2365
ALL CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) NEURO- AND VASCULAR-COMMUNICATION CHANNELS ARE SURROUNDED WITH CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)1Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences, Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, United States, 2Neurology, Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, United States, 3Radiology, Wayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, United States, 4Neurology, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, MI, United States
Synopsis
It's well-established that the CNS is completely submerged in CSF; but to what extent is this true regarding the finer spaces within the CNS itself? We used MRI to simultaneously map the presence of CSF within all peri-neural and peri-vascular spaces in vivo in humans. Our findings indicated that all peri-neural spaces surrounding cranial and spinal nerves, as well as all peri-vascular spaces, were filled with CSF. These findings suggest that anatomically, substance exchange between the brain parenchyma and outside tissues (i.e. lymphatics) can only occur through CSF, warranting further investigation into its cerebral waste clearance and immunomodulation implications.
Introduction
CSF penetrates and interacts with the brain parenchyma through the glymphatic pathway.1 Dysfunctions of this glymphatic pathway have been associated with a broad range of neurological diseases including, but not limited to, Alzheimer’s disease and stroke.2-10 Therefore, it has become apparent that gaining a complete understanding of CSF physiology is an essential prerequisite to understanding the pathophysiology underlying neurological disease.It is already very well-established that the CNS is completely submerged in CSF on the outside; but to what extent is this true regarding the finer spaces within the CNS itself? Most studies have asynchronously investigated these spaces and these investigations have been mainly conducted in animals and human cadavers.11-25 Moreover, although CSF-filled peri-vascular spaces in several brain regions have been illustrated in several studies, to our knowledge, there is no systematic study focusing on whether all cerebral vasculature (with the exception of capillaries) are surrounded with CSF, and this can only be revealed using in vivo imaging methods. Therefore, the objective of this study was to use MRI to simultaneously map the presence of CSF within all peri-neural (cranial and spinal nerves) and peri-vascular spaces in vivo in humans.
Methods
Upon IRB approval, we performed four types of experiments, each with 5 participants, using a 3T magnet to image the CSF in the brain and spinal cord. The first experiment employed a 3D T2-weighted (T2W) ‘Sampling Perfection with Application optimized Contrasts using different flip angle Evolution’ (T2W-SPACE) sequence to image the CSF and cranial nerves with hyperintense CSF signal and hypointense signal for cranial nerves and blood vessels. For the second experiment, in order to image CSF in peri-vascular spaces and to demonstrate that all MRI-visible cerebral blood vessels were surrounded by CSF, we used high-resolution ‘STrategically Acquired Gradient Echo’ (STAGE) imaging to simultaneously obtain bright-blood and dark-blood images.26-28 The STAGE imaging included a proton density weighted (PDW) scan and a T1-weighted (T1W) scan. Both images were fully flow compensated with bright blood signal. By subtracting the PDW from the inverted T1W image, one could obtain a synthetic T2W dark-blood image (sT2W) presenting bright-CSF and uniform grey matter and white matter intensities. In addition, we acquired a pure CSF image by using a 3D turbo-spin echo (TSE) sequence. The third experiment was performed on the cervical spinal cord at the C4/C5 level. A 2D T2* weighted spoiled gradient echo sequence (Multiple Echo Data Image Combination, MEDIC) was used to acquire images with hyperintense CSF and blood vessels, and hypointense nerves. The fourth experiment was performed on the lumbar spinal nerves at L3/L4 level. A regular T2W-TSE sequence was used.Results
