2212
Feasibility of 1H-[13C] MRS of hippocampal and hypothalamic metabolism in the very same mouse with dynamic shim update (DSU)
Hikari Yoshihara1, Nicolas Kunz2, and Hongxia Lei2,3
1EPFL-LIFMET, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2EPFL-CIBM, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3United-Imaging Co. Ltd, Wuhan, China
1EPFL-LIFMET, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2EPFL-CIBM, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3United-Imaging Co. Ltd, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
13C MRS of the very same mouse hippocampus and hypothalamus at 14.1T is feasible using dynamic shimming update
Introduction
With increased interests in the hippocampus as a potential regulator of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical (HPA) axis, the final common pathway in the stress response, differentiate glucose metabolism between dorsal hippocampus and hypothalamus in the very same subject may lay foundation for investigating relevant evidence to the underlying mechanism how the hippocampal regulation of HPA sensitivity.Although 13C Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) has shown to be a very promising tool to study brain metabolism in vivo. For instance, indirect carbon spectroscopy (1H-[13C] MRS) is a technique that allows measuring 13C-labelled metabolites with higher sensitivity. Metabolic fluxes including TCA cycle in mouse hypothalamus were assessable using 1H-[13C] MRS upon infusion of [1,6-13C2] glucose at 14.1T. However, at high magnetic field, challenges are substantially amplified for multivoxel MRS in murine brains. For instance, first- and second-order shims become essential to improve local field homogeneity. Given recent studies showing feasibility of acquire 1H MRS from two distinct brain regions in the very same subject using dynamic shim updates (DSU) ,1 thus we aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of acquiring in vivo high-field 1H-[13C] MR spectra2 concurrently from the mouse hippocampus and hypothalamus at 14.1T on both shims without any supplementary hardware.
Methods
AnimalsMale C57BL/6 mice (n=6, 8-12 weeks, 25±2g) were scanned under isoflurane anesthesia (1-2%) in a horizontal 14.1T/26cm Varian magnet (Agilent Inc., USA). A homemade 1H surface coil in quadrature combined with a linear 13C coil was designed specific for 1H-[13C] MRS. The bilateral dorsal hippocampi (2×6×1.5 mm3) and hypothalamus (2×2.7×2.2 mm3) were localized using a set of T2-weighted FSE images. Field inhomogeneity was adjusted using FASTMAP to reach a water linewidth <25Hz.3 On the target VOI, localized indirect 1H-[13C] detection was applied using the full signal intensity BISEP-SPECIAL sequence (TE/TR=2.8/4000ms, 2) together with OVS and water suppression. Glucose metabolism of both dorsal hippocampus and hypothalamic was evaluated upon infusion of an intial bolus of 99% enriched and followed by 70% enriched 20% (w/v) [1,6-13C2] glucose up to 4 hours. MR methods All experiments were performed in a horizontal 14.1T scanner, equipped with a 400mT/m gradient (200msec) interfaced to a DirectDrive (vnmrj, Agilent Inc.). 2nd order shim coils with maximum strengths of Z2 = 5.3 × 10−2mT/cm2, YZ = 1.2 × 10−1mT/cm2, XZ = 1.2 × 10−1mT/cm2, XY = 4.5 × 10−2mT/cm2 and X2Y2 = 4.2 × 10−2mT/cm2. A home-made quadrature surface coil (two geometrically decoupled 12mm-diameter loops) resonating 600MHz was used for radio-frequency transceiver. Anatomical MR images were acquired using fast-spin-echo images (TEeff/TE=50/4000ms, nt=8). The optimized spectral parameters, including excitation, water suppression, out volume suppression and the number of averages per scan (e.g. 16 averages per scan), for cortex and hippocampus were stored separately.
