1032
Anisotropic Mechanical Properties of White Matter Tracts Estimated with Multi-Excitation MRE and TI-NLI1Biomedical Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, United States, 2Thayer School of Engineering, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, United States, 3Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science, Washington University in St. Lous, St. Louis, MO, United States, 4Mechanical Engineering, Universite de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, QC, Canada
Synopsis
In this study, we used multi-excitation MR elastography (MRE) in conjunction with transversely isotropic NLI (TI-NLI) to estimate the anisotropic viscoelastic parameters of the human brain. We collected data on ten subjects and took averages of the parameters within individual regions of the brain. Through comparison of regions of interest, we found significant differences between the parameter estimate of gray matter and white matter and between individual white matter tracts. The results of this study indicate that multi-excitation MRE and TI-NLI can generate consistent anisotropic parameter estimates for WM that capture innate differences in individual tract structure.
Introduction
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) uses propagating shear waves to estimate the viscoelastic mechanical properties of soft tissues, including the brain. However, most inversion algorithms assume material isotropy, and tissues with highly-aligned, fiber regions, such as white matter (WM) tracts, require an anisotropic material model incorporated in the inversion algorithm to more accurately estimate mechanical properties. We have developed an approach to incorporate a finite element representation of the nearly incompressible, transversely isotropic (NITI) material model[1] into a non-linear inversion algorithm (TI-NLI), to solve for three parameters describing tensile and shear anisotropy in the model while accounting for material heterogeneity[2,3]. These parameters are estimated from multi-excitation MRE[4] (ME-MRE) data combining multiple actuations to generate waves with unique propagation and polarization[5], which are necessary for accurate property estimation[6]. In this study, we use these methods for the first time to estimate the anisotropic mechanical properties of WM tracts in the human brain.Methods
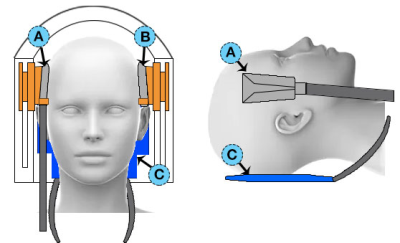
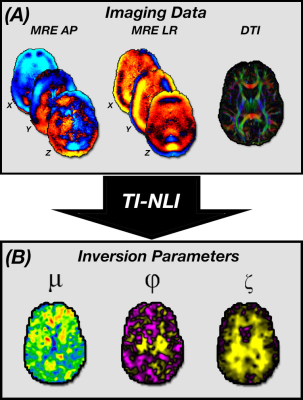
We scanned ten healthy subjects (5/5 M/F; ages 22-30) using a Siemens 3T Prisma scanner with a 20-channel head coil. MRE scans with anterior-posterior (AP) and left-right (LR) excitation were acquired sequentially (Figure 1). Excitations were generated at 50 Hz by the Resoundant (Rochester, MN) pneumatic actuator with one passive driver per direction. We used a custom driver on the right side of head for LR excitation and the pillow-driver behind the head for AP excitation. MRE scans used a 3D multiband, multishot spiral sequence[7] with 2x2x2 mm3 isotropic voxels with a total field of view of 240x240x128 mm3. We acquired diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) scans with resolution and FOV matched to the MRE scans to estimate fiber direction for TI-NLI and high-resolution T1-weighted MPRAGE scans at 0.9 mm isotropic resolution for anatomical localization.Using TI-NLI in conjunction with the AP and LR wave motion fields, along with fiber directions acquired from DTI, we generated maps of the three mechanical parameters describing the NITI material: μ, φ, and ζ. Substrate shear modulus (μ) is the shear modulus perpendicular to the fiber direction (i.e. μ2), φ=(μ1/μ2)-1 is the shear anisotropy, and ζ=(E1/E2)-1 is the tensile anisotropy. These two anisotropy parameters describe differences in mechanical properties parallel (μ1, E1) and perpendicular (μ2, E2) to the fibers.
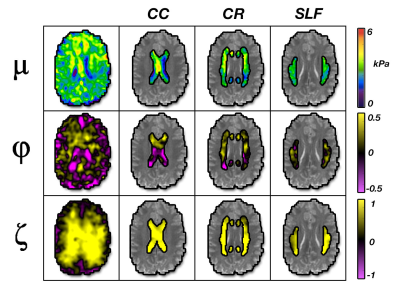
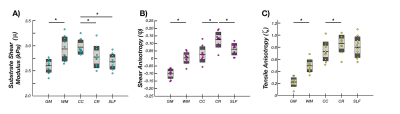
Average anisotropic properties were determined in gray matter (GM) and WM regions, and several major WM tracts. We used FAST in FSL[8] to separate GM and WM and isolated the corpus callosum (CC), corona radiata (CR), and superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) using WM atlases. Differences between regions and major tracts were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with a post-hoc Tukey test.
