1819
MRI contrast agent for myocardial infarction based on novel manganese-based nanoparticles1Department of Radiology, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital (SRRSH), Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
Synopsis
Gadolinium is a commonly used contrast agent for myocardial infarction during CMR examinations, but its nephrotoxicity and short examination time window limited its application to some extent. We try to develop new contrast agents with superior imaging performance and good biocompatibility, which can achieve clinical translation.
Introduction and purpose
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a life-threatening cardiac emergency. Delayed enhancement with gadolinium (Gd) contrast is clinically predominant for displaying myocardial infarction. Unfortunately, gadolinium is an extracellular nonspecific contrast agent, lacks specificity for accurate assessment of myocardial infarction, has a short blood circulation time, and its potential nephrotoxicity should not be overlooked. In recent years, manganese compounds have attracted more and more attention because they can be used in magnetic resonance imaging. On this basis, we attempted to develop novel manganese-based contrast agents for the diagnosis and evaluation of myocardial infarction.Materials and methods
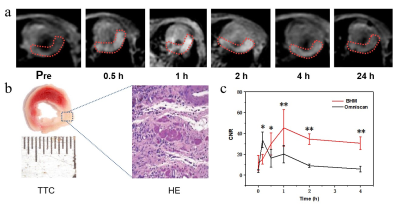
Hypericin-BSA-MnO2 nanoparticles (BHMNP) was synthesized in one pot via biomineralization. We first characterized BHMNP, and then tested its biological toxicity in vivo and in vitro. MTT assay and flow cytometry were used to detect the cytotoxicity of contrast agent. Afterward, to examine its imaging ability in MI area in vivo, C57BL/6 male mice after MI modeling were injected with BHMNP at the dose of 0.1 mmol kg-1 Mn and performed MRI. Histology and immunofluorescence were performed and observed.HE and TTC staining were used for histological verification.Result
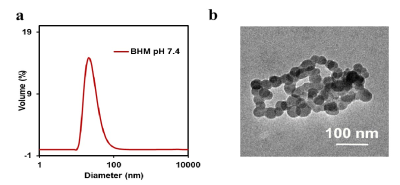
In this study, the novel manganese-based nanoparticle BHMNP had superior imaging capability for myocardial infarction and good biocompatibility. The main results were as follows: 1) The particle size of 1)BHMNP was about 67 nm, and the particles were regular and uniform spherical under the transmission electron microscope; 2)BHM was easily hydrolyzed in an acidic environment, and manganese ions were released for imaging, which was suitable for the acidic cellular microenvironment after myocardial infarction. R1 was about 9.04 mm-1 s-1; 3) The proliferation of rat cardiomyocyte line (H9C2) was not inhibited by 3)MTT assay, and no significant apoptosis was observed by flow cytometry, indicating good biosafety; 4) After injection into mice with myocardial infarction, the signal in the myocardial infarction area continuously increased, reaching the peak within 1 hour. With the prolongation of time, the signal gradually decreased, and there was a longer examination time window than that of gadolinium which was commonly used clinically.5) No obvious histological damage was found to the main organs.Conclusion
1)The novel manganese-based nano-particle (BHMNP) had high relaxation rate and uniform nano particle size.2)BHMNP had good myocardial infarction imaging performance and certain clinical conversion value.
3)The preparation process of BHMNP was simple, the property was stable, and the biological safety was good.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr. Yuxin Han for his guidance on project design.
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. (Grant Number 81873908; to Hongjie Hu).
References
(1)Puymirat E, Simon T, Cayla G, et al. Acute Myocardial Infarction: Changes in Patient Characteristics, Management, and 6-Month Outcomes Over a Period of 20 Years in the FAST-MI Program (French Registry of Acute ST-Elevation or Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) 1995 to 2015. Circulation. 2017. 136(20): 1908-1919.
(2) Bulluck H, Dharmakumar R, Arai AE, Berry C, Hausenloy DJ. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Acute ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: Recent Advances, Controversies, and Future Directions. Circulation. 2018. 137(18): 1949-1964.
(3)Xiao B, Zhou X, Xu H, et al. Integration of Polymerization and Biomineralization as a Strategy to Facilely Synthesize Nanotheranostic Agents. ACS Nano. 2018. 12(12): 12682-12691.