2339
Diagnosis of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Diffusion-tensor Imaging1The First Affiliated Hospital of DaLian Medical University, DaLian , China., Dalian, China, 2GE Healthcare China, Beijing, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Treatment options differ significantly between ICC and HCC; the only curative treatment option for ICC is surgical resection, whereas for HCC, liver transplantation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and radiofrequency ablation are available. So, it is very important to accurately distinguish between these two tumors before therapy is planned. The purpose of this study is to evaluate and compare the FA value of DTI and the ADC value of DWI in ICC and HCC.
Introduction
Compared with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) has more aggressive features, such as a higher frequency of lymph node metastasis and a poorer prognosis [1, 2]. Treatment options differ significantly between ICC and HCC; the only curative treatment option for ICC is surgical resection, whereas for HCC, liver transplantation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and radiofrequency ablation are available [3]. So, it is very important to accurately distinguish between these two tumors before therapy is planned. In this study, we set to evaluate and compare the fractional anisotropy (FA) of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in ICC and HCC.Materials and methods
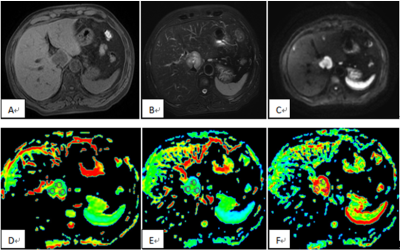
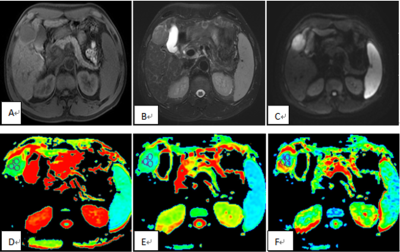
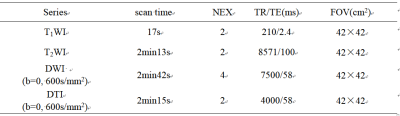
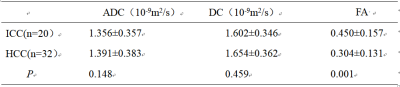
Of the 145 patient records retrieved from the MR database, 52 patients met the criteria for the study, and was thus the final cohort. Twenty patients (10 men and 10 women; range 49-84 years, mean age, 64.60±9.39 years old) had histopathologically confirmed ICC, and 32 patients (27 men and 5 women; range 45-90 years, mean age, 62.72±9.89 years old) had histopathologically confirmed HCC. Liver MRI exams were performed on all patients on a 1.5T MR system (GE-Signa HDXT), contain the routine T1WI, T2WI, contrast-enhanced MRI, DWI (b value=0, 600s/mm2), and DTI (b value=0, 600s/mm2, in 6 directions) (Table 1). The MR images were blindly reviewed and analyzed by two observers who had 3 and 10 years’ experience in MR diagnosis respectively. The values of ADC, diffusion coefficient D, and FA of the focus were measured (Figure 1, 2). A P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Intraclass correlation coefficient test was applied to test the consistency of the two observers; FA and ADC value of two groups were compared by t-test.Results
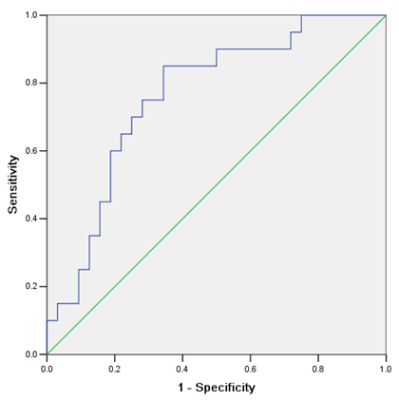
The Intraclass correlation coefficient value of all the parameters were higher than 0.90. The mean FA of ICC was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that of HCC, while the mean ADC and D values in ICC group were all found to be lower (p > 0.05) than that in HCC group (Table2). The AUC of FA value was 0.763 (Figure 3); when the cut-off was 0.313, the Youden index was largest (0.506); the sensitivity and specificity was 85% and 65.6%.Conclusion
In our study the FA value of ICC was significantly higher than that of HCC, had a high AUC value, and high sensitivity and specificity. A possible reason could be the higher tumor cell density and higher malignant potential in ICC. The FA value showed a stronger capability than the ADC value of DWI and DTI in differentiating the ICC from HCC. The FA value is suggested to be measured in the diagnosis of ICC and HCC.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Park MJ, Kim YK, Park HJ, Hwang J, Lee WJ. Scirrhous Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Gadoxetic Acid–Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Diffusion-Weighted Imaging: Emphasis on the Differentiation of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Computer Assisted Tomography, 2013, 37(6) : 872-881.
[2] Fattach HE, Dohan A, Guerrache Y, Dautry R, Boudiaf M, Hoeffel C, et al. Intrahepatic and hilar mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma: Qualitative and quantitative evaluation with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. European Journal of Radiology, 2015, 84: 1444-1451.
[3] Sheng RF, Zeng MS, Rao SX, Ji Y, Chen LL. MRI of small intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma and atypical small hepatocellular carcinoma (≤3 cm) with cirrhosis and chronic viral hepatitis: a comparative study. Clinical Imaging, 2014, 38: 265–272.
Figures