1728
On the generalizability of diffusion MRI signal representations across acquisition parameters: chronicles of the MEMENTO challenge.1Department of Neurology, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2PROVIDI Lab, Image Sciences Institute, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, Netherlands, 3Champalimaud Research, Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown, Lisbon, Portugal, 4Centre for Medical Imaging Computing, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 5Centre for Medical Image Computing, University College London, London, United Kingdom, 6Clinical Science, Department of Radiology, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 7Inria Sophia Antipolis – Méditerranée, Université Côte d'Azur, Sophia Antipolis, France, 8Istanbul Technical University, Instanbul, Turkey, 9Therapanacea, Paris, France, 10Cardiff University Brain Research, Imaging Centre (CUBRIC), School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 11AGH University of Science and Technology, Krakow, Poland, 12LPI, ETSI Telecomunicacion, Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain, 13Department of Biomedical Engineering, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 14Center for Medical Image Science and Visualization, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden, 15School of Instruments and Electronics, North University of China, Taiyuan, China, 16Department of Physics, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, United States, 17NVIDIA Corporation, Bethesda, MD, United States, 18National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, National Institute of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States, 19Imec-Vision Lab, Department of Physics, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium, 20Intelligent Systems Engineering, Indiana University Bloomington, Bloomington, IN, United States, 21Leibniz Institute for Materials Engineering - IWT, University of Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 22Department of Psychology and the eScience Institute, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States, 23QMENTA Inc, Barcelona, Spain, 24Institute of Imaging Science, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, United States
Synopsis
The acquisition and modelling of diffusion MRI (dMRI) data offer many opportunities to explore the organization of the brain. A variety of methods has been proposed to this end, but their generalizability to different diffusion encodings and stronger gradients remains unknown. In the MEMENTO challenge, we asked participants to predict dMRI signals collected with single, double and double oscillating diffusion encodings in combination with a variety of weighting parameters. We received eighty-three submissions ranging from signal representations to multicompartment models and deep learning-based predictions, which offer a unique perspective to investigate the status quo of the field.
Introduction
Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging (dMRI) is a powerful tool to investigate microstructural properties of biologic tissues1,2. To date, a manifold of methods have been proposed for brain dMRI, often to describe properties of the white matter (WM) in combination with single diffusion encoding3 (SDE) acquisitions.Recent innovations are making it possible to acquire dMRI data well-beyond classic SDE, with the promise to unveil further details of the tissue organization. This can be achieved, for example, with ultra-strong diffusion weightings in SDE, or by considering time dependency with double diffusion encoding4 (DDE) and double oscillating diffusion encoding schemes5 (DODE). In the MEMENTO challenge, we aimed to understand how existing quantification methods generalize to signals collected with these novel acquisition trends.
Methods
This study took place as part of the MEMENTO microstructure challenge organized during ISBI 2019. Briefly, for a given acquisition, subjects were a subset of the full dataset and asked to predict the remaining unseen signal (https://www.qmenta.com/memento-challenge).MRI acquisition
We selected two datasets containing extensively sampled dMRI brain data with 4 encoding schemes: multi-shell SDE (SDE-MS), cartesian SDE (SDE-GRID), DDE and DODE. The SDE acquisitions were performed in a healthy volunteer with a 3T scanner as part of the MASSIVE6 datasets. The DDE and DODE data were sampled from an ex-vivo mouse brain at 16.4T7.
Five voxels were selected for each dataset from brain locations in the WM, the deep gray matter (DGM) and cortical gray matter (CGM), as shown in Fig. 1.
Training and evaluation data
We provided a subset of the 20 selected signals (5 signal locations x 4 diffusion encodings) and asked collaborators to predict the remaining measurements with any method of choice. The provided/unprovided measurements were 515/2495 for SDE-MS, 500/1170 for SDE-GRID, 320/480 for DDE and 960/1040 for DODE.
Data analysis
For each signal, we determined the best prediction based on the lowest residuals sum of squares (RSS), and visually investigated the residuals. A ranking of all considered models was derived according to increasing RSS, then the best fitting model was established per encoding type. Non-parametric tests were performed between each prediction and the best to establish whether they could be considered equivalent.
