1902
Comparation of the image quality between a modified 3D RT-SPACE-MRCP and routine 3D RT-SPACE-MRCP sequence in bile duct disease1XIAN DAXING HOSPITAL, Xi'an, China, 2MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthineers, Xi'an, China
Synopsis
MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an method allowing noninvasive investigation of biliary and pancreatic disorders. However, the respiratory-triggered 3D MRCP technique requires long acquisition time depending on the breathing rate of patients, which leads to image blurring and motion artifacts. The purpose of this study was to compare the modified RT-SPACE-MRCP protocol and the conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP protocol with respect to image quality as well as the acquisition time.
Introduction
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a efficient imaging technique which can provide detailed information of the pancreaticobiliary anatomy and pathology. Most initial study focused on 2D MRCP technique using breath-hold acquisition sequences, while they suffered from decreased spatial resolution and acquired non-isotropic voxel datasets. Therefore, for the purpose of obtaining high-resolution isotropic images, 3D respiratory-triggered with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle Evolutions MRCP(RT-SPACE-MRCP) sequences had been performed principally with a respiratory-triggered technique during the last 10 years[1]. However, there is a clinical burden that the acquisition time of the respiratory-triggered 3D MRCP sequence often need take more than 6 minutes despite the use of parallel acquisition technique[2]. Such a long acquisition time is often associated with suboptimal image quality due to image blurring and motion artifacts. For this reason, further reduction of MRCP acquisition time have been studied. The aim of this study was to compare the MRCP image quality between conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP and modified RT-SPACE-MRCP in a routine clinical setting of bile duct disease.Subjects and methods
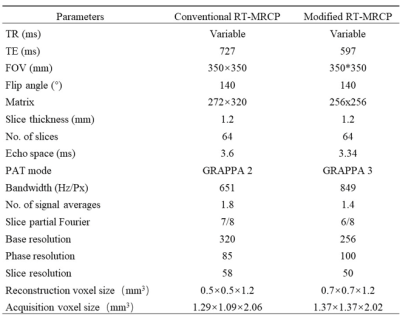
Thirty-nine patients (20 males and 19 females, mean age, age range 15-83 years) were enrolled in this study. All the patients underwent conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP, modified RT-SPACE-MRCP on a 1.5 T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Aera, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) using a 6-channel body coil and 24-channel spine coil. The parameters about three different types of SPACE sequences were given in Table 1.The acquisition time for each MRCP images was noted. Two radiologists with five years of experience in abdominal radiology assessed the images independently. The visualization of pancreaticobiliary tree which was subdivided into seven segments on a 5-point scale, and overall image quality, image sharpness and background suppression on a 4-point scale were reviewed by two radiologists independently. Quantitative evaluation included signal-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-noise ratio (CNR) between the common bile duct (CBD) and periductal tissues. A paired t test was used to assess differences in the qualitative and quantitative evaluations between the two acquisition methods. Interobserver agreement was assessed by calculating the Cohen kappa statistic (kappa< 0.00: poor agreement, kappa = 0.00-0.20: slight agreement, kappa = 0.21-0.40: fair agreement, kappa = 0.40-0.60: moderate agreement, kappa = 0.61-0.80: substantial agreement; kappa = 0.81-1.00: almost complete agreement). A p-value of less than 0.05 indicated statistically significant differences.Results
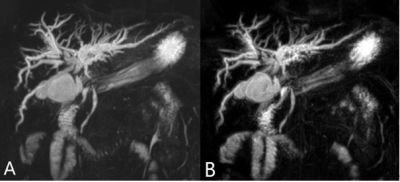
There was significant difference in the mean acquisition time between conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP and modified RT-SPACE-MRCP (168.9±34.9 seconds vs 42.8±12.1 seconds, P<0.001). There were no significant difference in image quality for each segment, CNR and SNR between two groups (P >0.05,Fig 1). The interobserver agreement was high between two sequences, 0.68-0.91, 0.65-0.86 and 0.61-0.83, respectively.Discussion and Conclusion
In the present study, we prospectively evaluated the image quality and acquisition time of 3D MRCP using a sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts (SPACE) sequence. The study discovered that modified RT-SPACE-MRCP exhibited the equal overall image quality to conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP. More importantly, the acquisition time of the modified RT-SPACE- MRCP was approximately fourfold faster than that of the conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP. In conclusion, compared with conventional RT-SPACE-MRCP, the modified RT-SPACE-MRCP sequence had the same overall image quality and visualization effect of pancreaticobiliary tree at 1.5T, and significantly reduced the imaging time.Acknowledgements
We thank Shaoyu Wang of Siemens Healthcare, Ltd., Xi’an, China, for technical support.References
[1] Yasokawa K, Ito K, Tamada T, et al.Noninvasive investigation of exocrine pancreatic function: Feasibility of cine dynamic MRCP with a spatially selective inversion-recovery pulse.J Magn Reson Imaging.2015,42(5):1266-1271.
[2] Matos C, Cappeliez O, Winant C, et al.MR imaging of the pancreas: a pictorial tour.Radiographics.2002,22(1):2-0.