1710
Spiral diffusion imaging at 800 µm resolution using a scanner with 300 mT/m gradients and gradient field monitoring1Department of Neurophysics, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 2Gengenbach, Germany, 3Institute of Medical Physics and Radiation Protection, TH Mittelhessen University of Applied Sciences, Giessen, Germany, 4NMR Group, Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences, Leipzig, Germany, 5Center for Cognitive Neuroscience Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 6Felix Bloch Institute for Solid State Physics, Leipzig University, Leipzig, Germany
Synopsis
Spiral diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) with field monitoring and iterative reconstruction offers potentially reduced echo time (TE) and higher effective resolution (less blurring) compared to EPI. Coupled with a scanner with ultra-strong gradients, it enabled an 800 µm DWI protocol for imaging fine structures of the brain in vivo. Compared to EPI, the shorter TEs provided distinctly different contrast in iron-rich areas (U-fibres and sub-cortical nuclei), which could enhance investigations of these regions. The protocol did, however, come with a reduction in SNR/(unit time) compared to EPI due to differences in readout time.
Introduction
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) of brain tissue allows access to microstructural properties of brain in vivo1. However, high resolution is required to separate and segment fine structures like cortex2, sub-cortical nuclei3, or U-fibres4.Spiral trajectories are more efficient than rectilinear k-space trajectories5 and enable shorter effective echo time6,7,8 (TE). Shorter TEs retain higher signal levels and increase the range of TEs that can be sampled. Importantly, varying TE can provide additional microstructural information9,10. This is especially pertinent for U-fibres and deep gray matter, because their high relative iron content11,12 means that behaviour in the low TE-regime is likely to be interesting.
MRI scanners with ultra-strong gradients have recently enabled enhanced in vivo DWI U-fibre imaging in lower visual areas using a protocol optimised for the occipital lobe4. Here, we demonstrate the potential of spiral acquisitions to allow for shorter TE in this protocol, while ensuring high image quality using field monitoring and iterative reconstruction.
Methods
Data were recorded from a young healthy participant on a Siemens Connectom 3T scanner with a 32-channel receive-only head coil.Spiral data: spin echo DWI sequence with spiral readout13; TE 33 ms; TR 6500 ms; 800 µm isotropic resolution; $$$220\times220$$$ mm$$$^2$$$ field of view (FoV); 62 slices; oblique axial, tilted along the calcarine sulcus; 41 ms readout time; bandwidth (BW) 952 Hz/px; $$$4\times$$$ radially undersampled; acquisition repeated $$$4\times$$$ with initial azimuthal phase $$$(n-1)\pi/2$$$ (4 arms); $$$b=8,18$$$ ms/µm$$$^2$$$; 60 non-colinear directions per shell distributed over the sphere; 15 interleaved $$$b=0$$$ ms/µm$$$^2$$$ ($$$b_0$$$) volumes; total acquisition time (TA) ~1hr. Multi-echo GRE images were recorded at 1.5 mm isotropic resolution to calculate B0 and coil sensitivity maps, TA ~3mins. Additionally, $$$20\times{}b_0$$$ images were recorded for temporal signal-to-noise ratio (tSNR) comparison with EPI, TA ~9mins.
The spiral trajectory was measured up to spatial second-order14 in a separate calibration on a phantom using a 64-channel receive-only head coil15,16 with built in field monitoring probes connected to a field monitoring system (Skope Magnetic Resonance Technologies).
Spiral data were reconstructed using iterative SENSE reconstruction in the Skope-i software (Skope Magnetic Resonance Technologies), incorporating the recorded trajectories and the B0 and coil-sensitivity maps14. Spiral arms were combined using an implementation of MUSE17 in Skope-i. Scanner-side eddy current correction18 was removed before reconstruction using simulations of the trajectory (https://github.com/SkopeMagneticResonanceTechnologies/siemens_to_ismrmrd) so that the measured values could be used.
EPI data: measured in a separate session and previously published4. Parameters different from spiral acquisition: spin echo EPI sequence16,19; TE 66 ms; TR 8900 ms; $$$206\times206$$$ mm$$$^2$$$ FoV; 81 ms readout time; BW 1148 Hz/px; GRAPPA20 2; partial Fourier 5/8; two repetitions; one additional $$$b_0$$$ image with opposed phase encoding recorded for susceptibility correction21,22; total TA ~45mins. In addition, one repetition of $$$20\times{}b_0$$$ images were recorded in the same session as the spiral for tSNR comparison, TA ~5mins.
DWI data were preprocessed as per Attar, et al.4, except that because eddy current and susceptibility corrections are incorporated into the spiral reconstruction, in that case these steps were replaced with correction for inter-volume motion using the ACID toolbox23. Diffusion tensors24, and multi-tissue CSD segmentations and fibre orientation distribution functions25 (fODFs) were computed from the DWI data using MRtrix326.
