2468
Single-shot measurement of sub-millisecond, time-dependent diffusion using optimized, unequal pulse spacings in a static field gradient1Section on Quantitative Imaging and Tissue Sciences, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda, MD, United States, 2Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 3National Institute of General Medical Sciences, Bethesda, MD, United States, 4Celoptics, Inc., Rockville, MD, United States
Synopsis
Time-dependent diffusion contains rich information about the tissue microstructure. Conventional methods to measure the time-varying diffusivity probe a single timescale per acquisition, limiting time resolution. Furthermore, access to sub-millisecond timescales is limited by the pulsed gradient hardware. An alternative method is presented here. We extend the static field gradient, Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill cycle by incrementing the $$$\pi$$$-pulse spacings to isolate the on-resonance signal. The resulting spin echo train probes a range of short timescales (50 – 500 microseconds) in one shot and enables a 1-minute time-dependent diffusivity measurement. Proof-of-principle simulations and experimental results on pure liquids and yeast are presented.
Introduction
Time-dependent diffusion is observed in heterogeneous porous media such as biological tissue [1–4]. This time-varying behavior is related to microstructural parameters such as the barrier surface-to-volume ratio [2,5–7], $$$S/V$$$, and permeability [8–10], $$$\kappa$$$. The short-time behavior [2] of the time-dependent diffusion coefficient, $$$D(t)$$$, with a linear permeability correction [10] is $$D(t)\simeq D_0\left[1-\frac{S}{V}\left(\frac{4\sqrt{D_0t}}{9\sqrt{\pi}}-\kappa t\right)\right],\;t \ll \tau_D,$$ where $$$D_0=D(t)|_{t = 0}$$$ is the free diffusivity, $$$\tau_D=\bar{a}^2/(2D_0)$$$ is the time to diffuse across the mean pore size of $$$\bar{a}\equiv6V/S$$$. NMR methods to characterize $$$D(t)$$$ conventionally use a signal representation [11,12] (with Gaussian phase approximation [13–16]) that relates the normalized echo attenuation to the spectrum of the velocity autocorrelation function, $$\boldsymbol{\mathcal{D}}(\omega)=\frac{1}{2}\int_0^{\infty}e^{i\omega t}\langle \textbf{v}(t)\textbf{v}^\mathrm{T}(0)\rangle dt,$$ and the truncated spectrum of the gradient wavevector, $$\textbf{F}(\omega)=\int_0^{T}e^{i\omega t}\left(\gamma\int_0^{t}\textbf{G}(t')dt'\right)dt,$$ where $$$\gamma$$$ is the gyromagnetic ratio, $$$\textbf{G}(t)$$$ is the gradient waveform, and $$$T$$$ is the time of echo formation, via $$\frac{I(T)}{I_0}=\exp{\left(-\frac{1}{\pi}\int_0^{\infty}\textbf{F}^{\mathrm{T}}(\omega)\boldsymbol{\mathcal{D}}(\omega)\textbf{F}(\omega)d\omega\right)}.$$ This signal representation naturally suggests the use of unidirectional oscillating [17] or “modulated” [12,18,19] gradients to concentrate the spectral density of the 1D $$$F(\omega)$$$ near some frequency, $$$\omega_F$$$. The signal becomes well-approximated by $$\frac{I(T)}{I_0}\approx \exp{\left(b\times\hat{\mathbf{g}}^{\mathrm{T}}\boldsymbol{\mathcal{D}}(\omega_F)\hat{\mathbf{g}}\right)},$$ where $$$b=\int_0^{T}|F(t)|^2dt$$$ and $$$\hat{\mathbf{g}}$$$ is the gradient direction. $$$\hat{\mathbf{g}}^{\mathrm{T}}\boldsymbol{\mathcal{D}}(\omega)\hat{\mathbf{g}}$$$ can then be related back to $$$D(t)$$$ [7,20]. This oscillating gradient, “temporal diffusion spectroscopy” [21] approach has limited time resolution because it individually probes $$$\omega_F$$$. Moreover, the largest probe-able $$$\omega_F$$$ is limited by slew rates to $$$\sim$$$100 Hz [4]. The rich, short-time behavior is inaccessible for structures with $$$\bar{a}\lesssim\mu\mathrm{m}$$$. The static gradient (SG), Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill (CPMG) cycle produces a triangle wave $$$F(t)$$$ and can serve as a high-frequency temporal diffusion spectroscopy method [18,22,23] . SG-CPMG diffusion measurements, however, can be difficult to quantitatively interpret due to off-resonance signal contributions from incorrect coherence transfer pathways (CTPs) [24–26].Theory
We extend the SG-CPMG experiment by discretely incrementing the $$$\pi$$$-pulse spacings in the form: $$$2\tau+m_j\delta$$$, where $$$\tau$$$ is the time between the $$$\pi/2$$$-pulse and the $$$\pi$$$-pulse, $$$j$$$ indexes the pulse-to-pulse spacing, $$$m_j\in\mathbb{N}$$$, and $$$\delta$$$ is a unit time increment. We term this spacing method the SG, time incremented echo train acquisition (SG-TIETA). Timing rules are derived to systematically avoid off-resonance CTPs [27,28]:- $$$h_n$$$ values, i.e., the peaks of $$$|F(t)/\gamma g|$$$, may not be repeated (see Fig. 1)
- $$$m_j$$$ and $$$m_{j\pm\Delta j}$$$ with odd $$$\Delta_j$$$ may not be the same
- Twice any $$$m_j$$$ may not equal the sum of $$$m_{j+\Delta j}$$$ and $$$m_{j-\Delta j}$$$ for even $$$\Delta j$$$
- Any two $$$m_j$$$ with even $$$j$$$ may not equal the sum of any two $$$m_j$$$ with odd $$$j$$$
- Twice any $$$m_j$$$ with even $$$j$$$ may not equal the sum of any two $$$m_j$$$ with odd $$$j$$$ and vice versa
- $$$\delta$$$ and $$$\tau$$$ satisfy $$$(\tau\bmod\delta)=\delta/2$$$ and $$$\delta >2\tau_p$$$, where $$$\tau_p$$$ is the length of the $$$\pi$$$-pulse.
