2260
Predicting Early Neonatal Bilirubin Encephalopathy Based on Radiomics Nomogram of T1weighted Imaging1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
The T1WI hyperintensity of bilateral globus pallidus(GP)is considered to be a typical imaging manifestation of bilirubin encephalopathy(BE), but the diagnosis ability is insufficient for the early stage of the disease (hyperbilirubinemia and T1WI negative). In this study, a better early prediction model of BE based on T1WI radiomics was obtained, which provided a new image marker for early diagnosis and monitoring of BE.
Introduction
Bilirubin encephalopathy (BE) is the most serious complication of hyperbilirubinemia (HB), which can lead to lifelong neurodevelopmental disorders and even death 1. Early BE is reversible, early accurate diagnosis and timely intervention and treatment can improve the prognosis. The purpose of this study was to analyze the predictive value for early brain injury caused by HB in neonates using nomogram based on MR T1-weighted imaging (T1WI).Methods
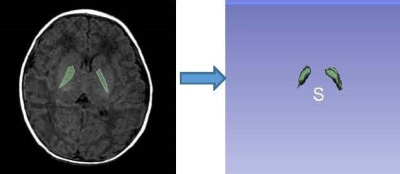
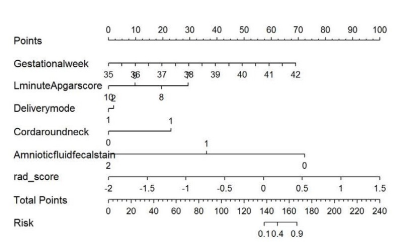
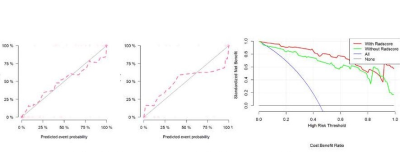
Clinical and imaging data of sixty-one neonates with clinically confirmed hyperbilirubinemia from March 2016 to March 2019 were collected retrospectively, including 42 males and 19 females, median age of 9.0(7.0-10.0)days, mean weight (3.23±0.52) kg. In addition, fifty healthy neonates were recruited as controls,including 31 males and 19 females, with median age of 11.5(5.7-20.0)days and mean weight of (3.41±0.60) kg. The clinical data included 12 items, including gender, age, weight, history of asphyxia, maternal blood type, placenta, amniotic fluid, premature rupture of membranes and single twins. All children were scanned using a GE Signa HDXT 1.5T MR scanner with eight -channel combined head and neck coil for brain scans. High-throughput extraction and analysis of the radiomics features based on T1WI mainly included five key procedures: ①Image segmentation: based on axis T1WI image, the three maximum adjacent layers of globus pallidum (GP) were manually delineated along bilateral GP edge using 3D Slicer software to obtain 3D volume of interest (VOI)(Fig.1).②Feature extraction: one hundred and six radiomics features, including first-order features, morphological features and second-level GLCM (Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix) 、GLDM(Gray-Level dependent Matrix)and GLRLM (Gray -Level Run Length Matrix) texture features were extracted automatically by using Radiomics plugin(http//:www.slicer.org).③ Feature selection :all samples were randomly divided into training set (n=77)and validation set(n=34) based on the ratio of 7∶3. In the training set, using R studio software (Version 1.1.463).The maximal relevance and minimal redundancy (mRMR) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) methods were used for data dimension reduction to establish radiomics mode. ④Model construction: binary logistic regression analysis was used to screen clinical risk factors (including gestational week, one minute Apgar score, delivery method and cervical contraction), the retained imaging features and clinical features were incorporated into Logistic regression analysis to construct a model, and a nomogram was drawn(Fig.2). ⑤Model validation: the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of radiomics model and the combined model, and the calibration curve (CCV) and decision curve (DCV) are drawn to evaluate the predictive efficacy and clinical application value of the model.Results
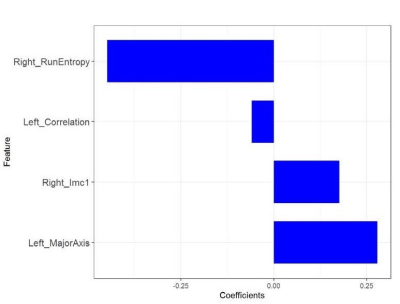
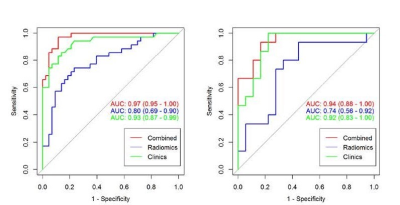
Four most valuable imaging features were ultimately screened out (Fig.3). After modeling, the radiomics model shows good predictive performance. The AUC value in the training set was 0.80(95%CI: 0.69-0.90), and the accuracy, specificity and sensitivity were 0.86, 0.88, and 0. 83, respectively. The AUC value of verification set was 0.74(95%CI: 0.56-0.92),and the accuracy, specificity and sensitivity were 0.85、0.88、0.81.After combining imaging radiomics and clinical features, the predictive power of the model is further improved(AUC=0.97(95%CI:0.95-1.00)for training set, AUC=0.94(95%CI:0.88-1.00)for validation set) (Fig.4).Discussion
Elevated T1WI signal of GP is recognized as a characteristic imaging manifestation of BE2 . However, it is interfered by many factors. It is not accurate to judge the increase of GP signal only by visual observation or threshold of GP. Therefore, in this study, the signal changes of the GP that cannot be discerned by the naked eye can be observed through the imaging radiomics method to observe the microscopic changes of the GP. The results show that the imaging radiomics model can effectively distinguish children with early BE from healthy children. It also provides a quantitative standard for early detection of brain damage. In order to further improve and optimize the discrimination ability, this study combined clinical risk factors to construct a clinical- radiomics model and draw a visual nomogram.Conclusion
The radiomics model and nomogram based on magnetic resonance T1WI can distinguish children with early BE from normal healthy children, and can effectively predict the occurrence of early BE. The combined radiomics and clinical features are better than single imaging radiomics, and which has high clinical application value.(Fig.5)Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Bahr TM, Christensen RD, Agarwal AM, et al. The Neonatal Acute Bilirubin Encephalopathy Registry (NABER): Background, Aims, and Protocol [J]. Neonatology, 2019, 115(3):242-246.
2. Yan RF, Han DM, Ren JP, et al. Diagnostic value of conventional MRI combined with DTI for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia [J]. Pediatrics & Neonatology, 2018, 59(2).161-167.