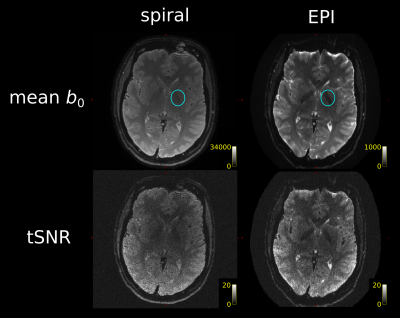
The $$$b_0$$$ data for tSNR comparison was not preprocessed. tSNR was computed voxelwise over the $$$b_0$$$ repetitions as (signal mean)/(signal standard deviation). Separately for spiral and EPI images, the mean $$$b_0$$$ image was segmented using SPM12, and white matter (WM) probability maps were thresholded at 99% to generate WM masks. The distribution of tSNR was compared in these WM masks.
Results
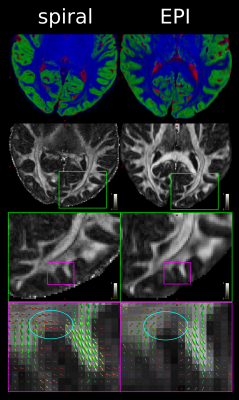
Fig. 1 demonstrates that the spiral acquisition gives higher effective spatial resolution in terms of crisper delineation of tissue classes and less blurring. It also suggests that the shorter TE for the spiral gives differential sensitivity to U-fibres, in line with their increased iron content12.The tSNR comparison (Fig. 2) demonstrated comparable tSNR for 4-arm spiral and single-repetition EPI. Over the WM, spiral tSNR (mean$$$\,\pm\,$$$standard deviation) was $$$4.5\pm{}1.6$$$ in ~9mins, EPI tSNR $$$4.7\pm{}1.3$$$ in ~5mins. The distribution of tSNR was seen to be flatter for the spiral, in line with previous results7, though this may be in part due to the lack of susceptibility correction in the EPI case. The effect of the shorter TE on deep gray matter contrast was also apparent.
Discussion and Conclusion
Unlike in previous work7, our spiral acquisition was less SNR/(unit time) efficient than the EPI. The main reason for this is that the EPI has a readout time twice as long as the spiral. A further contributing factor is that the partial Fourier encoding leads to blurring and thus a lower effective resolution in the phase-encoding direction of the EPI. However, two repetitions of the EPI protocol can be run in the same time as the spiral protocol.On the other hand, the spiral DWI offered a higher (and isotropic) effective resolution and shorter minimal TE, though the contributions of TE, field monitoring, and iterative reconstruction to the higher resolution remain to be disentangled. Spiral DWI holds the potential to enhance investigations of diffusion properties of thin and small structures like cortex, U-fibres, and deep grey matter nuclei in vivo in the low TE-regime at sub-millimetre resolution.
Acknowledgements
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) / ERC grant agreement no. 616905. This project has received funding from the BMBF (01EW1711A & B) in the framework of ERA-NET NEURON.References
[1] Alexander, D.C., Dyrby, T.B., Nilsson, M., Zhang, H. (2019), "Imaging brain microstructure with diffusion MRI: practicality and applications", NMR Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.3841
[2] Edwards, L.J., Kirilina, E., Mohammadi, S., Weiskopf, N. (2018), "Microstructural imaging of human neocortex in vivo", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.02.055
[3] Keuken, M.C., Bazin, P.-L., Crown, L., Hootsmans, J., Laufer, A., Müller-Axt, C., Sier, R., van der Putten, E.J., Schäfer, A., Turner, R., Forstmann, B.U. (2014), "Quantifying inter-individual anatomical variability in the subcortex using 7T structural MRI", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.032
[4] Movahedian Attar, F., Kirilina, E., Haenelt, D., Pine, K.J., Trampel, R., Edwards, L.J., Weiskopf, N. (2020), "Mapping Short Association Fibers in the Early Cortical Visual Processing Stream Using In Vivo Diffusion Tractography", Cereb. Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhaa049
[5] Delattre, B.M.A., Heidemann, R.M., Crowe, L.A., Vallée, J.-P., Hyacinthe, J.-N. (2010), "Spiral demystified", Magn. Reson. Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2010.03.036
[6] Mueller, L., Rudrapatna, S.U., Tax, C.M.W., Wise, R., Jones D.K. (2019), "Diffusion MRI with b=1000 s/mm2 at TE < 22 ms using single-shot spiral readout and ultra-strong gradients: Implications for microstructure imaging", Proc. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med.