Dynamic Shim Update (DSU)
With the corresponding shims and the optimized spectral parameters, dynamic shim update (DSU) acquisition scheme (Figure 1) was applied on mouse hippocampus and hypothalamus, in which glutamatergic neurons are abundant in hippocampus. Data processing The unsuppressed water signals acquired from the same VOIs were used for quantification. Spectra were frequency corrected and summed (5.5min of hippocampus and 11.0min for hypothalamus) for LCModel quantification. Non-edited 1H MR spectra contain 1H resonances coupled to both 12C and 13C and thus can be quantified with a standard basis set for neurochemical profiles of mouse hippocampus.2,3 The 13C-editing spectra were quantified using another simulated basis set as previously.2,3 The fraction of isotope enrichment (FE) in lactate (Lac, LacC3), glutamate (Glu, GluC4), glutamine (Gln, GlnC4), the sum of Glu and Gln (Glx, GlxC3) and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA, GABAC2 and GABAC3) was obtained.
Results and Discussion
DSU both first- and second-order shims without any extra hardware is feasible for dual-voxel 1H-[13C] spectroscopy at 14.1T, as shown in Figure 1. With the DSU, dynamic quality spectra were obtained in an interleaved fashion from two brain regions (Figure 2, 3&4). Sufficient FEs of labeled substrates can be reliably measured (Figure 5).Without any modeling, we showed that DSU of interleaved high-field spectral acquisition is feasible on 13C MRS. This study shows for the first time an in vivo comparison of 13C MRS of glucose in both hippocampus and hypothalamus of the very same mouse using indirect 1H-[13C] MRS upon [1,6-C2] 13C-glucose infusion.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the CIBM of the UNIL, UNIGE, HUG; CHUV, EPFL and Leenaards and Louis-Jeantet Foundations.References
1. Koch KM et al. Magn Reson Med. 2007:57:587-591
2. Xin LJ, Lanz B, Lei H and Gruetter R. J. Cereb. Blood Flow and Metab. (2015) 35, 759-765;
3. Gruetter R, Tkac I. Magn Reson Med. 2000;43:319‐323.
Figures
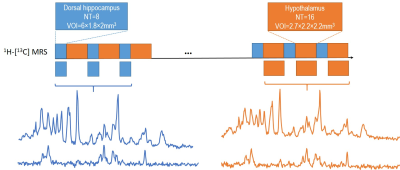
Figure 1. Schematic layout of the experimental
design for 1H-[13C] MRS acquisition of both hippocampus
and hypothalamus with dynamic shim update (DSU) (a), and typical non-edited (b)
and edited (c) MR spectra of hippocampus (blue) and hypothalamus (orange).
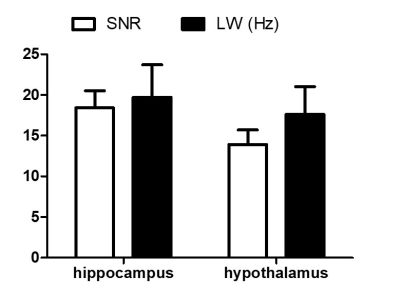
Figure 2. Quality of non-edited 1H MRS spectra
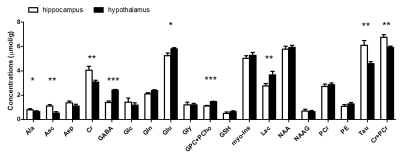
Figure 3. Neurochemical profiles of hippocampus and
hypothalamus
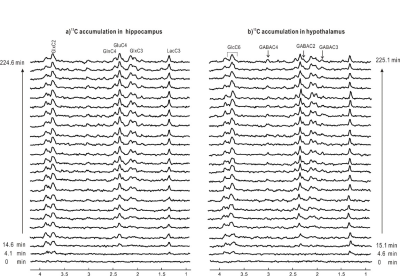
Figure 4 One typical stack of 1H-[13C]
edited spectra of each time course accumulation of labeling
into hippocampus (lb=5) and hypothalamus (lb=7) of
one animal.
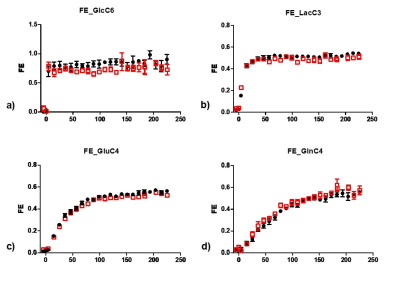
Figure 5 Time courses of 13C accumulation towards GlcC6, LacC3,
GluC4 and GlnC4 (AVG3)