One satisfactory sequence is $$$\tau=49\;\mu\mathrm{s}$$$, $$$\delta = 14\;\mu\mathrm{s}$$$, and $$m_j =\left\{\begin{matrix}1&3&6&7&10&12&11&15&20&21\\24&26&20&21&33&35&33&34&33& ...\end{matrix}\right\}.$$ Extraneous signal decay due to $$$T_2$$$ relaxation and pulse inaccuracy remains. $$$T_2$$$ may be ignored if $$$2\tau+m_j\delta\ll T_2\forall j$$$. Pulse inaccuracy cannot be ignored and is describable using an $$$n$$$-dependent pulse accuracy factor, $$$A_p(n)$$$ [24]. The bandwidth excited by refocusing $$$\pi$$$-pulses has inconsistent frequency content [26,29] such that $$$A_p(n) < 1$$$. With each pulse, spins which rotate by angles other than $$$\pi$$$ do not refocus until a stable, central slice remains. The signal is then corrected as $$$I(T_n)/I_0\times\left[1/\prod_{l=1}^n A_p(l)\;\right].$$$
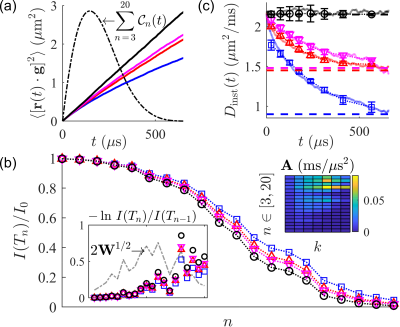
An SG-TIETA experiment produces a range of adjacent, inter-echo timescale sensitivities in one shot, but the spin echo $$$F(\omega)$$$ is too broad to be useful. Ning. et al. [30] showed that an equivalent (1D) time-dependent signal representation is $$\frac{I(T)}{I_0}=\exp{\left(-\int_0^{T}\mathcal{C}(t)D_{\mathrm{inst}}(t)dt\right)},$$ where $$$D_{\mathrm{inst}}(t)=d\left[tD(t)\right]/dt$$$, and $$\mathcal{C}(t)=\gamma^2\int_0^{t}\left(\int_0^{t’}G(t’’)G(t’’+s)ds\right)dt.$$ For each SG-TIETA echo, $$\mathcal{C}_n(t)=\gamma^2g^2\begin{cases} t\left(-\frac{3}{2}t+2h_n\right)&0\leq t\leq h_n\\t\left(\frac{1}{2}t-h_n\right)+2h_n^2&h_n\leq t\leq 2h_n\end{cases}.$$ The problem can now be recast into a weighted and regularized log-linear least squares (LLS) form by discretizing the time domain into bins, $$$\Delta t(k)$$$: $$||\textbf{W}^{1/2}\left(\textbf{A}\textbf{X}-\textbf{B}\right)||_2^2+\lambda||\boldsymbol{\Gamma} \textbf{X}||_2^2,$$ with coefficients, $$\textbf{A}=\begin{bmatrix}\int_{0}^{\Delta t(1)}\mathcal{C}_1(t)\,dt&...&\int_{\Delta t(K-1)}^{\Delta t(K)} \mathcal{C}_1(t)\,dt\\\vdots&&\vdots\\\int_{0}^{\Delta t(1)}\mathcal{C}_N(t)\,dt&...&\int_{\Delta t(K-1)}^{\Delta t(K)}\mathcal{C}_N(t)\,dt\\\end{bmatrix},$$ where $$$\textbf{X}$$$ consists of time-interval $$$D_{\mathrm{inst}}(t)$$$ averages, $$$\textbf{B}^{\mathrm{T}}=-\ln\,\begin{bmatrix}I(T_1)/I_0&...&I(T_N)/I(T_{N-1})\end{bmatrix}$$$, $$$\textbf{W}$$$ consists of signal differences, and $$$\boldsymbol{\Gamma}$$$ contains first and second-order finite difference matrices. This LLS inversion is demonstrated on simulated data in Fig. 2.