Results
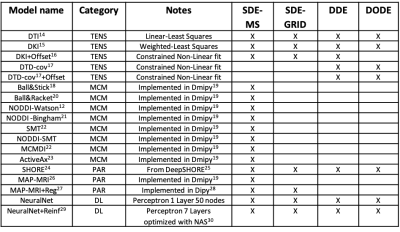
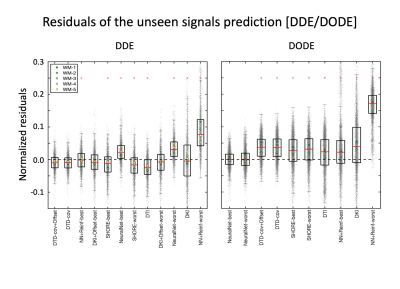
We received initial submissions from 9 teams through the Qmenta platform8, 2 of which did not provide valid submissions and were not included in this analysis. The remaining 7 teams submitted a total of 83 valid signal predictions that were considered in the subsequent analyses.A summary of the submissions with reference to the used fit method is shown in Table 1. Fig. 2 shows the residuals of all SDE-MS predictions ranked by RSS when considering the 5 provided signals together. The predictions of the first 7 methods were remarkably accurate with tight confidence interval of the residuals of about ±3%, which occasionally reached values up to 10%. MAP-MRI and NeuralNet did not differ statistically and provided the best SDE-MS prediction. A tendence towards a better prediction of WM signals as compared to CGM and DGM was observed.
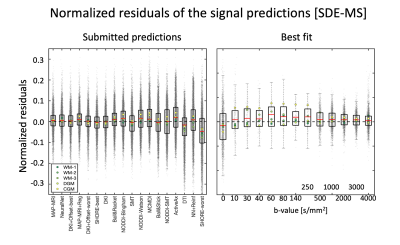
The residuals of the SDE-GRID submissions ranked by RSS are shown in Fig. 3. The top 7 submissions performed remarkably similar, and MAP-MRI+Reg, DKI+Offset and NeuralNet equivalently provided the best predictions. When looking at the prediction with MAP-MRI+Reg, significant biases were observed at low diffusion weighting (b<800 s/mm2), around b ~ 3000 s/mm2 and beyond b=6000 s/mm2.
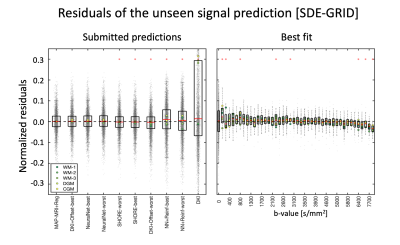
Fig. 4 presents the normalized residuals for the DDE/DODE submissions, averaged over voxels, b-values and diffusion times/frequencies. For DDE, DTD-cov+Offset provided the best prediction of the signal. For DODE data, the best prediction comes from NeuralNet, whereas the remaining submissions overestimated the signal. For both DDE and DODE, the predictions show similar trends in the 5 different WM voxels. For the DODE data, both frequencies also show similar trends of the predicted signal.
Discussion and conclusion
Most submissions could predict SDE data remarkably well within commonly employed diffusion weightings (e.g., 1000 <= b <= 4000 s/mm2), whereas the prediction of low (b < 800 s/mm2) and strong (b > 6000 s/mm2) diffusion weightings was generally less accurate. This might originate from Rician-related biases9, but also highlights the limited specificity of existing models to genuine components such as perfusion10 and WM-restriction11. The prediction of DDE and DODE data seems more challenging than that of SDE, likely due to diffusion time / frequency dependencies that are not considered by most submissions. When taking into account tissue-specific differences, a trend towards a better fit of WM than GM becomes appreciable, which is reasonable given the few number of methods explicitly accounting for GM-specific properties12,13.User choices can remarkably affect the prediction accuracy: the SHORE method, for example, achieved both one of the best predictions and the worst. Similarly, the addition of a degree of freedom to DKI or DTD-cov (i.e., +Offset) appreciably improved its accuracy to fit SDE-GRID and DDE. Importantly, the definition of “best prediction” is arbitrary: we used RSS as a criterion, but other choices (e.g., information criteria) would likely lead to different rankings.
In conclusion, MEMENTO is a community effort to highlight strength and limitations of the field at representing dMRI acquired with trending encoding schemes.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M. & Field, A. S. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 4, 316–29 (2007).
2. Le Bihan, D. Diffusion MRI: What water tells us about the brain. EMBO Mol. Med. 6, 569–573 (2014).
3. Stejskal, E. O. & Tanner, J. E. Spin Diffusion Measurements: Spin Echoes in the Presence of a Time-Dependent Field Gradient. J. Chem. Phys. 42, (1965).
4. Shemesh, N. et al. Conventions and nomenclature for double diffusion encoding NMR and MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 75, 82–87 (2016).
5. Ianuş, A., Shemesh, N., Alexander, D. C. & Drobnjak, I. Double oscillating diffusion encoding and sensitivity to microscopic anisotropy. Magn. Reson. Med. 78, 550–564 (2017).
