1644
Vessel-selective 4D MRA Based on ASL for Treatment Evaluation in Patients with Bypass Surgery: Comparison with 3D TOF MRA and DSA
Maoxue Wang1, Yi Wang1, Yongbo Yang1, Yongbo Yang1, Ming Li1, Jilei Zhang1, and Bing Zhang1,2
1The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Institute of Brain Science, Nanjing University Nanjing, Nanjing, China
1The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China, 2Institute of Brain Science, Nanjing University Nanjing, Nanjing, China
Synopsis
A comparison of 4D MRA and 3D TOF MRA in patients with moyamoya vasculopathy after revascularization.
introduction
Revascularization is a common treatment strategy in patients with intra-extracranial symptomatic arterial occlusive disease1. Conventional digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the gold standard reference for evaluating patients with intracranial vasculopathy and is an invasive technique. Four-dimensional (4D) MR angiography (MRA) based on pseudocontinuous ASL (pCASL) combined with the keyhole and view-sharing techniques (4D-PACK) as a nonenhanced method provides better visualization of peripheral arteries compared with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRA in patients with moyamoya disease not treated by surgery2, 3. This study aimed to assess and compare the visualization of bypass patency and intracranial collaterals from the external carotid artery (ECA) by 4D-sPACK versus 3D time-of-flight MRA (3D TOF MRA) in patients with extra-intracranial revascularization. DSA was used as a reference.Methods
The MRI data of 23 patients who underwent bypass surgery were collected on an Ingenia 3.0T CX scanner (Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands). The image quality of 4D-sPACK was evaluated using a 4-point grading system. Patency of anastomosis was assessed on 4D-sPACK and 3D TOF MRA images using DSA as the gold standard. Visualization of intracranial collateral vessels was assessed with another 4-point grading by two radiologists on the images of 4D-sPACK and 3D TOF MRA using DSA as the reference. The interobserver agreement of intracranial vessel visualization scores was assessed with the weighted kappa statistic.results
Twenty-seven hemispheres of 22 patients (9 male, age 44 ± 11.72 years) with occlusive intracranial vascular disease were included in the study. The 4D-sPACK images were successfully obtained in 24 (24/27, 88.89%) hemispheres with a higher sensitivity compared with 3D TOF MRA (95.65% vs 78.26%) for visualizing anastomoses. Significant differences were found between 4D-sPACK (scores, 3.10 ± 1.20) and 3D TOF MRA (scores, 1.67 ± 0.62) in the visualization of intracranial collaterals from the ECA obtained using DSA as a reference (P < 0.001). The interobserver agreement for intracranial collateral assessment was almost substantial for 4D-sPACK (kappa = 0. 719) and 3D TOF MRA (kappa = 0.801).conclusion
The 4D-sPACK provided better performance than 3D TOF MRA in the treatment evaluation of patients after bypass surgery, and it had high consistency with DSA. Hence, 4D-sPACK could serve as a novel noninvasive method to visualize flow dynamics when labeling the ECA and to evaluate the patency of anastomoses and intracranial collaterals in patients with bypass surgery.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81720108022 B.Z., 81971596, X.Z., 82071904, Z.Q.); Supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Nanjing University (2020-021414380462); The key project of Jiangsu Commission of Health (K2019025); Key medical talents of the Jiangsu province, the "13th Five-Year" health promotion project of the Jiangsu province (ZDRCA2016064); Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Discipline (Laboratory) (ZDXKA2016020); the project of the sixth peak of talented people (WSN -138).References
1. Kim T, Oh CW, Bang JS, et al. Moyamoya disease: treatment and outcomes. J Stroke. 2016. 18(1):21-30.
2. Obara M, Togao O, Beck GM, et al. Non-contrast enhanced 4D intracranial MR angiography based on pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling with the keyhole and view-sharing technique. Magn Reson Med. 2018.80(2):719-725.
3. Togao O, Hiwatashi A, Obara M, et al. 4D ASL-based MR angiography for visualization of distal arteries and leptomeningeal collateral vessels in moyamoya disease: a comparison of techniques. Eur Radiol. 2018. 28(11):4871-4881.
Figures

Table 1.
Results for anastomosis patency in 4D-sPACK and 3D TOF MRA images using DSA
as the gold standard.
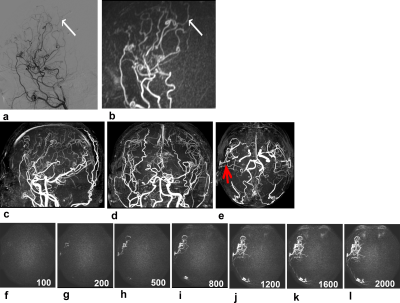
Figure
1. A 33-year-old male patient with bilateral MMV after
bilateral bypass surgery. The vasculopathy was observed approximately 35 months
after the surgery was performed on the right side. Intracranial collaterals originating
from the right external carotid artery were clearly shown on sagittal 4D-sPACK
(b), consistent with DSA (a); however, they were not clearly observed on axial,
coronal, and sagittal images (c–e) obtained on TOF MRA because of overlap with other vessels.
The anastomosis was shown on axial TOF MRA image (e, red arrow) and axial 4D-sPACK (f–i).