Results
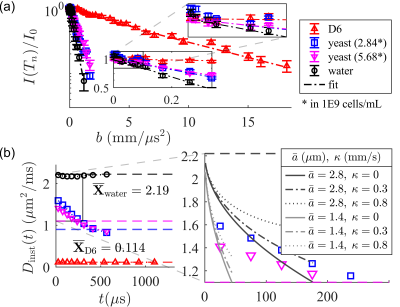
NMR measurements were performed at $$$B_0=0.3239\;\mathrm{T}$$$ (proton $$$\omega_0=13.79\;\mathrm{MHz}$$$) using a PM-10 NMR MOUSE single-sided permanent magnet [31] (Magritek, Aachen Germany) and a Kea 2 spectrometer (Magritek, Wellington, New Zealand). The decay of the magnetic field produces a strong SG with amplitude $$$g=15.3\;\mathrm{T/m}$$$. Measurements used a home-built test chamber and a $$$13\times2$$$ mm solenoid RF coil and RF circuit. Additional information can be found in Ref. [32]. If, indeed, the derived SG-TIETA rules avoid off-resonance CTPs, then (1) the echo shape should reflect a loss of frequency content, and (2) the observed $$$A_p(n)$$$ should be independent of the diffusion weighting. We validate (1) by observing an increase in echo width (Fig. 3) and we validate (2) by obtaining similar calibration $$$A_p(n)$$$ values for liquids with vastly different diffusivities (Fig. 4). SG-TIETA decays for dodecamethylcyclohexasiloxane (D6) and yeast were corrected using the obtained $$$A_p(n)$$$ values for 1-octanol and water, respectively. Decays were then fit with a piece-wise linear function in the log-$$$b$$$ domain specified to produce a $$$(0,0)$$$-intercept and monotonically decreasing slope. The fit serves as non-negativity constraint. Each repetition consisted of $$$32$$$ scans, totaling to a $$$\sim1$$$-minute experiment. Results are summarized in Fig. 5.Acknowledgements
TXC, VW, RR, and PJB were supported by the IRP of the NICHD, NIH. NHW was funded by the NIGMS PRAT Fellowship Award #FI2GM133445-01.References
[1] L. L. Latour, K. Svoboda, P. P. Mitra, and C. H. Sotak, Time-Dependent Diffusion of Water in a Biological Model System., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 1229 (1994).
[2] P. P. Mitra, P. N. Sen, and L. M. Schwartz, Short-Time Behavior of the Diffusion Coefficient as a Geometrical Probe of Porous Media, Phys. Rev. B 47, 8565 (1993).
[3] J. E. Tanner, Self Diffusion of Water in Frog Muscle, Biophys. J. 28, 107 (1979).
[4] O. Reynaud, Time-Dependent Diffusion MRI in Cancer: Tissue Modeling and Applications, Front. Phys. 5, 58 (2017).
[5] L. L. Latour, P. P. Mitra, R. L. Kleinberg, and C. H. Sotak, Time-Dependent Diffusion Coefficient of Fluids in Porous Media as a Probe of Surface-to-Volume Ratio, J. Magn. Reson., Series A 101, 342 (1993).
[6] M. D. Hurlimann, K. G. Helmer, L. L. Latour, and C. H. Sotak, Restricted Diffusion in Sedimentary Rocks. Determination of Surface-Area-to-Volume Ratio and Surface Relaxivity, J. Magn. Reson., Series A 111, 169 (1994).
[7] D. S. Novikov and V. G. Kiselev, Surface-to-Volume Ratio with Oscillating Gradients, J. Magn. Reson. 210, 141 (2011).
[8] P. N. Sen, Time-Dependent Diffusion Coefficient as a Probe of the Permeability of the Pore Wall, J. Chem. Phys. 119, 9871 (2003).
[9] J. E. Tanner, Transient Diffusion in a System Partitioned by Permeable Barriers. Application to NMR Measurements with a Pulsed Field Gradient, J. Chem. Phys. 69, 1748 (1978).
[10] D. S. Novikov, E. Fieremans, J. H. Jensen, and J. A. Helpern, Random Walk with Barriers, Nat. Phys. 7, 508 (2011).