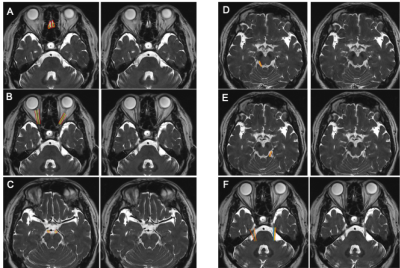
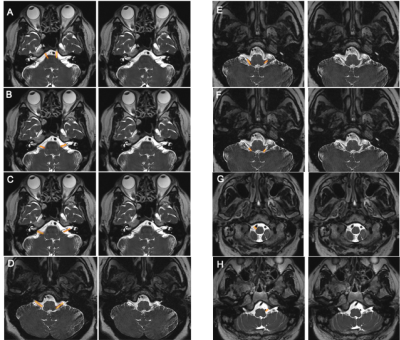
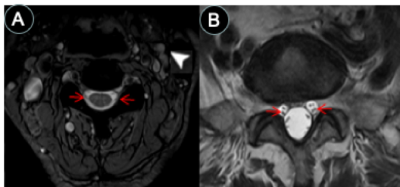
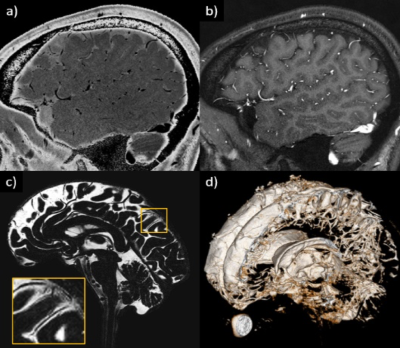
Images from the first experiment were used to visualize all 12 pairs of the cranial nerves (Fig. 1-2). As illustrated, the cranial nerves were hypointense, while the peri-neural spaces surrounding the cranial nerves were hyperintense, indicating the presence of CSF within these spaces. The spinal nerves were visualized on the images from the third and fourth experiments (Fig. 3). Similarly, the spinal nerves were hypointense, while the peri-neural spaces surrounding the spinal nerves were hyperintense, indicating the presence of CSF. The high-resolution (in the order of 100 µm) sT2W (Fig. 4A, bright CSF and dark blood) and T1W (Fig. 4B, bright blood and dark CSF) derived from STAGE imaging demonstrated that all MRI-visible vasculature were surrounded with CSF. By comparing these two images, we found that all MRI-visible vasculature were indeed surrounded by CSF. Moreover, in order to further confirm these findings, we used a T2W-TSE image acquired with a very long echo time to generate “pure” CSF images, with bright CSF and dark blood (Fig. 4C-D). Once again, all MRI-visible vasculature were indeed surrounded with CSF.Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first study to simultaneously and systematically verify that all 12 pairs of cranial nerves, all MRI-visible vasculature and spinal nerves are surrounded with CSF in vivo in humans; as opposed to previous studies that have asynchronously investigated this, mainly in animals and human cadavers. Our findings indicate that all brain parenchyma and spinal cord communication channels, both neuro- and vascular-communication channels, are encased in CSF. Therefore, it logically follows that CSF must play a critical role in substance exchange between the brain parenchyma/spinal cord and its communication channels as well as its surrounding environment/tissue—a role that has been historically underestimated and understudied. Our findings are consistent with previous literature that have asynchronously investigated CSF-filled peri-neural spaces, mostly in the context of CWC lymphatic-associated CSF outflow pathways, as well as peri-vascular spaces.2,29-32Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the following NIH grants: R01-NS108491, RF1-AG057494 and R01-NS108463.References
1. Wang M, Iliff JJ, Liao Y, et al. Cognitive deficits and delayed neuronal loss in a mouse model of multiple microinfarcts. J Neurosci. 2012;32(50):17948-17960.
2. Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid beta. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(147):147ra111.
3. Rangroo Thrane V, Thrane AS, Plog BA, et al. Paravascular microcirculation facilitates rapid lipid transport and astrocyte signaling in the brain. Sci Rep. 2013;3:2582.
4. Plog BA, Dashnaw ML, Hitomi E, et al. Biomarkers of traumatic injury are transported from brain to blood via the glymphatic system. J Neurosci. 2015;35(2):518-526.
5. Mestre H, Tithof J, Du T, et al. Flow of cerebrospinal fluid is driven by arterial pulsations and is reduced in hypertension. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4878.
6. Jiang Q, Zhang L, Ding G, et al. Impairment of the glymphatic system after diabetes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(4):1326-1337.
7. Louveau A, Da Mesquita S, Kipnis J. Lymphatics in Neurological Disorders: A Neuro-Lympho-Vascular Component of Multiple Sclerosis and Alzheimer's Disease? Neuron. 2016;91(5):957-973.
8. Jessen NA, Munk AS, Lundgaard I, Nedergaard M. The Glymphatic System: A Beginner's Guide. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(12):2583-2599.
9. Arbel-Ornath M, Hudry E, Eikermann-Haerter K, et al. Interstitial fluid drainage is impaired in ischemic stroke and Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;126(3):353-364.
10. Mestre H, Du T, Sweeney AM, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid influx drives acute ischemic tissue swelling. Science. 2020;367(6483).
