1512
Evaluation of brain structure and function changed in vestibular migraine patients: a MRI MP2RAGE and SMS-Rs-fMRI study1Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining, China, 2Siemens Healthineers, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Headache caused by paroxysmal vestibular symptoms Known as vestibular migraine (VM), its pathophysiology and related mechanisms are less understood at this stage. The purpose of this study was to apply Simultaneous Multi-Slice Resting State functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (SMS-Rs-fMRI) to explore the gray matter volume (GMV), brain function, and brain default in patients with VM..Compared with the control group, patients with VM had lower GMV in multiple brain areas, higher ALFF values in multiple brain areas, and changes in the brain default network function connection in the resting state.
Introduction
Headache caused by paroxysmal vestibular symptoms Known as vestibular migraine (VM), its pathophysiology and related mechanisms are less understood at this stage. With the rapid development of MRI neuroimaging, the brain changes of VM patients can be analyzed and the pathogenesis of VM can be further explored. The purpose of this study was to apply Simultaneous Multi-Slice Resting State functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (SMS-Rs-fMRI) to explore the gray matter volume (GMV), brain function, and brain default in patients with vestibular migraine (VM) .The unique change characteristics of the functional connection (Functional Connection, FC) of the network (Default mode network, DMN).Methods
17 VM patients (case group) who met the International Headache Association (3rd edition) diagnostic criteria for VM and 31 normal volunteers (normal group) were enrolled in this study. , All the scanning were performed on a 3T MR scanner(MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) with a 64-channel head-neck coil. Brain structure image was acquired using magnetization-prepared two rapid acquisition gradient echoes sequence (MP2RAGE) . The Rest-fMRI sequence was preformed with simultaneous multi slice (SMS)technique for getting better SNR about raw date. Different brain regions of GMV and ALFF values were extracted and compared between two groups using Voxel-based morphology (VBM) and amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) method.The related functional connection analysis method of posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) seed point was used to extract the brain areas changed by DMN in the resting state; independent sample t test was used between groups.Results
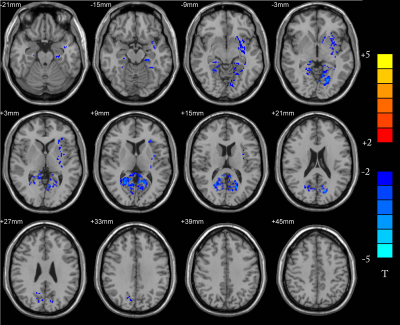
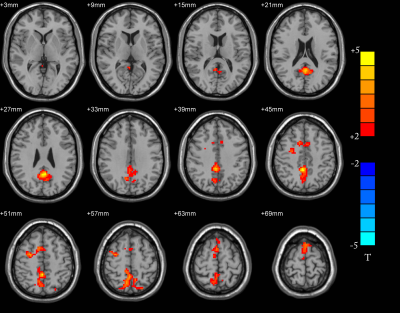
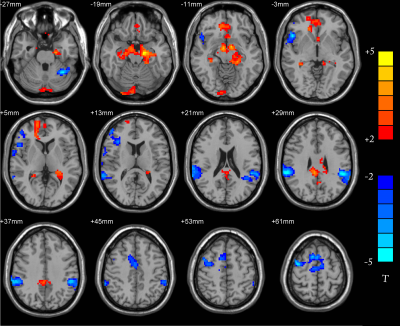
Compared with the normal group, gray matter volume was decreased in bilateral talus fissure cortex, bilateral lingual gyrus, right precuneus, bilateral posterior cingulate gyrus, bilateral parahippocampal gyrus, left insula and the bean-shaped putamen about the patient group (p<0.05, AlphaSim correction). The ALFF values about patient group were increased in bilateral anterior cuneiform lobes, bilateral medial and lateral cingulate gyrus, bilateral posterior cingulate gyrus, bilateral supplementary motor areas, bilateral dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus, left cuneiform lobe, right In the lateral middle frontal lobe, the right central anterior gyrus, the left paracentral lobule and the left medial superior frontal gyrus, there were no brain areas with reduced ALFF values in the whole brain. Compared with the normal group, the brain areas in the patient group with enhanced functional connection between DMN and PCC were bilateral cerebellar area 9, bilateral parahippocampal gyrus, bilateral hippocampus, bilateral superior frontal gyrus in the orbit, left fusiform gyrus, right medial superior frontal gyrus, right lingual gyrus, and the brain areas with weakened connections are bilateral Superior marginal gyrus, bilateral superior temporal gyrus, bilateral middle temporal gyrus, bilateral parietal-inferior marginal angular gyrus, bilateral supplementary motor areas, left cerebellar area 6, left cerebellar foot area 1, right dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus , Right middle frontal gyrus, right inferior frontal gyrus of triangle, right inferior frontal gyrus of right insula, inferior frontal gyrus of right orbit, right central insula, right medial and lateral cingulate gyrus (p <0.05, AlphaSim correction).Conclusion
Compared with the control group, patients with VM had lower GMV in multiple brain areas, higher ALFF values in multiple brain areas, and changes in the brain default network function connection in the resting state. The brain structure of the patient group and the normal group was consistent. The differences in brain function and functional connection provide theoretical support for the timely treatment of vestibular migraine in clinical practice.Acknowledgements
Thanks to my mentor, Professor Haihua Bao , her meticulous attitude towards work and scientific research has deeply affected me, but no matter how busy or tired, she will also find time to guide my scientific research progress and share precious valuables with me life experience. Thanks to Dr. Shaoyu Wang for his careful guidance and valuable suggestions on my thesis during his busy schedule.References
[1]Marina de Tommaso, Anna Ambrosini, Filippo Brighina, et al. Altered processing of sensory stimuli in patients with migraine. 2014, 10(Suppl. 1):144-155.
[2]. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition.[J]. Cephalalgia : an international journal of headache,2018,38(1).
[3]Xia Zhe,Jie Gao,Li Chen,Dongsheng Zhang,Min Tang,Xuejiao Yan,Fuxia Bai,Xin Zhang,Ze Zou,Weibo Chen,Xiaoyan Lei,Xiaoling Zhang. Altered structure of the vestibular cortex in patients with vestibular migraine[J]. Brain and Behavior,2020,10(4).
[4]S. Wang,H. Wang,D. Zhao,X. Liu,W. Yan,M. Wang,R. Zhao. Grey matter changes in patients with vestibular migraine[J]. Clinical Radiology,2019,74(11).
[5]Liu Li,Hu Xiaofei,Zhang Yixin,Pan Qi,Zhan Qunling,Tan Ge,Wang Kuiyun,Zhou Jiying. Effect of Vestibular Rehabilitation on Spontaneous Brain Activity in Patients With Vestibular Migraine: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.[J]. Frontiers in human neuroscience,2020,14.
Figures