2131
Comparison of integrated-shimming EPI and conventional SS-EPI diffusion-weighted MR imaging in Liver lesions1Department of Radiology, the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
The purpose of this study is to compare image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value between single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) and integrated slice-specific dynamic shimming (iShim) DWI methods in liver. Compared to SS-EPI, iShim had better image quality and showed more small lesions. No significant differences of ADC values were found between the two methods.
Introduction
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a very important technique in the detection and diagnosis of the tumor of whole body. In clinical application of the liver DWI, single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) is commonly used due to the short scan time. However, SS-EPI is easily distorted, especially in the interface due to different susceptibility of different tissues. Recently, a new technique, integrated slice-specific dynamic shimming (iShim), have been proved that it have less distortions and less signal voids compared to SS-EPI in some organs, such as bladder, thyroid, and Prostate [1-3]. iShim DWI has not been used in Liver. The purpose of this study is to compare image quality and evaluate the detectability of lesions between SS-EPI and iShim DWI in liver.Methods
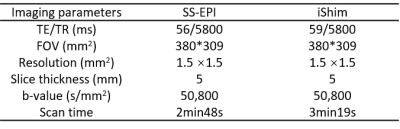
This prospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital, and informed consents were obtained from 8 patients with liver hydatoncus or tumor. Liver MRI examinations of all patients were performed on a 3T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using 18-channel abdominal phase array coil and 32-channel Tim spinal array coil. The T1w, T2w, and DWI images using SS-EPI and iShim were acquired. The parameters of DWI sequences are summarized in Table 1. The image quality of the two sequences were assessed independently in terms of the artifacts, distortion, uniform and image blur degrees. Then, several regions of interest (ROIs) were draw on the healthy liver tissue and lesions, which were on the same position and the same size for the two sequences. The mean apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value of ROI was calculated. The paired t-test was used to evaluate the ADC differences, and p<0.05 was considered statically significant. The Bland-Altman plot was used to evaluate the ADC agreements between two methods.Results
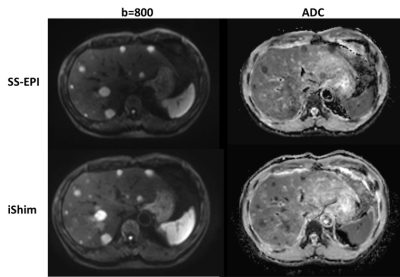
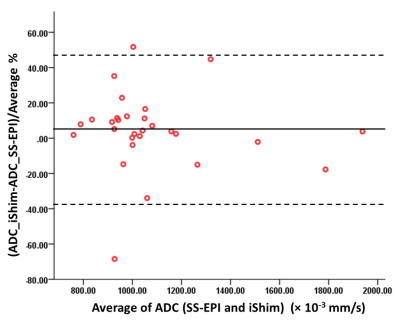
Compared to SS-EPI, iShim had better image quality and showed more small lesions (Figure 1). No significant differences of ADC values were found between the two methods (p=0.354). Bland-Altman results showed that the mean ADC difference was 4.4% and the mean ADC values had good agreement between the two methods (Figure 2).Discussion and Conclusion
In our study, the significant improvements in image quality were observed from iShim DWI, and more small lesions were detected compared to the conventional SS-EPI, which were consistence with previous studies [1-4]. The main reason was that iShim DWI combines integrated slice-specific dynamic shimming and pixel-wise unwrapping distortion correction, so it can reduce distortions and signal voids caused by local B0 inhomogeneity. In addition, previous studies been proved that ADC values has relations with tumor aggressiveness and has potential clinical implications. In our study, we found that ADC values from SS-EPI and iShim had no statistically significant differences and had a good agreement. The consistency of ADC values indicated that the new iShim technique may replace conventional SS-EPI technique for routine examination in liver.In conclusion, iShim DWI technique leads to significant improvement in image quality, and it is useful for the detection of liver lesions.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Daniel Stocker, Andrei Manoliu, Anton S. Becker, et al. Image Quality and Geometric Distortion of Modern Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Sequences in Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Prostate, Investigative Radiology, 2017.
2. Hongyi Li, Lin Liu, Qinglei Shi, et al. Bladder cancer: detection and image quality compared among iShim, RESOLVE, and ss-EPI diffusion-weighted MR imaging with high b value at 3.0 T MRI, Medicine, 2017,96: 50.
3. Luguang Chen, Peipei Sun, Qiang Hao, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the evaluation of the thyroid nodule: Comparison between integrated-shimming EPI and conventional 3D-shimming EPI techniques, Oncotarget, 2018, 9: 26209-26216.