2198
A registration approach for cardiac PET/CT and MR images1Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Life Science, Beijing institute of technology, beijing, China, 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Tsinghua University School of Medicine, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Multi-modality images can provide comprehensive information for clinical diagnosis. In this study, a registration method for cardiac PET and MR images was proposed by combining global registration and local registration. During global registration, axial PET and CT images were transformed to short axis with MR-survey as link. Then local registration was performed between PET/CT and MR-cine images, it was found that using the fusion of PET and CT images performed better compared with that only using a single modality image.
Introduction
The registration between 11C-acetate PET/CT and MR could provide a viable evaluation of myocardial blood flow and metabolism on different segments. However, the motion caused by heartbeat and breath made it a big challenge.1-2 In the present study, a scheme for the registration of multi-modality cardiac images using Elastix3 was proposed based on the space consistency of MR-survey and Cine as well as that of PET and CT.Methods
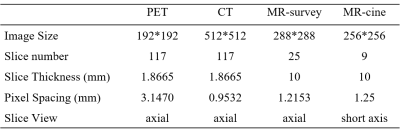
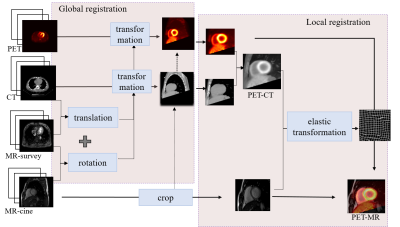
Study sample: Ten male subjects (age: 45.6 ± 9.4 years) were included in this study. Each subject underwent MR imaging and PET/CT scanning. The study protocol was approved by a local institutional review aboard, and a written consent form was obtained from each subject. MR-survey and CINE sequence were performed on a 3.0 Tesla MR scanner (Achieva TX, Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) with a 32-channels coil. After 11C-acetate was injected intravenously with a dose of 740 MBq, PET imaging was conducted on a hybrid PET/CT scanner (PoleStar m660, Sinounion, Healthcare Inc., Beijing). The parameters of MR, PET, CT images were listed in table 1.Registration method: Preprocessing: Bedplate in CT image was removed with a morphological method. The PET, CT, MR images were adjusted to the same size (256 × 256), pixel spacing (1.25 mm) and intensity range [0, 255]. Registration: The registration was divided into global and local registration. global registration was aimed to remove translation between MR-survey and CT image via minimizing the mutual information. The translation matrix between MR-survey and CT image, and the rotation matrix between MR-survey and CINE were used to roughly align PET and CINE images. All images were cropped to a 144 × 144 image after the reviewer selected a point in the center of heart on CINE images. Local registration with B-spline transformation and mutual information maximization was performed for registration of PET and CINE images. All the registrations were performed on Matlab 2017A using Elastix toolbox.
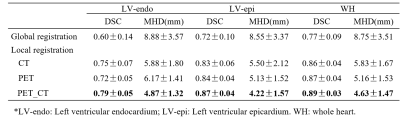
Evaluation: The contours of whole heart, left ventricular epi- and endocardium were manually delineated by an experienced radiologist. The performance of the global registration, and that of local registration with the different moving images (only CT, only PET, and the fusion of PET and CT) were compared. Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) and modified Hausdorff distance (MHD) were used as the evaluation indexes.
Results
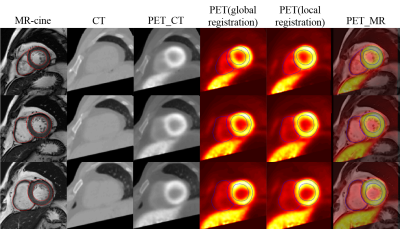
The registration results were shown in Figure 2 and Table 2. The combination of global and local registration can be improved significantly compared with only global registration. In addition, among three moving images, the fusion of PET and CT images performed best in both indexes, while the PET images performed worst.Discussion
In the present study, a solution for multi-modality images registration was proposed by combining global registration and local registration. The global registration relied on the structure of the thorax to remove the translation of a same subject between different modality images, while local registration improved the final result considering the transformation of whole heart.In addition, the performance of local registration using different moving images were also evaluated in the present study. The CT images provided a clear contour of whole heart, and PET images offered more details of myocardium. Consequently, the local registration using the fusion of PET and CT images performed better compared with that only using a single modality image.
Conclusion
The combination of global and local registration could be a viable scheme for multi-modality images registration. The fusion of PET and CT images could provide more details on epi- and endocardium, and thus improve the performance of local registration.Acknowledgements
NoneReferences
[1] Stéphanie Bricq, Kidane, H. L., Zavala-Bojorquez, J., Oudot, A., & Lalande, A. (2018). Automatic deformable PET/MRI registration for preclinical studies based on b-splines and non-linear intensity transformation. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 56(10), 1-9.
[2] Makela, T., Clarysse, P., Sipila, O., Pauna, N., Pham, Q. C., & Katila, T., et al. (2002). A review of cardiac image registration methods. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 21(9), p.11-21.
[3] Klein S, Staring M, Murphy K, et al. Elastix: A toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration [J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2010, 29(1): 196-205.
Figures