[7] Lee, Y., Wilm, B.J., Brunner, D.O., Gross, S., Schmid, T., Nagy, Z., Pruessmann, K.P. (2020), "On the signal‐to‐noise ratio benefit of spiral acquisition in diffusion MRI". Magn. Reson. Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.28554
[8] Wilm, B.J., Hennel, F., Roesler, M.B., Weiger, M., Pruessmann, K.P. (2020), "Minimizing the echo time in diffusion imaging using spiral readouts and a head gradient system", Magn Reson Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.28346
[9] Jones, D.K., Alexander, D.C., Bowtell, R., Cercignani, M., Dell'Acqua, F., McHugh, D.J., Miller, K.L., Palombo, M., Parker, G.J.M., Rudrapatna, U.S., Tax, C.M.W. (2018), "Microstructural imaging of the human brain with a 'super-scanner': 10 key advantages of ultra-strong gradients for diffusion MRI", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.05.047
[10] Barakovic, M., Tax, C.M.W., Rudrapatna, U.S., Chamberland, M., Rafael-Patino, J., Granziera, C., Thiran, J.P., Daducci, A., Canales-Rodríguez, E.J., Jones, D.K. (2020), "Resolving bundle-specific intra-axonal T2 values within a voxel using diffusion-relaxation tract-based estimation", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117617
[11] Deistung, A., Schäfer, A., Schweser, F., Biedermann, U., Turner, R., Reichenbach, J.R. (2013), "Toward in vivo histology: A comparison of quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) with magnitude-, phase-, and R2*-imaging at ultra-high magnetic field strength", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.09.055
[12] Kirilina, E., Helbling, S., Morawski, M., Pine, K., Reimann, K., Jankuhn, S., Dinse, J., Deistung, A., Reichenbach, J.R., Trampel, R., Geyer, S., Müller, L., Jakubowski, N., Arendt, T., Bazin, P.-L., Weiskopf, N. (2020), "Superficial white matter imaging: Contrast mechanisms and whole-brain in vivo mapping", Sci. Adv. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz9281
[13] Herbst, M., Deng, W., Ernst, T. and Stenger, V.A. (2017), "Segmented simultaneous multi‐slice diffusion weighted imaging with generalized trajectories", Magn. Reson. Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.26545
[14] Wilm, B.J., Barmet, C., Pavan, M. and Pruessmann, K.P. (2011), "Higher order reconstruction for MRI in the presence of spatiotemporal field perturbations", Magn. Reson. Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22767
[15] Keil, B., Blau, J.N., Biber, S., Hoecht, P., Tountcheva, V., Setsompop, K., Triantafyllou, C. and Wald, L.L. (2013), "A 64‐channel 3T array coil for accelerated brain MRI". Magn. Reson. Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.24427
[16] Setsompop, K., Kimmlingen, R., Eberlein, E., Witzel, T., Cohen-Adad, J., McNab, J.A., Keil, B., Tisdall, M.D., Hoecht, P., Dietz, P., Cauley, S.F., Tountcheva, V., Matschl, V., Lenz, V.H., Heberlein, K., Potthast, A., Thein, H., Van Horn, J., Toga, A., Schmitt, F., Lehne, D., Rosen, B.R., Wedeen, V., Wald, L.L. (2013), "Pushing the limits of in vivo diffusion MRI for the Human Connectome Project", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.078
[17] Chen, N.-k., Guidon, A., Chang, H.-C., Song, A.W., (2013), "A robust multi-shot scan strategy for high-resolution diffusion weighted MRI enabled by multiplexed sensitivity-encoding (MUSE)", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.038
[18] Ma, R., Akçakaya, M., Moeller, S., Auerbach, E., Uğurbil, K., Van de Moortele, P.-F. (2020), "A field-monitoring-based approach for correcting eddy-current-induced artifacts of up to the 2nd spatial order in human-connectome-project-style multiband diffusion MRI experiment at 7T: A pilot study", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116861
[19] Setsompop, K., Cohen-Adad, J., Gagoski, B.A., Raij, T., Yendiki, A., Keil, B., Wedeen, V.J., Wald, L.L. (2012), "Improving diffusion MRI using simultaneous multi-slice echo planar imaging", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.06.033
[20] Griswold, M.A., Jakob, P.M., Heidemann, R.M., Nittka, M., Jellus, V., Wang, J., Kiefer, B. and Haase, A. (2002), "Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA)", Magn. Reson. Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.10171
[21] Andersson, J. L. Skare, S., Ashburner, J. (2003), "How to correct susceptibility distortions in spin-echo echo-planar images: application to diffusion tensor imaging", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00336-7
[22] Smith, S.M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M.W., Beckmann, C.F., Behrens, T.E., Johansen-Berg, H., Bannister, P.R., De Luca, M., Drobnjak, I., Flitney, D.E., Niazy, R.K., Saunders, J., Vickers, J., Zhang, Y., De Stefano, N., Brady, J.M., Matthews, P.M. "Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051
[23] Mohammadi, S., Möller, H.E., Kugel, H., Müller, D.K. and Deppe, M. (2010), "Correcting eddy current and motion effects by affine whole‐brain registrations: Evaluation of three‐dimensional distortions and comparison with slicewise correction", Magn. Reson. Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22501
[24] Veraart, J., Sijbers, J., Sunaert, S., Leemans, A., Jeurissen, B. (2013), "Weighted linear least squares estimation of diffusion MRI parameters: Strengths, limitations, and pitfalls", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.028
[25] Jeurissen, B., Tournier, J.-D., Dhollander, T., Connelly, A., Sijbers, J. (2014), "Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.07.061
[26] Tournier, J.D., Smith, R., Raffelt, D., Tabbara, R., Dhollander, T., Pietsch, M., Christiaens, D., Jeurissen, B., Yeh, C.-H., Connelly, A. (2019) "MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation", Neuroimage. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116137
Figures