6. Froeling, M., Tax, C. M. W., Vos, S. B., Luijten, P. R. & Leemans, A. ‘MASSIVE’ brain dataset: Multiple acquisitions for standardization of structural imaging validation and evaluation. Magn. Reson. Med. 77, 1797–1809 (2017).
7. Ianuş, A. et al. Accurate estimation of microscopic diffusion anisotropy and its time dependence in the mouse brain. Neuroimage 183, 934–949 (2018).
8. Lazowski, N., Ramos, M. & Rodrigues, P. Web-cloud platform for storing, processing and analyzing multi-modal neuroimaging data. in ISMRM 2015: 6th Annual Meeting of the Italian Chapter of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. (2015). doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.13285.24803.
9. Sijbers, J. & den Dekker, A. J. Maximum likelihood estimation of signal amplitude and noise variance from MR data. Magn. Reson. Med. 51, 586–94 (2004).
10. Le Bihan, D. et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168, 497–505 (1988).
11. Tax, C. M. W., Szczepankiewicz, F., Nilsson, M. & Jones, D. K. The dot-compartment revealed? Diffusion MRI with ultra-strong gradients and spherical tensor encoding in the living human brain.Neuroimage 210, 116534 (2020).
12. Zhang, H. G., Schneider, T., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. a & Alexander, D. C. NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage 61, 1000–16 (2012).
13. Palombo, M. et al. SANDI: A compartment-based model for non-invasive apparent soma and neurite imaging by diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 215, 116835 (2020).
14. Basser, P. J., Mattiello, J. & LeBihan, D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys. J. 66, 259–67 (1994).
15. Jensen, J. H., Helpern, J. a, Ramani, A., Lu, H. & Kaczynski, K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 53, 1432–40 (2005).
16. Morez, J., Sijbers, J., Vanhevel, F. & Jeurissen, B. Constrained spherical deconvolution of nonspherically sampled diffusion MRI data. Hum. Brain Mapp. 1–18 (2020) doi:10.1002/hbm.25241.
17. Westin, C. F. et al. Q-space trajectory imaging for multidimensional diffusion MRI of the human brain. Neuroimage 135, 345–362 (2016).
18. Behrens, T. E. J. et al. Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 50, 1077–88 (2003).
19. Fick, R. H. J., Wassermann, D. & Deriche, R. The Dmipy Toolbox: Diffusion MRI Multi-Compartment Modeling and Microstructure Recovery Made Easy. Front. Neuroinform. 13, 1–26 (2019).
20. Sotiropoulos, S. N., Behrens, T. E. J. & Jbabdi, S. Ball and rackets: Inferring fiber fanning from diffusion-weighted MRI. Neuroimage 60, 1412–1425 (2012).
21. Tariq, M., Schneider, T., Alexander, D. C., Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A. & Zhang, H. Bingham-NODDI: Mapping anisotropic orientation dispersion of neurites using diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 133, 207–223 (2016).
22. Kaden, E., Kelm, N. D., Carson, R. P., Does, M. D. & Alexander, D. C. Multi-compartment microscopic diffusion imaging. Neuroimage 139, 346–359 (2016).
23. Alexander, D. C. et al. Orientationally invariant indices of axon diameter and density from diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 52, 1374–89 (2010).
24. Ozarslan, E., Koay, C. G., Shepherd, T. M., Blackband, S. J. & Basser, P. J. Simple harmonic oscillator based reconstruction and estimation for three-dimensional q-space MRI. in (2009).
25. Nath, V. et al. Enabling multi-shell b-value generalizability of data-driven diffusion models with deep SHORE. arXiv 1–9 (2019).
26. Özarslan, E. et al. Mean apparent propagator (MAP) MRI: a novel diffusion imaging method for mapping tissue microstructure. Neuroimage 78, 16–32 (2013).
27. Fick, R. H. J., Wassermann, D., Caruyer, E. & Deriche, R. MAPL: Tissue microstructure estimation using Laplacian-regularized MAP-MRI and its application to HCP data. Neuroimage 134, 365–385 (2016).
28. Garyfallidis, E. et al. Dipy, a library for the analysis of diffusion MRI data. Front. Neuroinform. 8, 1–17 (2014).
29. Willia, R. J. Simple Statistical Gradient-Following Algorithms for Connectionist Reinforcement Learning. Mach. Learn. 8, 229–256 (1992).
30. Zoph, B. & Le, Q. V. Neural architecture search with reinforcement learning. 5th Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. ICLR 2017 - Conf. Track Proc. 1–16 (2017).
Figures