1755
Deep J-Sense: An unrolled network for jointly estimating the image and sensitivity maps1Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, United States, 2Diagnostic Medicine, Dell Medical School, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, United States, 3Oden Institute for Computational Engineering and Sciences, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, United States
Synopsis
Accurate reconstruction using parallel imaging relies on estimating a set of sensitivity maps from a fully-sampled calibration region, which can lead to reconstruction artifacts in poor signal-to-noise ratio conditions. We introduce Deep J-Sense as a deep learning approach for jointly estimating the image and the sensitivity maps in the frequency-domain. We formulate an alternating minimization problem that uses convolutional neural networks for regularization and train the unrolled model end-to-end. We compare reconstruction performance with model-based deep learning methods that only optimize the image and show that our approach is superior.
Introduction
Combining unrolled iterative optimization with deep learning has greatly improved reconstruction performance in accelerated multi-coil MRI scans when compared to compressed sensing (CS) methods1,2,3,4. Most approaches rely on estimates of the coil sensitivity maps obtained either through calibration data or via deep neural networks5,6. When the quality of the estimated sensitivity maps is poor, e.g., low signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR), this can introduce reconstruction artifacts. The need for calibration data also limits the feasible search space for optimal sampling, which could otherwise subsample the center of k-space, making a robust estimator for the sensitivity maps an important practical issue.In this work, we introduce Deep J-Sense: an approach that jointly estimates the sensitivity maps and the image with the aid of two deep neural networks. Our method combines a model-based approach with deep learning3 to account for the effect of the sensitivity maps in the coil image formation model. We treat the maps as optimization variables and formulate an unrolled alternating minimization problem7,8, augmented by a denoising convolutional neural network (CNN) for each variable.
We train and evaluate reconstruction performance on the public fastMRI knee dataset9. Comparing against MoDL, we demonstrate that our method improves reconstruction performance, increases convergence speed, and accounts for poor SNR conditions.
Theory
J-Sense formalizes image reconstruction as a joint optimization problem and assumes that coil images are formed by pointwise multiplication between an image variable$$$\:\mathbf{x}\:$$$and a set of sensitivity maps$$$\:\mathbf{s}\:$$$7,8:$$\min_{\mathbf{x},\mathbf{s}}\lvert\lvert\mathbf{y}-\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{x}\cdot\mathbf{s})\rvert\rvert_2+\lambda_{x}\lvert\lvert\mathbf{x}\rvert\rvert_2+\lambda_{s}\lvert\lvert\mathbf{s}\rvert\rvert_2,$$
where$$$\:\mathbf{A}\:$$$is the forward model incorporating FFT and k-space masking,$$$\:\mathbf{y}\:$$$is the vector of sampled k-space data, and$$$\:\lambda_{x},\lambda{s}\:$$$are regularization coefficients.
We extend the formulation above by defining the variables$$$\:\mathbf{f}=\textrm{IFFT}(\mathbf{x})\:$$$and$$$\:\mathbf{m}=\textrm{IFFT}(\mathbf{s})\:$$$in k-space and replacing the regularization terms with$$$\:\mathcal{N}(f;\mathbf{\theta}_{f})=\lvert\lvert\mathbf{f}-\textrm{FFT}(R_f(\textrm{IFFT}(\mathbf{f});\mathbf{\theta}_f))\rvert\rvert_2\:$$$and$$$\:\mathcal{N}(m;\mathbf{\theta}_{m})=\lvert\lvert\mathbf{m}-\textrm{FFT}(R_m(\textrm{IFFT}(\mathbf{m});\mathbf{\theta}_m))\rvert\rvert_2,\:$$$similar to MoDL3.$$$\:R_f\:$$$and$$$\:R_m\:$$$are learnable CNNs parameterized by weights$$$\:\mathbf{\theta}_{f}\:$$$and$$$\:\mathbf{\theta}_{m},\:$$$respectively. The optimization problem becomes:
$$\min_{\mathbf{f},\mathbf{m}}\lvert\lvert\mathbf{y}-\mathbf{P}(\mathbf{f}\star\mathbf{m})\rvert\rvert_2+\lambda_{f}\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{f};\mathbf{\theta}_f)+\lambda_{m}\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{m};\mathbf{\theta}_m),$$
where$$$\:\mathbf{P}\:$$$is the sampling operator and$$$\:\star\:$$$is a linear convolution. The optimization is unrolled with the iterative steps:
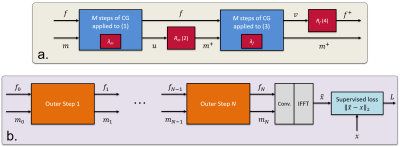
$$$(1)\:\mathbf{u}=\textrm{arg}\min_\mathbf{u}\lvert\lvert\mathbf{y}-\mathbf{A}_{f}\mathbf{u}\rvert\rvert_2+\lambda_m\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{u};\mathbf{\theta}_m)$$$
$$$(2)\:\mathbf{m}=R_m(\mathbf{u};\mathbf{\theta}_m)$$$
$$$(3)\:\mathbf{v}=\textrm{arg}\min_\mathbf{v}\lvert\lvert\mathbf{y}-\mathbf{A}_{m}\mathbf{v}\rvert\rvert_2+\lambda_f\mathcal{N}(\mathbf{v};\mathbf{\theta}_f)$$$
$$$(4)\:\mathbf{f}=R_f(\mathbf{v};\mathbf{\theta}_f)$$$
$$$\mathbf{A}_f\:$$$and$$$\:\mathbf{A}_m\:$$$are forward operators that include linear convolution with$$$\:\mathbf{f}\:$$$or$$$\:\mathbf{m},\:$$$and sampling. Steps (1) and (3) are approximately solved with$$$\:M\:$$$iterations of the Conjugate Gradient (CG) algorithm. Steps (2) and (4) represent a forward pass through a CNN. We treat$$$\:\lambda_f\:$$$and$$$\:\lambda_m\:$$$as learnable parameters. Without steps (1) and (2), our approach becomes a frequency-domain version of MoDL.
