1484
Differential diagnosis rectal cancer with and without lymph node metastasis using amide proton transfer-weighted imaging and T1 map1Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Amide proton transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging can be used to assess changes of intracellular protein concentration and the pH value. Non-invasive visualization and quantification of tissue composition could be detected by T1 map. In this study, we aim to explore the value in difference of rectal cancer with and without lymph node metastasis using APTw imaging combined with T1 map. High diagnostic efficacy (AUC: 0.891; sensitivity: 81.8%; specificity: 100.0%) was achieved with combination of APT and T1 values.
Introduction
Rectal cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death1. Accurate prediction lymph node metastasis is of great significance for the staging and treatment of rectal cancer2. By detecting proton exchange between amide protons of endogenous mobile proteins/peptides and bulk-water protons, Amide Proton Transfer-weighted (APTw) imaging can assess changes of the intracellular protein concentration and the pH value. It has been used for diagnoses of diseases, especially tumors, in regions such as brain and prostate3-5. Non-invasive visualization and quantification of tissue composition were measured by T1 map. The purpose of this study is to investigate the potential of APTw and T1 map imaging in difference of rental cancer patients with and without lymph node metastasis.Materials and Methods
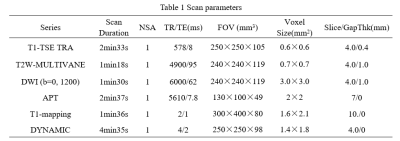
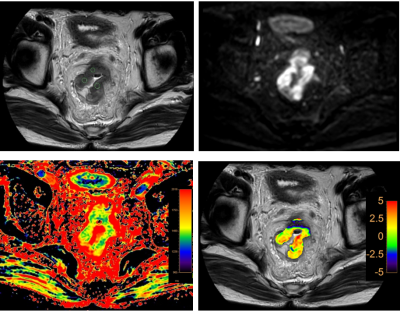
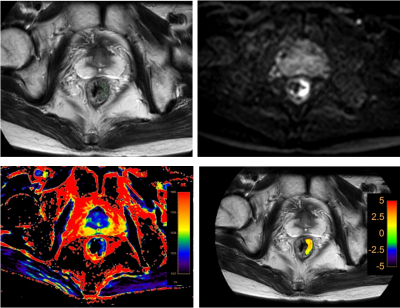
This study has been approved by the local IRB. 21 patients with rectal cancer lesions were retrospectively analyzed. According to the presence of lymph node metastasis, all patients were divided into two groups: 11 patients with lymph node metastasis (group A, 8 males, 3 females, age 61.36±10.20 years) and 10 patients without lymph node metastasis (group B, 7 males, 3 female, age 66.00±3.83 years). ATPw, T1 map and conventional MRI sequences included T1W, T2W, DWI and DYNAMIC were performed on a 3.0T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, the Netherlands) (detail parameters listed in Table 1). Raw data of APTw and T1 map were uploaded to a workstation (Intellispace Portal 9, Philips Healthcare) for post-processing. T2-weighted, DWI and DYNAMIC images were used for the anatomical location of lesion (Figure 1, 2). Three circle ROIs were manually placed on the slice with largest area of lesion with high signal intensity and obvious enhancement on APTw and T1 map images, respectively. The ICC (Inter-class correlation coefficient) was used to test the measurement consistency of mean values of the ATP and T1 values measured from the three ROIs between the two observers. The mean values of the ATP and T1 values were used for comparison between groups A and B using the Mann-Whitney U test. ROC curves of the above parameters were plotted to analyze the diagnostic efficacy in rectal cancer with and without lymph node metastasis. Logistic regression was also used to calculate the value of APT combined with T1 map parameters in the comparison of rectal cancer patients with (group A) and without (group B) lymph node metastasis. The difference between AUCs was compared using Delong test. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
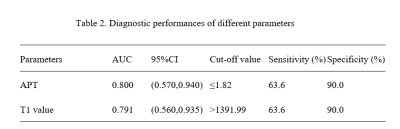
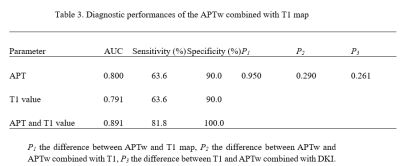
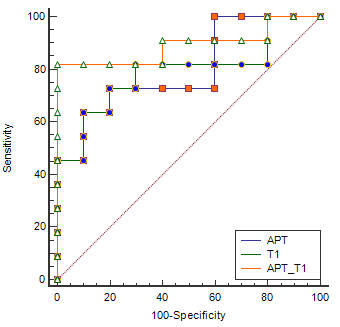
APT values and T1 values measured by the two observers were well consistent (ICC > 0.75). The median (25th Percentile, 75th Percentile) of APT and T1 values for group A were 1.81 (1.30, 2.77) %, 1411.64 (1384.85, 1527.64) ms, and for group B were 2.17 (1.87, 3.44) %, 1368.03 (1320.89, 1390.77) ms, respectively. APT and T1 values showed significant difference between two groups (p<0.05)(Table 2). Areas under the ROC curve (AUC) of APT and T1 values were 0.800 and 0.791. The sensitivity and specificity of APT and T1 values were both 63.6% and 90.0%. With combination of APT and T1 values for rectal cancer with and without lymph node metastasis, the diagnostic efficacy was increased (AUC=0.891), as well as the sensitivity (81.8%) and the specificity (100.0%)(Table 3, Figure 3).Discussion and conclusions
APTw imaging combined with T1 map imaging can effectively reflect lesion changes between rectal cancers with and without lymph node metastasis. APT values were significantly lower in the group with lymph node metastasis than group without lymph node metastasis. T1 values were significantly higher in the group with lymph node metastasis than group without lymph node metastasis.Acknowledgements
-References
[1] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020[J]. Ca A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2020, 0:1-20.
[2] Yukiharu Hiyoshi, Yuji Miyamoto, Yuki Kiyozumi,,et al. Risk factors and prognostic significance of lateral pelvic lymph node metastasis in advanced rectal cancer[J]. International Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2019.
[3] Zhou Jinyuan, HeoHye-Young, Knutsson Linda, et al. APT-weighted MRI: Techniques, current neuro applications, and challenging issues[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50: 347-364.
[4] Takayama Y, Nishie A, Sugimoto M, et al. Amide proton transfer(APT) magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer: comparison with Gleason scores. MAGMA 2016; 29: 671-679.
[5] He Yong-Lan, Li Yuan, Lin Cheng-Yu, et al. Three-dimensional turbo-spin-echo amide proton transfer-weighted mri for cervical cancer: A preliminary study[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50: 1318-1325.
Figures