11. Svane-Knudsen V. Resorption of the cerebro-spinal fluid in guinea-pig; an experimental study. Acta Otolaryngol. 1958;49(3):240-251.
12. Bradbury MW, Cserr HF, Westrop RJ. Drainage of cerebral interstitial fluid into deep cervical lymph of the rabbit. Am J Physiol. 1981;240(4):F329-336.
13. Pile-Spellman JM, McKusick KA, Strauss HW, Cooney J, Taveras JM. Experimental in vivo imaging of the cranial perineural lymphatic pathway. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1984;5(5):539-545.
14. Mollanji R, Papaiconomou C, Boulton M, Midha R, Johnston M. Comparison of cerebrospinal fluid transport in fetal and adult sheep. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;281(4):R1215-1223.
15. Mollanji R, Bozanovic-Sosic R, Silver I, et al. Intracranial pressure accommodation is impaired by blocking pathways leading to extracranial lymphatics. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001;280(5):R1573-1581.
16. Mollanji R, Bozanovic-Sosic R, Zakharov A, Makarian L, Johnston MG. Blocking cerebrospinal fluid absorption through the cribriform plate increases resting intracranial pressure. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2002;282(6):R1593-1599.
17. Johnston M, Zakharov A, Papaiconomou C, Salmasi G, Armstrong D. Evidence of connections between cerebrospinal fluid and nasal lymphatic vessels in humans, non-human primates and other mammalian species. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2004;1(1):2.
18. Liu H, Ni Z, Chen Y, et al. Olfactory route for cerebrospinal fluid drainage into the cervical lymphatic system in a rabbit experimental model. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(10):766-771.
19. Krishnamurthy S, Li J, Shen Y, Duncan TM, Jenrow KA, Haacke EM. Normal macromolecular clearance out of the ventricles is delayed in hydrocephalus. Brain Res. 2018;1678:337-355.
20. Ma Q, Ineichen BV, Detmar M, Proulx ST. Outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is predominantly through lymphatic vessels and is reduced in aged mice. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1434.
21. Czerniawska A. Experimental investigations on the penetration of 198Au from nasal mucous membrane into cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Otolaryngol. 1970;70(1):58-61.
22. Kida S, Pantazis A, Weller RO. CSF drains directly from the subarachnoid space into nasal lymphatics in the rat. Anatomy, histology and immunological significance. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1993;19(6):480-488.
23. Boulton M, Young A, Hay J, et al. Drainage of CSF through lymphatic pathways and arachnoid villi in sheep: measurement of 125I-albumin clearance. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1996;22(4):325-333.
24. Zakharov A, Papaiconomou C, Djenic J, Midha R, Johnston M. Lymphatic cerebrospinal fluid absorption pathways in neonatal sheep revealed by subarachnoid injection of Microfil. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2003;29(6):563-573.
25. Brierley JB, Field EJ. The connexions of the spinal sub-arachnoid space with the lymphatic system. J Anat. 1948;82(Pt 3):153-166.
26. Chen Y, Liu S, Wang Y, Kang Y, Haacke EM. STrategically Acquired Gradient Echo (STAGE) imaging, part I: Creating enhanced T1 contrast and standardized susceptibility weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017.
27. Wang Y, Chen Y, Wu D, et al. STrategically Acquired Gradient Echo (STAGE) imaging, part II: Correcting for RF inhomogeneities in estimating T1 and proton density. Magn Reson Imaging. 2017.
28. Haacke EM, Chen Y, Utriainen D, et al. STrategically Acquired Gradient Echo (STAGE) imaging, part III: Technical advances and clinical applications of a rapid multi-contrast multi-parametric brain imaging method. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;65:15-26.
29. Sakka L, Coll G, Chazal J. Anatomy and physiology of cerebrospinal fluid. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2011;128(6):309-316.
30. Pollay M. The function and structure of the cerebrospinal fluid outflow system. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2010;7:9.
31. Chen L, Elias G, Yostos MP, Stimec B, Fasel J, Murphy K. Pathways of cerebrospinal fluid outflow: a deeper understanding of resorption. Neuroradiology. 2015;57(2):139-147.
32. Rennels ML, Gregory TF, Blaumanis OR, Fujimoto K, Grady PA. Evidence for a 'paravascular' fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 1985;326(1):47-63.
Figures