1573
An 8-channel transmit loop array for body imaging at 5T1United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 2Lauterbur Imaging Research Center, Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China
Synopsis
In this study, an 8-channel (8ch) loop and a 2-channel (2ch) birdcage in 5T frequency are built and compared. Basic electrical characteristics, engineering issues in implementation, transmitting efficiency, perturbation sensitivity, B1+ uniformity and local SAR are compared between these two coils. Measurement result of the B1+ distribution in torso region with these coils are obtained from a whole body 5T MRI scanner.
Introduction
MRI systems operating at high field predominantly focus on brain and extremity imaging because of the extreme B1 non-uniformities encountered in the body[1-3].So, it's a challenge to design body coils for imaging a large region of interest (ROI) such as the torso[4]. To solve this problem, an 8ch transmit coil can be adopted. In this study, an 8-channel loop array and a 2ch birdcage in 5T frequency are built and compared. Meanwhile the engineering issues in implementation are discussed.Methods
An 8ch loop array is built with 60 cm in patient bore diameter, as shown in Figure1(a). There are 12 capacitors per loop. The capacitors on the end ring are about 12 pf, and the capacitors on the rung are about 15 pf. Adjacent loops are decoupled by capacitors on the common rung. A large number of adjustable capacitors are used for tuning, matching and decoupling of the 8 loops. The birdcage coil is the most commonly used whole body RF-transmitting coil in clinical MRI currently[5][6]. Figure1(b) shows a 32-rungs high pass birdcage coil with 60 cm in diameter. Transmitting efficiency of the two coils are compared when driven in circular polarization (CP) mode. Meanwhile, couplings of channels and perturbation sensitivities of the two coils are also compared. SAR in CP mode are compared by simulations. The simulation software is CST-Microwave-Studio, loaded with the Gustav human body model (2.08×2.08×2mm3)[7] at resonance frequencies as shown in Figure2. The B1+ field distribution is not only simulated, but also measured with volunteer at abdomen landmark in a 5T MRI scanner (United Imaging Healthcare,Shanghai, China). The parallel RF transmission system consists of eight independent RF power amplifiers (RFPAs) with peak power 8 kW. Two-channels RFPA with peak power 32 kW is synthesized by a power combiner and used for 2-channel birdcage coil.Results
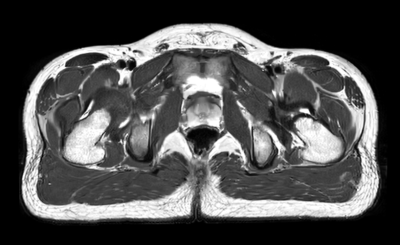
The 2ch birdcage coil is more sensitive to the perturbation of the receiving coils and the load. When the load is increasing, the resonance frequency and couplings of the channels are changed larger compared with the 8ch loop coil. For birdcage coil, the minimum coupling of channels is -16 dB in the case of no-load . As the load increases, the coupling decreases. The minimum coupling of channels is under -20 dB in the case of load. The coupling between the channels is slightly stronger. For 8ch loop coil, the minimum coupling of channels is -12 dB in the case of no-load. The minimum coupling of channels is under -18 dB in the case of load. The 8ch loop coil adopts a large number of adjustable capacitors to increase the decoupling of channels and adjust element matching, resulting in higher manufacture costs and more difficult tuning. With regard to transmitting efficiency, in the case of no-load, the birdcage coil is 0.223 μT/√W when the 8ch loop coil is 0.147 μT/√W. When the coils are loaded with a phantom equivalent to a 100 kg patient, the transmitting efficiency of birdcage coil is 0.0996 μT/√W when the 8ch loop coil is 0.0690 μT/√W. Abdomen uniformity of the two coils are evaluated by simulations and reality measurement. The B1+ field distribution of two coils are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen that they have similar B1+ distributions and uniformity. The 8ch coil has a higher degree of freedom of B1 shimming. To evaluate local SAR (10g average), simulations have been performed and results are shown in Figure 4. The local SAR results of two coils are normalized to 1 W accepted power. In the selected slice (central transversal), the maximum SAR (10g average) of birdcage coil is 0.244 W/Kg when the 8ch loop coil is 0.161 W/Kg. The image performance in reality measurement of 8ch transmit coil is considered because of its high degree of freedom. Figure 5 shows the image of the pelvic at 5T.Discussion
The 2ch birdcage coil has better performance in transmitting efficiency and channels decoupling. The 8ch loop coil has better robustness to disturbances caused by receiving coils and load. The two coils have the similar B1+ field distribution (CP mode), but the 8ch loop coil has a better B1 shimming capability. It has a higher freedom degree of B1 shimming, and usually a more uniform B1 field can be obtained. Research MRI systems operating at high field predominantly focus on brain and extremity imaging because of the extreme B1 non-uniformities encountered in the body. The 8ch loop coil has the potential to alleviate these challenges, and is worthy of further research in the future.Acknowledgements
This work is supported by National Key R&D Program of China 2017YFC0108800.References
[1] Vaughan J T , Garwood M , Collins C M , et al. 7T vs. 4T: RF power, homogeneity, and signal-to-noise comparison in head images[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Official Journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2010, 46(1):24-30.
[2] Thomas B P , Welch E B , Niederhauser B D , et al. High-resolution 7T MRI of the human hippocampus in vivo.[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2010, 28(5):1266-1272.
[3] Beisteiner R , Robinson S , Wurnig M , et al. Clinical fMRI: Evidence for a 7T benefit over 3T[J]. Neuroimage, 2011, 57(3):1015-1021.
[4] Haiwei Chen et al, An 8-channel Loop Coil Array for Body Imaging Using Coupled Line Phase Shifters at 7T, Proceedings ISMRM 2020, 4074.
[5] Hayes C E , Edelstein W A , Schenck J F , et al. An efficient, highly homogeneous radiofrequency coil for whole-body NMR imaging at 1.5 T[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969), 1985, 63(3):622-628.
[6] Collins C M , Li S , Smith M B . SAR and B1 field distributions in a heterogeneous human head model within a birdcage coil[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2010, 40(6):847-856.
[7] CST Microwave Studio, Darmstadt, Germany.
Figures
Figure3: Central transversal B1+ field distributions in simulation and reality measurement. All results are normalized to the largest B1+ magnitude. (a) 2ch birdcage B1+ field distribution in simulation; (b) 8ch loop coil B1+ field distribution in simulation; (c) 2ch birdcage B1+ field distribution in reality measurement; (d) 8ch loop coil B1+ field distribution in reality measurement.