2362
ADC change during cardiac cycle in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus before and after tap test and shunt surgery1Division of Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 2Nagoya City University Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
Synopsis
To assess the dynamic changes in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) during the cardiac cycle (ΔADC) of the brain before and after the lumbar tap and shunt surgery for the purpose of determining changes in hydrodynamic and biomechanical properties in the brain after cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage for iNPH. The frontal white matter ΔADC in iNPH decreased after the lumbar tap and shunt surgery. ΔADC analysis may provide detailed information regarding changes in the hydrodynamic and biomechanical properties through CSF drainage.
INTRODUCTION
The causative mechanisms of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) 1 symptoms are currently unknown.2 To assess the dynamic changes in the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) during the cardiac cycle (ΔADC)3,4 of the brain before and after the lumbar tap and shunt surgery for the purpose of determining changes in hydrodynamic and biomechanical properties in the brain after cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage for iNPH.MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects: Overall, 22 patients suspected to have iNPH were examined before and after the lumbar tap and were divided into patients who showed symptomatic improvements (positive group, n = 17) and those without improvement (negative group, n = 5) after the lumbar tap. Seven patients in the positive group were examined after the shunt surgery. Field Strength/Sequence: 1.5T, electrocardiographically synchronized single-shot diffusion echo-planar imaging. Assessment: The frontal white matter ΔADC and mean ADC (ADCmean) were compared between before and 24 hours after lumbar tap and from 1 week to 1 month after the shunt surgery. Statistical Tests: Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
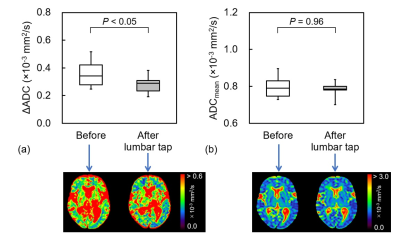
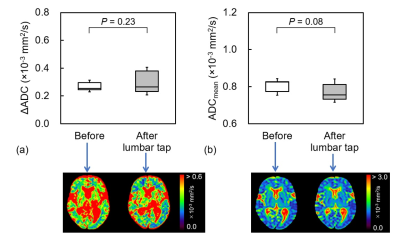
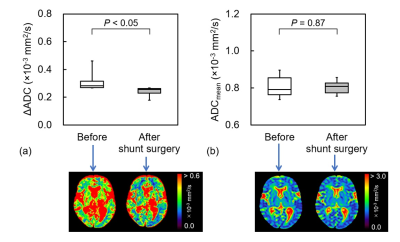
The ΔADC after the lumbar tap in the positive group (0.28 ± 0.06) was significantly lower than that before (0.35 ± 0.09, P < 0.05), whereas no significant difference was found in the negative group (P = 0.23) (Fig. 1). In the positive group, no significant differences were observed in the ΔADC and ADCmean before and after the lumbar tap (P = 0.23 and 0.08, respectively, Fig. 2). After the lumbar tap, ΔADC decreased in 16 of 17 patients in the positive group, whereas ADCmean did not significantly change (P = 0.96). After the shunt surgery, ΔADC decreased in all seven patients (0.24 ± 0.04, P < 0.05), whereas ADCmean did not significantly change (P = 0.87) (Fig. 3).CONCLUSION
The frontal white matter ΔADC in iNPH decreased after the lumbar tap and shunt surgery. ΔADC analysis may provide detailed information regarding changes in the hydrodynamic and biomechanical properties through CSF drainage.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Adams RD, Fisher CM, Hakim S, et al., Symptomatic occult hydrocephalus with “normal” cerebrospinal fluid pressure: A treatable syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1965; 273: 117-26.
2. Marmarou A, Bergsneider M, Klinge P, et al., The value of supplemental prognostic tests for the preoperative assessment of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57: S17-S28.
3. Ohno N, Miyati T, Mase M, et al., Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: temporal changes in ADC during cardiac cycle. Radiology. 2011; 261: 560-5.
4. Takatsuji-Nagaso M, Miyati T, Ohno N, et al., Hemodynamically self-corrected ΔADC analysis in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Br J Radiol. 2019; 92: 20180553.
Figures