[11] J. Stepišnik, Time-Dependent Self-Diffusion by NMR Spin-Echo, Physica B: Condensed Matter 183, 343 (1993).
[12] P. T. Callaghan and J. Stepišnik, Frequency-Domain Analysis of Spin Motion Using Modulated-Gradient NMR, J. Magn. Reson., Series A 117, 118 (1995).
[13] D. C. Douglass and D. W. McCall, Diffusion in Paraffin Hydrocarbons, J. Chem. Phys. 62, 1102 (1958).
[14] J. Stepišnik, Validity Limits of Gaussian Approximation in Cumulant Expansion for Diffusion Attenuation of Spin Echo, Physica B: Condensed Matter 270, 110 (1999).
[15] A. L. Sukstanskii and D. A. Yablonskiy, Gaussian Approximation in the Theory of MR Signal Formation in the Presence of Structure-Specific Magnetic Field Inhomogeneities, J. Magn. Reson. 163, 236 (2003).
[16] S. Axelrod and P. N. Sen, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spin Echoes for Restricted Diffusion in an Inhomogeneous Field: Methods and Asymptotic Regimes, J. Chem. Phys. 114, 6878 (2001).
[17] M. Schachter, M. D. Does, A. W. Anderson, and J. C. Gore, Measurements of Restricted Diffusion Using an Oscillating Gradient Spin-Echo Sequence, J. Magn. Reson.147, 232 (2000).
[18] J. Stepišnik, S. Lasič, A. Mohorič, I. Serša, and A. Sepe, Spectral Characterization of Diffusion in Porous Media by the Modulated Gradient Spin Echo with CPMG Sequence, J. Magn. Reson.182, 195 (2006).
[19] P. T. Callaghan and J. Stepišnik, Generalized Analysis of Motion Using Magnetic Field Gradients, in Advances in Magnetic and Optical Resonance, edited by W. S. Warren, Vol. 19 (Academic Press, 1996), pp. 325–388.
[20] D. S. Novikov and V. G. Kiselev, Effective Medium Theory of a Diffusion-Weighted Signal, NMR Biomed. 23, 682 (2010).
[21] J. C. Gore, J. Xu, D. C. Colvin, T. E. Yankeelov, E. C. Parsons, and M. D. Does, Characterization of Tissue Structure at Varying Length Scales Using Temporal Diffusion Spectroscopy, NMR Biomed. 23, 745 (2010).
[22] L. J. Zielinski and M. D. Hürlimann, Probing Short Length Scales with Restricted Diffusion in a Static Gradient Using the CPMG Sequence, J. Magn. Reson. 172, 161 (2005).
[23] S. Lasič, J. Stepišnik, and A. Mohorič, Displacement Power Spectrum Measurement by CPMG in Constant Gradient, J. Magn. Reson. 182, 208 (2006).
[24] Y.-Q. Song, Categories of Coherence Pathways for the CPMG Sequence, J. Magn. Reson. 157, 82 (2002).
[25] M. D. Hürlimann and D. D. Griffin, Spin Dynamics of Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill-like Sequences in Grossly Inhomogeneous B0 and B1 Fields and Application to NMR Well Logging, J. Magn. Reson. 143, 120 (2000).
[26] I. Serša, F. Bajd, and A. Mohorič, Effects of Off-Resonance Spins on the Performance of the Modulated Gradient Spin Echo Sequence, Journal of Magnetic Resonance 270, 77 (2016).
[27] Y.-Q. Song, Multiple Modulation Multiple Echoes: A One-Shot Method, Magn. Reson. Imaging 23, 301 (2005).
[28] E. E. Sigmund, H. Cho, and Y.-Q. Song, Multiple-Modulation-Multiple-Echo Magnetic Resonance, Concepts Magn. Reson., Part A 30A, 358 (2007).
[29] B. Geil, Measurement of Translational Molecular Diffusion Using Ultrahigh Magnetic Field Gradient NMR, Concepts Magn. Reson. 10, 299 (1998).
[30] L. Ning., K. Setsompop, C.-F. Westin, and Y. Rathi, New Insights about Time-Varying Diffusivity and Its Estimation from Diffusion MRI, Magn. Reson. Med. 78, 763 (2017).
[31] G. Eidmann, R. Savelsberg, P. Blümler, and B. Blümich, The NMR MOUSE, a Mobile Universal Surface Explorer, J. Magn. Reson. 122, 104 (1996).
[32] N. H. Williamson, R. Ravin, D. Benjamini, H. Merkle, M. Falgairolle, M. J. O’Donovan, D. Blivis, D. Ide, T. X. Cai, N. S. Ghorashi, and others, Magnetic Resonance Measurements of Cellular and Sub-Cellular Membrane Structures in Live and Fixed Neural Tissue, eLife 8, e51101 (2019).
Figures