2329
The measurements of APTw in Rectal Cancer: the impact of ROI methods on APTw values and interobserver variability1Shaanxi Provincial People's Hospital, Xi-an, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The study aimed to explore the impact of three methods of delineating region of interest (ROI) methods on the measurement of tumor amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) values. The result showed that whole volume ROI method was reproducible and could reflect the pathophysiological condition of the tumor.
Introduction
Rectal carcinoma is one of the major causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide, accounting for one- third of all colorectal cancers[1].APTw imaging, a novel imaging tool can provide the information of high revolution free protein and amino compound proton of peptide in vivo, reflect the distribution of protein in the tumor. It aids in predicting tumor grade and discriminating treatment-related necrosis from recurrence[2,3]. Therefore, it is great important to measure accurately APTw value, but so far, no agreement has been reached on the measurement method of APTw value. The purpose of this study is to explore the impact of difference ROIs on the measurement of APTw value and to provide reference for future research.Objective
To investigate the impact of ROIon tumor APTw measurements and interobserver variability in rectal cancer.Methods
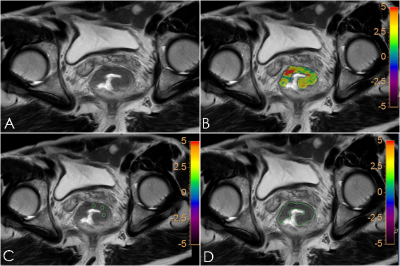
Eleven patients (age 70.82±9.28) with pathology -proven rectal adenocarinoma were selected. Patients had undergone MR examination for APTwon 3.0T MR (Ingenia CX, Philips) and none of them received neoadjuvant therapy. Two radiologists(2, 5 years of experience for diagnose, respectively) measured tumor APTwvalues on axial imaging according to three ROI methods: whole volume, single slice and small solid samples. Whole volume ROI methodis delineating along the tumor boundary including all the tumor layers and taking the mean value of them. Single slice ROI method is delineating along the tumor boundary on the largest layer.Small solid samples is delineating 3 circular ROIs on the largest layer and taking the mean value of them. It need to avoid necrosis, cystic changes and large blood vessels (Fig 1). APTw images were transferred to a workstation (Intellispace Portal, Philips Healthcare) for post-processing. The scan parameters were TR 7.3ms, TE 8ms, Flip Angle 90°, FOV 230x180x60mm3, ACQ Voxel Size 1.8x1.8x6 mm3. The variabilityof two radiologists for each of the three methods was analyzed by calculating interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and according to Bland-Altman analysis. Friedman M test was used to compare the APTw values obtained by the three different ROI methods.Results
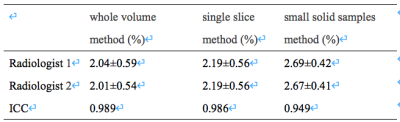
For whole volume ROI method, the ICC between two observers was 0.989, the mean absolute bias in APTw between the two observers was 0.03 %,and 95% limites of agreement was(-0.20, 0.26) %. For single slice ROI method were 0.986, -0.00%, (-0.26, 0.25) %. For small solid samples were 0.949, -0.01%, (-0.37,0.34) % (Table 1, Fig 2). Statistically significant differences were presented among the APTw values of three methods (P=0.014, F=4.902). The APTw values of small solid samples method (2.68±0.40) were significantly bigger than whole volume method (2.03±0.56) and single slice method (2.18±0.55) respectively (P= 0.005, 0.03). However, there is no difference of APTw values of tumour observed between whole volume method and single slice method (P=0.479).Conclusion
The ROI method has a considerable impact on APTw values of tumors,as well as interobserver variability. The APTw values measured by whole volume ROI method may reflect the entire circumstance of rectal cancer. Meanwhile, the interobserver variability is smallest and provide the most reproducible results.Discussion
This study showed whole volume ROI methodon APTw value measurement is the smallest interobserver variability and the highest repeatability among three methods. Whole volume ROI methodincluded the tumor as a whole, and APTw value reflected the heterogeneous characteristics of the tumor.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement foundReferences
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020;70(1):7-30.
[2] Zhou J, Heo HY, Knutsson L, Van Zijl PCM, Jiang S. APT-weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues. J Magn Reson Imaging 2019;50(2):347-364.
[3] Li L, Chen W, Yan Z, et al. Comparative Analysis of Amide Proton Transfer MRI and Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Assessing p53 and Ki Expression of Rectal Adenocarcinoma[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2020(1).