1047
Proton MR spectroscopy reveals metabolic alterations in generalized tonic clonic seizures before and after treatment: a longitudinal study1Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Department of Radiology, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2Department of Radiology, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Synopsis
The neurobiochemical mechanisms of Generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTCS) patients' brains and the effects of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) on metabolism are not yet clear. The purpose of this study was to use MRS to explore metabolic alterations of bilateral Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) in pre-/post-treatment GTCS patients. We included 23 initially diagnosed GTCS patients and 23 healthy controls (HC). The metabolite level (n-acetyl aspartate, creatine) in DLPFC of GTCS patients was changed compared with that of healthy control, and AEDs had an effect on the metabolites concentration, which may explain the neurobiochemical mechanism.
Introduction
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTCS) is one of the most common, severe, and life-threatening types of epileptic seizures, most of which are treated with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) of choice1,2. Drug-resistance is increasing but the neurobiochemical mechanisms of antiepileptic drugs are still unknown3,4. In recent years, more and more MRI-based studies have been conducted in GTCS patients, but they pay more attention to structural and functional changes of brain, less to metabolites concentration alterations and the effect of AEDs on metabolism5,6,7.Materials and Methods
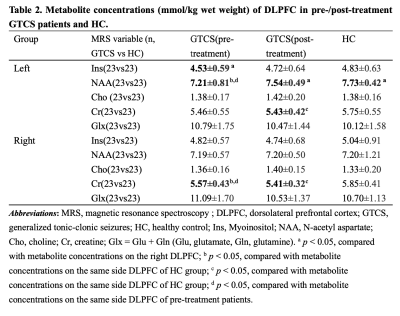
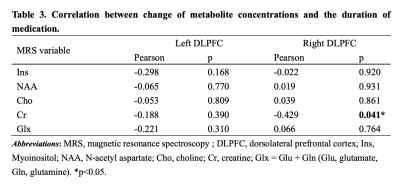
MRI scans were performed on 23 GTCS patients twice before and after treatment, and only once on 23 HC. All participants acquired high-resolution T1-weighted and 1H-MRS images. Metabolites including N-acetyl aspartate (NAA), myo-inositol (Ins), Choline (Cho), Creatine (Cr) and Glutamate + Glutamine (Glu + Gln, Glx) were quantified by using LCModel software and corrected for cerebrospinal fluid effects. Comparisons were performed between HC and GTCS patients before and after treatment respectively, and between pre-treatment and post-treatment patients. We also compared interhemispheric differences in metabolite concentrations on DLPFC both sides of each group. Correlation analyses were performed between the duration of medication and the difference of metabolite concentration before and after treatment.Results
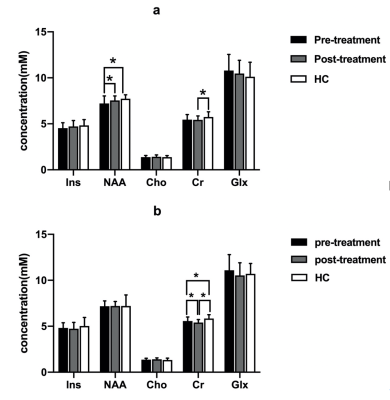
Ins concentration of pre-treatment patients(left < right), NAA concentration of post-treatment patients and HC (left > right)all showed hemispheric asymmetry (Fig.1). Concentrations of NAA in the left DLPFC and Cr in the right DLPFC in pre-treatment patients were lower than those of HC (table 2, Fig.2). NAA concentration of the left DLPFC increased while Cr concentration of the right DLPFC decreased in GTCS patients before and after treatment (table 2, Fig.3). Compared with HC, post-treatment GTCS patients showed significantly decreased Cr concentration in bilateral DLPFC (table 2, Fig.3). There was a negative correlation between the duration of medication and the difference of Cr before and after treatment (table 3).Discussion and Conclusion
The decrease of NAA concentration is related to mitochondrial dysfunctio8,9, and the pathogenesis of GTCS may mainly indicate affection on neuronal function. Cho concentration (stands for structural integrity of cells10) does not change, which supports this point. Creatine is mainly found in glial cells11. After AEDs, NAA concentration recovered and Cr concentration decreased again. Antiepileptic drugs are likely to target neuronal recovery. Our study also proves that DLPFC is a relatively important region in the pathophysiology of GTCS. This study may aid in understanding the pathogenesis of GTCS and the neurobiochemical mechanisms of AEDs action.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kodankandath TV, Theodore D, Samanta D. Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizure. BTI - StatPearls.
2. Shorvon SD, Bermejo PE, Gibbs AA, Huberfeld G, Kälviäinen R. Antiepileptic drug treatment of generalized tonic-clonic seizures: An evaluation of regulatory data and five criteria for drug selection. (1525-5069).
3. Gamkrelidze GN, Nanobashvili ZI, Bilanishvili IG, Lordkipanidze T, Kandashvili M, Kokaia M, et al. Concentration- and time-dependent effects of myo-inositol on evoked epileptic afterdischarge in the hippocampus in vivo. (1473-558X).
4. Löscher W, Potschka H, Sisodiya SM, Vezzani A. Drug Resistance in Epilepsy: Clinical Impact, Potential Mechanisms, and New Innovative Treatment Options. (1521-0081).
5. Huang W, Lu G Fau - Zhang Z, Zhang Z Fau - Zhong Y, Zhong Y Fau - Wang Z, Wang Z Fau - Yuan C, Yuan C Fau - Jiao Q, et al. Gray-matter volume reduction in the thalamus and frontal lobe in epileptic patients with generalized tonic-clonic seizures. (0150-9861).
6. Bernhardt BC, Rozen Da Fau - Worsley KJ, Worsley Kj Fau - Evans AC, Evans Ac Fau - Bernasconi N, Bernasconi N Fau - Bernasconi A, Bernasconi A. Thalamo-cortical network pathology in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: insights from MRI-based morphometric correlation analysis. (1095-9572).
7. Wandschneider B, Stretton J, Sidhu M, Centeno M, Kozák LR, Symms M, et al. Levetiracetam reduces abnormal network activations in temporal lobe epilepsy. (1526-632X).
8. Chang SJ, Yu BC. Mitochondrial matters of the brain: mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative status in epilepsy. (1573-6881).
9. Wang Y, Chen Z. An update for epilepsy research and antiepileptic drug development: Toward precise circuit therapy. (1879-016X).
10. Zhu H, Barker PB. MR spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging of the brain. (1940-6029).
11. Rae CD, Bröer S. Creatine as a booster for human brain function. How might it work? (1872-9754).
Figures
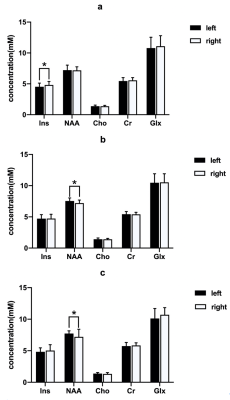
Fig.1 Metabolic difference between the left and right DLPFC in each group. (a) pre-treatment GTCS patients; (b) post-treatment GTCS patients; (3) HC. *p < 0.05. Abbreviations: DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; GTCS, generalized tonic-clonic seizures; HC, healthy control; Ins, Myoinositol; NAA, N-acetyl aspartate; Cho, choline; Cr, creatine; Glx = Glu + Gln (Glu, glutamate, Gln, glutamine).