Importantly, Deep J-Sense treats both the image and sensitivity maps as frequency domain kernels and assumes a linear convolution model in k-space. To account for the smoothness of the sensitivity maps in the image domain, we restrict the kernel$$$\:\mathbf{m}\:$$$to a small size in k-space. This is different than prior work that optimizes the sensitivity maps directly in the image domain5,10. To obtain a linear convolution in frequency, the image kernel$$$\:\mathbf{f}\:$$$has size$$$\textrm{dim}(\mathbf{y})+\textrm{dim}(\mathbf{m})-1$$$.
Optimization is initialized with$$$\:(f_0,m_0),\:$$$unrolled for a number of$$$\:N\:$$$times, and the output coils are computed as$$$\:\hat{\mathbf{x}}=\mathbf{f}_N\star\mathbf{m}_N$$$. The two networks and$$$\:\lambda\:$$$coefficients are reused across all unrolls. The parameters$$$\:\mathbf{\theta}_f,\mathbf{\theta}_m,\lambda_f,\lambda_m\:$$$are trained using a supervised loss on the root-sum-square (RSS) images. A block diagram is shown in Fig.1.
Methods
We implement Deep J-Sense using PyTorch. We use a CG algorithm defined over complex variables, and CNNs defined over real variables (with 2x channels). The networks use a ResNet11 architecture with three residual blocks, 64 hidden channels, and ReLU activations. Training data is used from the fastMRI multi-coil kneel dataset. We use five central slices from each scan, for a total of$$$\:4865\:$$$training slices from both fat-suppressed (FS) and non-fat-suppressed (NFS) contrasts. Validation is over$$$\:995\:$$$slices from both contrasts. We train our model with$$$\:(N,M)=(6,3)\:$$$for 20 epochs using the Adam optimizer with batch size$$$\:1,\:$$$learning rate$$$\:10^{-4},\:$$$gradient clipping and progressive unrolling3.For comparison, we implement MoDL with$$$\:(N,M)=(6,6)\:$$$and$$$\:R_f\:$$$of depth three (MoDL-3) or six (MoDL-6). We train with the same hyper-parameters, same number of epochs, and on the same data. We simulate J-Sense12 with$$$\:(N,M)=(6,3)\:$$$and$$$\:\lambda_{f}=\lambda_{m}=0.01\:$$$. We use a map kernel of size$$$\:25\times25\:$$$for Deep J-Sense, initialized with an RSS estimate from the undersampled data. For MoDL, we use sensitivity maps estimated with the auto-ESPIRiT13,14 algorithm using BART15. For J-Sense, we initialize the maps with zeroes.
