1137
The value of IVIM-DWI in early prediction of efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer1Radiology Department, Anhui Provincial Cancer Hospital, Hefei, China, 2Radiology department, Anhui Provincial Cancer Hospital, Hefei, China
Synopsis
The aim of our study was to investigate the early predictive value of IVIM-DWI in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. 43 cases of breast cancer confirmed by pathological puncture biopsy in our hospital were enrolled in this study. Four courses of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were used to evaluate the efficacy. The conclusion obtained via the present study is IVIM-DWI can predict the early curative effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer and evaluate its effectiveness. It can assist conventional MRI to evaluate the curative effect.
Objective
To investigate the early predictive value of IVIM-DWI in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.Methods
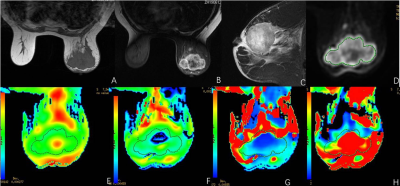
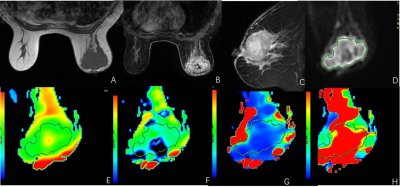
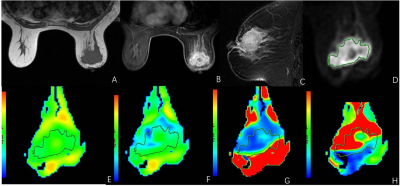
43 cases of breast cancer confirmed by pathological puncture biopsy in our hospital were collected. Four courses of neoadjuvant chemotherapy were used to evaluate the efficacy. IVIM-DWI was performed after each chemotherapy. IVIM-DWI parameters included standard apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), slow apparent diffusion coefficient (D), fast apparent diffusion coefficient (D*) and perfusion fraction (f). Referring to RECIST criteria, the study cases were divided into two groups: (1) effective group: complete remission (CR) and partial remission (PR); (2) ineffective group: progress disease (PD) and stable disease (SD). Multivariate analysis of variance was used to compare IVIM-DWI parameters before and after treatment, between effective and ineffective groups. The ROC curve was used to calculate the optimal diagnostic threshold for the effective group and the ineffective group.Results
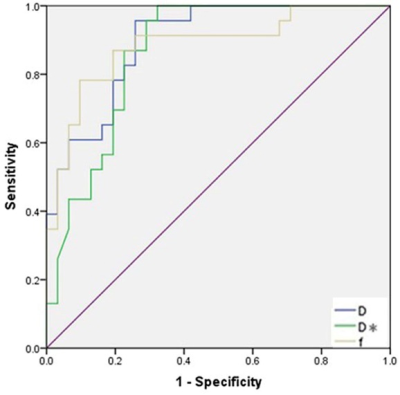
A total of 49 lesions were studied, including 33 in the effective group (CR: 7, PR: 26) and 16 in the ineffective group (SD: 11, PD: 5). There was significant difference in the volume of tumors in the effective group of pretherapy and the third treatment course, but there was no significant difference in the ineffective group. There were significant differences in D value, D* value and F value of IVIM-DWI parameters among three groups of pretherapy, 1st treatment and 3rd treatment in the effective group (F value was 30.487, 6.752 and 8.983, respectively, P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in ADC value (P > 0.05). There was no significant difference in parameters in the three groups before and after treatment in the ineffective group. There were significant differences in D value, D* value and F value of IVIM-DWI parameters between effective group and ineffective group before treatment (F value was 30.487, 6.752 and 8.983 respectively, P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in ADC value (P > 0.05). The area under curve (AUC) of D value, D* value and F value were 0.889, 0.910 and 0.879 respectively. The diagnostic thresholds were 0.716 mm2/s (specificity and sensitivity were 75.1% and 95.2%, respectively), 37.85 mm2/s (specificity and sensitivity were 71.2% and 98.3%, respectively) and 0.292 (specificity and sensitivity were 89.4% and 81.5%, respectively). (Table 1, Figure 1-2)Conclusion
IVIM-DWI can predict the early curative effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer and evaluate its effectiveness. It can assist conventional MRI to evaluate the curative effect.Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge Dr Xing-xiang Li for his help in analyzing the date of samples.References
1. Liu C, Liang C, Liu Z, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in evaluation of breast lesions: comparison with conventional DWI.[J]. European Journal of Radiology, 2013, 82(12):e782-e789.
2. Lee Y J, Kim S H, Kang B J, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM)‐derived parameters in diffusion‐weighted MRI: Associations with prognostic factors in invasive ductal carcinoma[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2017, 45(5).
3. Liu C, Wang K, Chan Q, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging for breast lesions: comparison and correlation with pharmacokinetic evaluation from dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging[J]. European Radiology, 2016, 26(11):1-11.
4. Bokacheva L, Kaplan J B, Giri D D, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI at 3.0 T differentiates malignant breast lesions from benign lesions and breast parenchyma.[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jmri, 2015, 40(4):813-823.
5. Kim Y, Kim S H, Lee H W, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI for predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2018, 48:27-33.
6. Rahbar H, Partridge S C. Multiparametric Breast MRI of Breast Cancer[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Clinics of North America, 2016, 24(1):223.
Figures