2335
The Value of Multiparametric Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Preoperative T Staging of Rectal Cancer1Changhai Hospital, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to explore the value of MP-DWI in the preoperative T staging of rectal cancer.
Objective
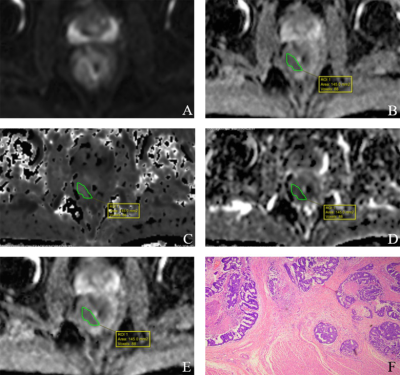
This study aimed to explore the value of multiparametric diffusion-weighted imaging (MP-DWI) in the preoperative T staging of rectal cancer.Methods
The images and clinical data of 127 patients with rectal cancer who underwent radical resection in our hospital from July 2017 to October 2019 were analyzed retrospectively. Before operation, MP-DWI was performed for each patient. The parameters were calculated based on IVIM (intravoxel incoherent motion) and DKI (diffusion kurtosis imaging) models: ADC (approximate diffusion coefficient), DT (true diffusion coefficient), PF (perfusion fraction), D* (pseudo-diffusion coefficient), Dapp (diffusion coefficient),Kapp(kurtosis). Patients were categorized into T1-2 (group A, n=39) and T3-4 (group B, n=88) groups according to postoperative pathological T staging. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to evaluate the relationship between multiparametric indicators and T staging, and to find the independent influencing factors and establish a combined model. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, area under curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, cut-off points of each indicator and the combined model were calculated. And the additive net reclassification index (NRI) of each indicator was compared with the combined model.Results
The sample was composed of 127 patients, including 39 cases in T1-2 group and 88 cases in T3-4 group. Univariate logistic regression showed that ADC, Dt, Dapp, Kapp were associated with T staging of rectal cancer(P<0.05). Multivariate logistic regression showed that Dt(OR=3.277,P=0.042), Dapp(OR=3.778,P=0.041), Kapp(OR=8.199,P=0.001), ADC(OR=85.241,P<0.0001)were correlated with T staging. The AUC of ROC curve of the combined model was 0.896, the specificity was 75.79%, and the sensitivity was 87.50%. NRI showed that the diagnostic efficiency of the combined model is better than that of single indicator.Conclusion
The ADC, Dt, Dapp and Kapp of MP-DWI were correlated with T staging of rectal cancer. The combined model was valuable in evaluating of preoperative T staging of rectal cancer.Acknowledgements
None.References
[1] Siegel R L, Miller K D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2020,70:7-30.
[2] Chen W, Sun K, Zheng R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2014[J]. Chin J Cancer Res,2018,30:1-12.
[3] Nougaret S, Reinhold C, Mikhael H W, et al. The use of MR imaging in treatment planning for patients with rectal carcinoma: have you checked the "DISTANCE"?[J]. Radiology,2013,268:330-344.
[4] Goshima S, Kanematsu M, Noda Y, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging to assess response to treatment in hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol,2015,204:W543-549.
[5] Roethke M C, Kuder T A, Kuru T H, et al. Evaluation of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Versus Standard Diffusion Imaging for Detection and Grading of Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer[J]. Invest Radiol,2015,50:483-489.
[6] Chen X, Ma Z, Huang Y, et al. Multiparametric MR diffusion-weighted imaging for monitoring the ultra-early treatment effect of sorafenib in human hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2017,46:248-256.
[7] Suo S, Cheng F, Cao M, et al. Multiparametric diffusion-weighted imaging in breast lesions: Association with pathologic diagnosis and prognostic factors[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2017,46:740-750.
[8] Filli L, Wurnig M C, Luechinger R, et al. Whole-body intravoxel incoherent motion imaging[J]. Eur Radiol,2015,25:2049-2058.
[9] Jensen J H, Helpern J A. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis[J]. NMR Biomed,2010,23:698-710.
[10] Zhu L, Pan Z, Ma Q, et al. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Study of Rectal Adenocarcinoma Associated with Histopathologic Prognostic Factors: Preliminary Findings[J]. Radiology,2017,284:66-76.
[11] Sun H, Xu Y, Song A, et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI of Rectal Cancer: Correlation of Diffusion and Perfusion Characteristics with Prognostic Tumor Markers[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2018,210: W139-W147.
[12] Lu B, Yang X, Xiao X, et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Primary Rectal Carcinoma: Correlation with Histopathology[J]. Med Sci Monit,2018,24:2429-2436.
[13] Taouli B, Beer A J, Chenevert T. et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging outside the brain: Consensus statement from an ISMRM-sponsored workshop[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2016,44:521-540.