0972
Application of cardiac magnetic resonance strain analysis in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy1Shanxi Cardiovascular Hospital, Taiyuan, China, 2GE Healthcare, MR Research, Beijing, China
Synopsis
CMR-FT can quantitatively evaluate myocardial motion. In this study, we find that the right ventricular global longitudinal, radial and circumferential strain in ARVC patients are significantly lower than those in normal controls. In ARVC patients with LVEF < 55%, the left ventricular global longitudinal, radial and circumferential strain decrease significantly. The left ventricular global longitudinal strain also decrease in ARVC patients with LVEF ≥ 55%. These results suggested that myocardial strain can be used to evaluate biventricular myocardial motion in ARVC patients.
Summary of Main Findings
Myocardial strain can sensitively detect abnormal myocardial motion and whether the left ventricle is involved in the early stage.Introduction
Patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) are prone to malignant arrhythmias and even sudden cardiac death. Early diagnosis can effectively prevent sudden death and improve prognosis. At present, the diagnosis of right ventricular motion abnormality remains subjective, lack of objective quantitative indicators. Cardiac magnetic resonance-feature tracking (CMR-FT) can be used to evaluate cardiac motion objectively and quantitatively. The purpose of this study was to explore the value of cardiac magnetic resonance strain analysis in the evaluation of biventricular function in ARVC patients.Methods
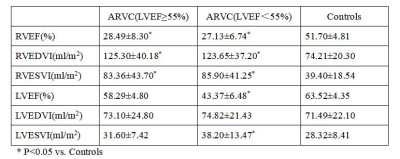
Fourteen patients with ARVC who underwent cardiac magnetic resonance examinations in Shanxi Cardiovascular Hospital from October 2015 to September 2020 were collected retrospectively. The diagnostic criteria were based on the clinical diagnostic criteria of ARVC revised in 2010. All images were acquired with breath holding. The imaging protocol included long-axial left ventricular two-chamber heart, left ventricular inflow and outflow tract, long-axial four-chamber heart and short-axis cine images with balanced steady state free precession (b-SSFP) sequence .The patients were divided into two groups: the preserved ejection fraction of left ventricle(LVEF) group (LVEF ≥ 55%, n=9) and the reduced LVEF group (LVEF < 55%, n=5). Fourteen normal subjects were collected as controls. The Canadian Circle Cardiovascular image software (CVI42) was used for image analysis. One-way ANOVA was used to compare the differences of biventricular function parameters and myocardial strain among the three groups. Receiver operating characteristics(ROC) analysis was used to assess the diagnostic performance.Results
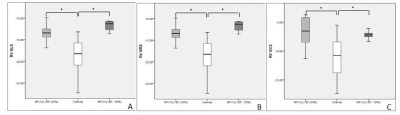
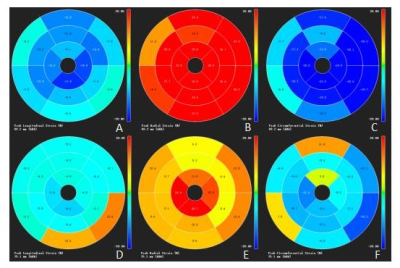
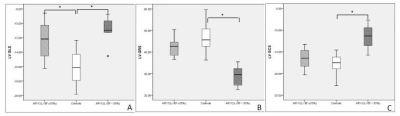
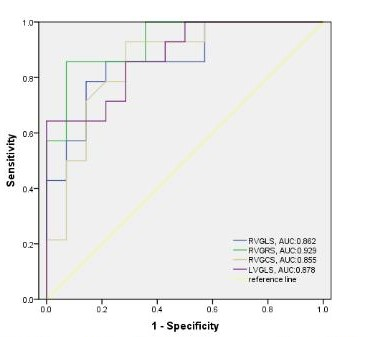
The right ventricular ejection fraction (RVEF), right ventricular end-diastolic volume index (RVEDVI) and right ventricular end-systolic volume index (RVESVI) in ARVC patients were significantly lower than those in the controls. The left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left ventricular end-diastolic volume index (LVEDVI) and left ventricular end-systolic volume index(LVESVI), in the patient group with LVEF ≥ 55% were haven’t shown statistically significance when compared wirh the controls, while LVESVI in the group with LVEF < 55% was significantly lower than that in the controls (Table 1). Compared with the controls, the global longitudinal strain (GLS), global radial strain (GRS) and global circumferential strain (GCS) of the right ventricle (RV) in ARVC patients were all decreased(Figure1). The left ventricle(LV) GLS of the patients with LVEF ≥ 55% was lower than that of the controls, and the LV GLS, GRS and GCS of the patients with LVEF < 55% were significantly lower than those of the controls (Figure2 and 3). The ROC analysis demonstrated that RV GLS, RV GRS, RV GCS and LV GLS with AUC of 0.862, 0.929, 0.855, 0.878, respectively,were all good indicators to diferentiate ARVC patients and controls(Figure 4). Among all these indicators, RV GRS shows the best performance with an AUC of 0.929 and LV GLS the second with an AUC of 0.878.Discussion
ARVC is characterized by progressive myocardial fiber fat replacement, and the normal myocardial tissue disappears, resulting in the weaken or even disappearance of RV global or local motion, as well as decreased the LV cardiac function. Therefore the GLS, GRS and GCS of the RV are significantly decreased. Even in ARVC patients with LVEF ≥ 55%, the LV GLS is lower than that of normal controls, indicating that myocardial strain can sensitively detect abnormal myocardial motion in the early stage.Conclusion
In conclusion, CMR-FT can effectively detect the changes of biventricular myocardial motion in ARVC patients, especially the left ventricular involvement when LVEF is normal, which is helpful for early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment for ARVC patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Heermann P,Fritsch H,Koopmann M,et al. Biventricular myocardial strain analysis using cardiac magnetic resonance feature tracking (CMR-FT) in patients with distinct types of right ventricular diseases comparing arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC), right ventricular outflow-tract tachycardia (RVOT-VT), and Brugada syndrome (BrS).[J] .Clin Res Cardiol, 2019, 108(10): 1147-1162.
[2] Chen X,Li L,Cheng H, et al. Early Left Ventricular Involvement Detected by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: The Effects of Left Ventricular Late Gadolinium Enhancement and Right Ventricular Dysfunction.[J] .J Am Heart Assoc, 2019, 8(17): e012989.
[3] Bourfiss M,Vigneault DM,Aliyari Ghasebeh M, et al. Feature tracking CMR reveals abnormal strain in preclinical arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/ cardiomyopathy: a multisoftware feasibility and clinical implementation study.[J] .J Cardiovasc Magn Reson, 2017, 19(1): 66.
[4] Shen MT,Yang ZG,Diao KY, et al. Left Ventricular Involvement in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy Predicts Adverse Clinical Outcomes: A Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking Study.[J] .Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 14235.
[5] Zghaib T,Ghasabeh MA,Assis FR, et al. Regional Strain by Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Improves Detection of Right Ventricular Scar Compared With Late Gadolinium Enhancement on a Multimodality Scar Evaluation in Patients With Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy.[J] .Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2018, 11(9): e007546.
Figures