1883
Role of mDixon quant imaging in evaluation of treatment outcome with vitamin K2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease1Radiology, No.4 Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Synopsis: Liver fat content in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is closely related to the progression of the disease. The objective of this study was to assess the effect of Vitamin K2 (VK2) supplementation on NAFLD using mDixon quant technique. Preliminary results showed supplementation of VK2 could can improve the condition of liver fat deposition of VK2 and related biomarkers to some extent.
Introduction
The liver is the largest digestive gland as well as the center of metabolisms in human body. NAFLD is an alarming global health problem that is anticipated to be the major cause of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and liver transplantation by next decade. More and more studies have shown that VK2 produced by bacteria has a protective effect on the liver, but the impact on NAFLD has barely been identified [1]. Magnetic resonance proton density fat fraction (MR PDFF) can be used as a tool for screening for NAFLD and determining the degree of fatty infiltration of the liver due to its noninvasiveness and good repeatability. . Our purpose is to evaluate the effect of K2 on the change of PDFF and blood lipid , and the correlation between PDFF and blood serum parameters.Method
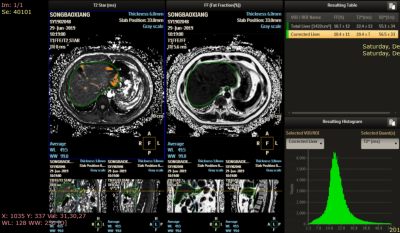
A total of 44 residents aged 50-75 were enrolled in this cohort study. All of the residents were supplemented with 55 μg/d VK2 for one year. [2]The changes of weight, blood biochemistry parameters including triglycerides (TG) and total-cholestrols (TC) were evaluated. All the residents underwent 3T MRI (Ingenia CX, Philips) to measure the liver PDFF before and after the supplementation using mDixon Quant. Paired sample T test was used to compare TC (mmol/L), TG(mmol/L)and PDFF values before and after treatment. Spearman correlation was used to analyze the correlation between liver fat PDFF and TC and TG. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Corrected liver segmentation is a new function that Liver is segmented automatically . Corrected liver volume is calculated by excluding all masked voxels, and is a more accurate quantification of average liver fat with a good repeatability .Result
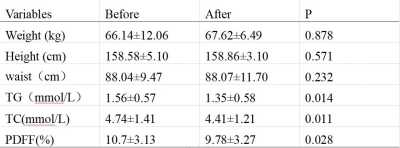
The TC(mmol/L)of patients were 1.56±0.57 and 1.35±0.58 before and after taking VK2, respectively (P=0.011). TG (mmol/L)were 4.74±1.41 and 4.41±1.21 before and after taking VK2, respectively(P=0.014). PDFF values were 10.7±3.13 and 9.78±3.27, respectively (P=0.028). Spearman correlation coefficient rs was 0.729 for PDFF and TG, and 0.304 for PDFF and TC.Discussion
The liver segmentation is a new function in mDixon quant ,automatically calculate the mean liver fat PDFF, a threshold is applied in the Total liver segmentation on T2* map to remove vessels and other artifacts . Corrected liver volume is calculated excluding all masked voxels, the accuracy has improved. Prior studies assessing changes in liver fat content have largely relied on MR spectroscopy, which is generally performed as a single-voxel measurement and may incorrectly estimate the fat content of the liver as a whole. In previous experiments using mDixon Quant imaging to evaluate liver fat, a circular region of interest (ROI) with a 1cm radius was placed manually in each of the nine Couinaud segments of the liver, so as to sample representative portions of the entire liver. But its accuracy is questionable because of the artificial differences in its operation. These problems were improved after we used liver segmentation in mDioxn quant.Conclusion
Vitamin K2 may improve blood lipid and liver fat infiltration to some extent. Serum biomarkers TC and TG change demonstrated significant correlation with change PDFF. Corrected Liver Segmentation shows high reliability and is suitable for use in clinical practice. PDFF is potentially a promising and valuable non-invasive method in detection of liver fat.Summary of Main Findings
In this study we investigated the effects of VK2 supplementation on NAFLD and related serum biomarkers. PDFF were used as a tool for determining the degree of fatty infiltration of the liver. After the one-year supplementation the blood biomarker and liver fat infiltration were improved to some degree.Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Philips Healthcare for its help, Xiuzheng Yue for his technical support and Yishi Wang for his valuable advice. And I would like to thank my tutor Zhang Tong for his suggestions.References
[1]. Sato, T., et al., Difference in the metabolism of vitamin K between liver and bone in vitamin K-deficient rats. Br J Nutr, 2002. 87(4): p. 307-14.
[2]. Knapen, M.H., et al., Steady-state vitamin K2 (menaquinone-7) plasma concentrations after intake of dairy products and soft gel capsules. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2016. 70(7): p. 831-6.