Results
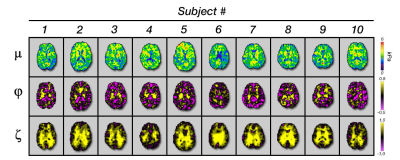
Figure 5 compares parameter averages between the ROIs in the ten subjects. Major WM tracts exhibited positive shear and tensile anisotropy, as expected. Average φ in the major tracts analyzed ranged from 0.026 to 0.124 (0.026, 0.124, and 0.061 for CC, CR, and SLF). Average ζ in tracts ranged from 0.731 to 0.861 (0.731, 0.861, and 0.801 for CC, CR, and SLF). These parameters were greater in tracts than overall WM, which exhibited φ = 0.003 and ζ = 0.492, which were greater than in GM (φ = -0.102 and ζ = 0.222). Estimates of all three parameters were significantly greater in WM compared to GM (p < 0.05). We also found significant differences in μ, φ, and ζ between the three tracts, with post-hoc tests showing all three parameters significantly differing between CC and CR, and significant differences in φ between CC and SLF and in ζ between CR and SLF.Discussion and Conclusions
In this study, we used ME-MRE in conjunction with TI-NLI to estimate the anisotropic viscoelastic parameters of the human brain. The differences between the anisotropic parameters of WM and GM agree with the expected response of highly-aligned vs. nonaligned fibrous tissue, and findings from isotropic property estimations that found a lower stiffness in GM than WM[9]. While the negative φ values in GM warrants future investigation, the overall φ in WM and the major WM tracts agrees roughly with previous anisotropic MRE studies, particularly those using the NITI material model that found φ estimated in the human brain at 15%[5] and in the porcine brain at 27-34%[10]. We also estimate ζ, which is ignored in previous approaches with simpler anisotropy models using only two parameters, and we recovered higher ζ values (~1) in WM tracts, which agrees with previous ex-vivo estimates[11] and strongly supports the inclusion of ζ as a necessary parameter in the material model. Parameter uncertainty and sensitivity to error in fiber direction from DTI is the subject of ongoing work.Our anisotropic MRE approach overcomes challenges from previous approaches[12], by using a model that captures tissue behavior while estimating a minimal number of parameters. We further acquire multi-excitation data to ensure sufficient tissue deformation to estimate parameters and combine this with the recently developed TI-NLI, which accounts for material heterogeneity present in the brain. Being able to observe consistent differences in anisotropic parameters between tracts in healthy individuals points to reliability of outcomes and sensitivity to changes that might occur due to pathology, such as aging, disease, or injury.
Acknowledgements
NIH R01-EB027577References
[1] Tweten, D. J., Okamoto, R. J., Schmidt, J. L., Garbow, J. R., and Bayly, P. V., 2015, “Estimation of Material Parameters from Slow and Fast Shear Waves in an Incompressible, Transversely Isotropic Material,” J. Biomech., 48(15), pp. 4002–4009.
[2] MDJ McGarry, EEW Van Houten, CA Guertler, RJ Okamoto, DR Smith, D Sowinski, CL Johnson, PV Bayly, JB Weaver, KD Paulsen, “A Heterogeneous, Time Harmonic, Nearly Incompressible Transverse Isotropic Finite Element Brain Simulation Platform for MR Elastography,” Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2020
[3] MDJ McGarry, EEW Van Houten, D Sowinski, PV Bayly, DR Smith, CL Johnson, JB Weaver, KD Paulsen, “Model-Based Heterogeneous Transverse Isotropic MR Elastography Inversion for Brain Tissue with Aligned Fiber Tracts,” 28th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, August 8-13, 2020.
[4] Anderson, A. T., Van Houten, E. E., McGarry, M. D., Paulsen, K. D., Holtrop, J. L., Sutton, B. P., Georgiadis, J. G., and Johnson, C. L., 2016, “Observation of Direction-Dependent Mechanical Properties in the Human Brain with Multi-Excitation MR Elastography.”
[5] Smith, D. R., Guertler, C. A., Okamoto, R. J., Romano, A. J., Bayly, P. V., and Johnson, C. L., 2020, “Multi-Excitation Magnetic Resonance Elastography of the Brain: Wave Propagation in Anisotropic White Matter,” J. Biomech. Eng., 142(7).
[6] Tweten, D. J., Okamoto, R. J., and Bayly, P. V., 2017, “Requirements for Accurate Estimation of Anisotropic Material Parameters by Magnetic Resonance Elastography: A Computational Study,” Magn. Reson. Med., 78(6), pp. 2360–2372
.[7] CL Johnson, JL Holtrop, AT Anderson, BP Sutton, “Brain MR Elastography with Multiband Excitation and Nonlinear Motion-Induced Phase Error Correction,” 24th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Singapore, May 7-13, 2016, p. 1951.
[8] Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., and Smith, S. M., 2012, FSL, Neuroimage, 62(2), pp. 782-790.
[9] Johnson, C. L., McGarry, M. D. J., Gharibans, A. A., Weaver, J. B., Paulsen, K. D., Wang, H., Olivero, W. C., Sutton, B. P., and Georgiadis, J. G., 2013, “Local Mechanical Properties of White Matter Structures in the Human Brain,” Neuroimage, 79, pp. 145–152.
[10] Schmidt, J. L., Tweten, D. J., Badachhape, A. A., Reiter, A. J., Okamoto, R. J., Garbow, J. R., and Bayly, P. V., 2018, “Measurement of Anisotropic Mechanical Properties in Porcine Brain White Matter Ex Vivo Using Magnetic Resonance Elastography,” J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 79, pp. 30–37.
[11] Velardi, F., Fraternali, · F, and Angelillo, · M, 2006, “Anisotropic Constitutive Equations and Experimental Tensile Behavior of Brain Tissue,” Biomech Model Mechanbiol, 5, pp. 53–61.
[12] Romano, A., Scheel, M., Hirsch, S., Braun, J., and Sack, I., 2012, “In Vivo Waveguide Elastography of White Matter Tracts in the Human Brain,” Magn. Reson. Med., 68(5), pp. 1410–1422.
Figures