Results and Discussion
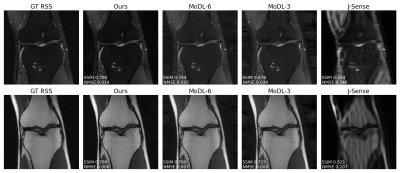
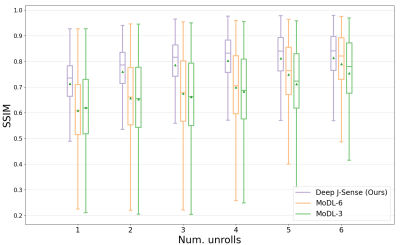
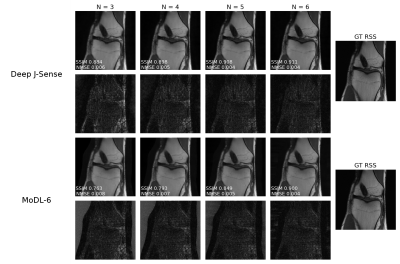
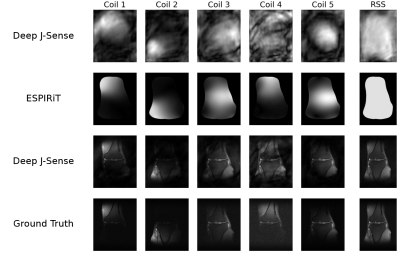
Fig.2 shows example reconstructions on two validation slices at acceleration factor$$$\:R=4\:$$$. Deep J-Sense gives the lowest reconstruction error, followed by MoDL and J-Sense. Because of the limited number of inner CG steps and the random sampling pattern, J-Sense converges to a poor solution, highlighting the role the networks$$$\:R_f\:$$$and$$$\:R_m\:$$$play in stabilizing the alternating optimization. Fig.3 shows the boxplot of the validation structural similarity index (SSIM). Deep J-Sense enjoys faster convergence and outperforms MoDL even when the latter uses a network twice as deep.Fig.4 plots the intermediate reconstruction results after each unroll for Deep J-Sense and MoDL. The end performance is comparable between the two, but Deep J-Sense converges faster, while MoDL spends iterations correcting errors outside of the region of interest. Fig.5 plots a subset of learned sensitivity maps and reconstructed coil images. Compared to the ESPIRiT estimate, our maps contain higher frequency components. This is likely a consequence of the existence of multiple optimal solution sets of maps that form a clean RSS solution, indicating that the scheme may learn a notion of uncertainty in poor SNR conditions. Although not explored here, the joint-estimation may also support non-autocalibrated sampling schemes.
Conclusion
Sensitivity map estimation can lead to artifacts and slow convergence of unrolled methods. We have introduced a deep learning approach to jointly estimate the maps and image in k-space.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Office of Naval Research grant N00014-19-1-2590.References
1. Lustig, M., Donoho, D. L., Santos, J. M., & Pauly, J. M. (2008). Compressed sensing MRI. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 25(2), 72-82.
2. Hammernik, K., Klatzer, T., Kobler, E., Recht, M. P., Sodickson, D. K., Pock, T., & Knoll, F. (2018). Learning a variational network for reconstruction of accelerated MRI data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 79(6), 3055-3071.
3. Aggarwal, H. K., Mani, M. P., & Jacob, M. (2018). MoDL: Model-based deep learning architecture for inverse problems. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 38(2), 394-405.
4. Recht, M.P., Zbontar, J., Sodickson, D.K., Knoll, F., Yakubova, N., Sriram, A., Murrell, T., Defazio, A., Rabbat, M., Rybak, L. & Kline, M., 2020. Using Deep Learning to Accelerate Knee MRI at 3 T: Results of an Interchangeability Study. American Journal of Roentgenology, 215(6), 1421-1429.
5. Sriram, A., Zbontar, J., Murrell, T., Defazio, A., Zitnick, C.L., Yakubova, N., Knoll, F. & Johnson, P., 2020. End-to-End Variational Networks for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.06688.
6. Peng, X., Perkins, K.,Clifford, B., Sutton, B., & Liang Z.-P., 2018. Deep-SENSE: Learning Coil Sensitivity Functions for SENSE Reconstruction Using Deep Learning. Proc. ISMRM 2018, Paris.
7. Ying, L., & Sheng, J. (2007). Joint image reconstruction and sensitivity estimation in SENSE (JSENSE). Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 57(6), 1196-1202.
8. Uecker, M., Hohage, T., Block, K. T., & Frahm, J. (2008). Image reconstruction by regularized nonlinear inversion—joint estimation of coil sensitivities and image content. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 60(3), 674-682.
9. Zbontar, J., Knoll, F., Sriram, A., Murrell, T., Huang, Z., Muckley, M.J., Defazio, A., Stern, R., Johnson, P., Bruno, M., & Parente, M., 2018. fastMRI: An open dataset and benchmarks for accelerated MRI. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.08839.
10. Jun, Y., Shin, H., & Eo, T., 2020. Joint-ICNet: Joint Deep Model-based MR Image and Coil Sensitivity Reconstruction Network for Fast MRI. fastMRI 2020 Competition Leaderboards, https://fastmri.org/leaderboards/challenge/.
11. He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 770-778).
12. Ong, F., & Lustig, M. (2019, May). SigPy: a python package for high performance iterative reconstruction. In Proceedings of the ISMRM 27th Annual Meeting, Montreal, Quebec, Canada (Vol. 4819).
13. Uecker, M., Lai, P., Murphy, M.J., Virtue, P., Elad, M., Pauly, J.M., Vasanawala, S.S., & Lustig, M., 2014. ESPIRiT—an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 71(3), pp.990-1001.
14. Iyer, S., Ong, F., Setsompop, K., Doneva, M., & Lustig, M., 2020. SURE‐based automatic parameter selection For ESPIRiT calibration. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 84(6), pp.3423-3437.
15. Uecker, M., Ong, F., Tamir, J. I, Bahri D., Virtue P., Cheng JY, Zhang T., & Lustig M., 2015. Berkeley Advanced Reconstruction Toolbox. Proc ISMRM 2015, Toronto
Figures