL), Serum creatinine(SCr), cholesterol(Cho), waistline and eGFR were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA, bonferroni post-hoc analysis, repeatability test, multivariable analysis, and Pearson correlation test.Results
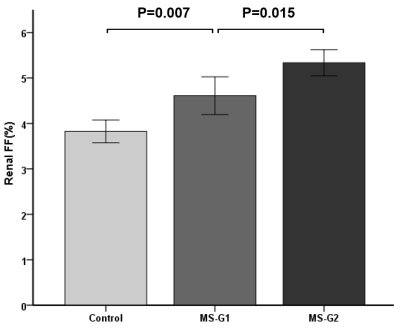
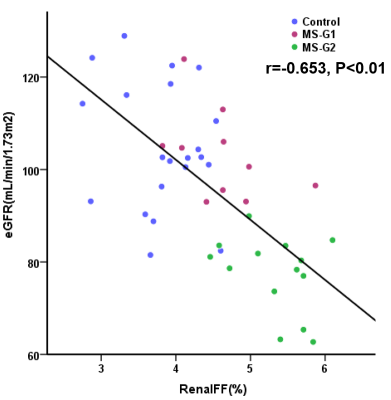
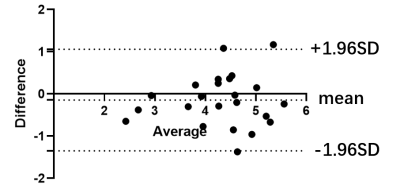
Renal FF of MS-G2 group (5.34 ±0.50%)was significantly higher than that of MS-G1group and non-MS groups (4.61±0.58% and 3.83±0.55% respectively, P<0.01) , shown as Figure 1 and 2. There was a significant negative correlation between eGFR and renal FF (r=-0.653, P<0.01, in all participants, shown in Figure 3). Multi factor analysis showed that Scr and renal FF were significantly correlated with eGFR (Model 1-2 R=0.778, 0.852 respectively). The repeatability of renal FF measurements was high and with a good interclass correlation coefficient of 0.845 for observer A and observer B(shown as Figure 4).Conclusion
The MS patients whose eGFR were mild decline had a highest renal FF compared with MS patients with nomal or elevated eGFR and healthy subjects. Renal fat deposition in patients with MS maybe majorly contributed to the early decrease of eGFR. The noninvasive quantitative Dixon-based MRI can be a new biomarker for the evaluation of early renal impairment.Acknowledgements
Xiaodong Zhang and Yongqiang Li are both co-corresponding authors.
Funding: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (81801653), Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2017B090912006)
References
1. Peng XG, Bai YY, Fang F, et al. Renal lipids and oxygenation in diabetic mice: noninvasive quantification with MR imaging. Radiology 2013; 269(3):748–757. 2. Weinberg JM. Lipotoxicity. Kidney Int2006;70(9):1560–1566 3. Yokoo T, Clark HR, Pedrosa I, et al. Quantification of renal steatosis in type II diabetes mellitus using Dixon-based MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 2016; 44(5):1312–1319. 4. Wang YC, Feng YL, Lu CQ, et al. Renal fat fraction and diffusion tensor imaging in patients with early-stage diabetic nephropathy. Eur Radio 2018; 288(8):3326-3334.Figures