2352
Preliminary Exploration and Analysis of MRI-based radiomics for Assessment of MSI-high metastatic colorectal cancer1Changhai Hospital, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In the current study, we evaluated Imaging and genomic data for patients with Microsatellite instability high (MSI-H) metastatic colorectal carcinoma (mCRC) to determine whether Radiomics Based on MRI could be used to select the patients with MSI-H status. Using the pretreatment MRI data, we developed a radiomics model with excellent performance for individualized, noninvasive prediction of MSI-H in patients with mCRC and potentially guide treatment.
Purpose
Microsatellite instability (MSI) is a biomarker for response to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPIs). PD-1 inhibitors in metastatic colorectal carcinoma (mCRC) with MSI-high (MSI-H) have demonstrated a high disease control rate and favorable progression-free survival (PFS). The purpose of this study was to investigate the value of high resolution T2-weighted–based radiomics in assessment of MSI-H in patients with mCRC.Materials and Methods
This retrospective study included 166 patients with mCRC who underwent rectal MR imaging in our hospital on a 3.0T scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany). MSI status is determined through Postoperative immunohistochemistry (IHC) to detect loss of MMR proteins. One radiologist segmented the volumes of interest (VOIs) on high resolution T2-weighted MRIs. 80% of the VOIs were randomly assigned to training set and 20% of VOIs to validation set. Features were extracted on a radiomics analysis platform (Radcloud, Huiying Medical Technology Co., Ltd, Beijing, China), then the optimal features were selected by least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method. In this study, the radiomics-based model was constructed with support vector machine (SVM) classifiers. To assess the diagnostic performance, the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under curve (AUC) were used both in training dataset and validation dataset respectively.Results
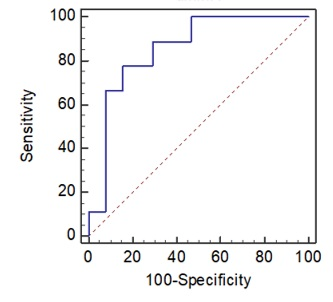
A total of 17 mCRC patients with MSI-H status. We firstly extracted 1409 features, then 4 optimal feature related to the MSI-H status were selected with LASSO algorithm finally. When training with SVM classifier, the AUC was 0.907 (95%CI: 0.730-1.00, sensitivity 86.55% and specificity 85.40%), the AUC of validation set was 0.854 (95%CI: 0.739-0.932, sensitivity 77.78% and specificity 84.31%), respectively (Figure 1).Conclusion
Our data demonstrated that the high resolution T2-weighted MRI-based radiomics showed good performance for MSI-H mCRC. Our proposed radiomics model could be as imaging biomarkers to evaluate MSI-H mCRC patients and has the potential to be applied in clinical treatment planning.Acknowledgements
NAReferences
[1] Robert JG, Paul EK, Hedvig H, et al. Radiomics: image are more than pictures, they are data[J]. Radiology. 2016; 278(2):563-577.
[2] Wu J, Tha KK, Xing L, et al. Radiomics and radiogenomics for precision radiotherapy[J]. J Radiat Res. 2018; 59(suppl_1): i25-i31.
[3] Horvat N, Veeraraghavan H, Khan M, et al. MR Imaging of Rectal Cancer: Radiomics Analysis to Assess Treatment Response after Neoadjuvant Therapy[J]. Radiology. 2018; 287(3):833-843.
[4] Schrock AB, Ouyang C, Sandhu J, et al. Tumor mutational burden is predictive of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in MSI-high metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2019;30(7):1096-1103.