0922
Precision MRI (pMRI) of Liver Metastasis enabled by Protein MRI contrast agents1Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlatna, GA, United States, 2Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA, United States, 3Emory University, Atlanta, GA, United States, 4Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA, United States
Synopsis
The liver is the most common organ for metastasis of various malignancies, especially for uveal melanoma (UM), colorectal cancer (CRC) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Precision medicine to chronic diseases, especially for liver cancer and metastasis, requires non-invasive precision diagnostics. Non-invasive precision imaging capable of early detection, staging and molecular subtyping/stratification of patients, is a major breakthrough. Rapid development and approval of precision medicine also requires precision imaging to evaluate drug efficacy at animal and patient levels. There is a pressing unmet medical need to develop MRI contrast agents and imaging methodologies with desired sensitivity and specificity .
Abstract
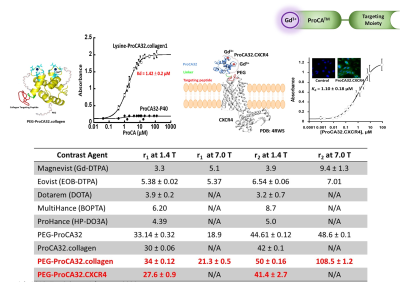
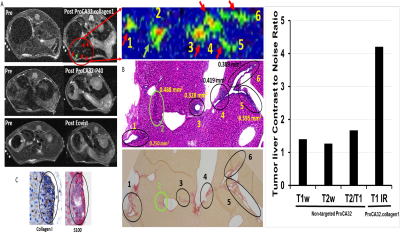
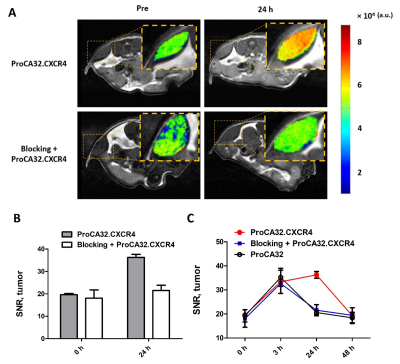
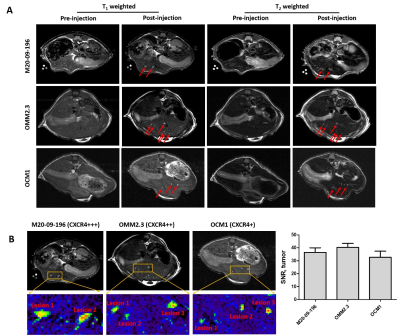
Introduction: The liver is the most common organ for metastasis of various malignancies, especially for uveal melanoma (UM), ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer (CRC) and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Precision medicine to chronic diseases, especially for liver cancer and metastasis, requires non-invasive precision diagnostics. Non-invasive precision imaging capable of early detection, staging and molecular subtyping/stratification of patients, is a major breakthrough. Rapid development and approval of precision medicine also requires precision imaging to evaluate drug efficacy at animal and patient levels. There is a pressing unmet medical need to develop MRI contrast agents and imaging methodologies with desired sensitivity and specificity to overcome the high heterogeneous background and in vivo properties as well as reduced toxicity. Here we report our development of a novel class of protein MRI contrast agents (ProCA32s) by engineering Gd3+ binding sites in a scaffold protein to enable precision imaging of molecular biomarkers by MRI (pMRI) using dual imaging. Methods: Patient samples of liver metastasis were used to determine the upregulation of the molecular biomarkers such as collagen 1 and chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) by histological analysis. Collagen and CXCR4 targeted MRI contrast agents (denoted as ProCA32.Collagen1 and ProCA32.CXCR4) were engineered by addition of the biomarker targeting moiety to ProCA32 with a flexible hinge (Fig 1). Their relaxivity at both 1.4 and 7.0 T were determined using relaxometer and 7T scanner. Their binding affinity to the biomarkers were determined using Elisa and cell imaging (Fig 1). Their metal binding and metal selectivity were further examined using Tb-sensitized FRET and competition assay as well as transmetallization. The sensitivity and specificity of both developed biomarker targeted MRI contrast agents in early detection of liver metastasis and burden from uveal melanoma and ovarian cancer were examined using several mouse models and histological analysis. A subcutaneous uveal melanoma (UM) murine model was developed for the CXCR4 blocking experiment. Around 2*106 Mel 290 cells were injected subcutaneous on the right and left side of the back of NU/NU mice to develop approximately 0.5 cm ×0.5 cm subcutaneous tumors in six weeks. We specifically constructed a CXCR4 blocking reagent by fusing the CXCR4-targeting moiety of ProCA32.CXCR4 at the C-terminal of GST tag to ensure a proper blocking with the similar interaction. Results: Both ProCA32.collagen and ProCA32.CXCR4 exhibit significant improvement of r1 and r2relaxivities compared with clinical approved contrast agents such as Eovist and ProHance at both 1.4 and 7.0 T, respectively (Fig 1). Both targeted contrast agents also have strong serum stability, resistance to transmetallation, and 102 and 1013-fold higher metal selectivity for Gd3+ over Ca2+ and Zn2+, respectively compared to clinical contrast agents. Both immunofluorescence staining and ELISA suggest that they specifically target biomarkers overexpressed in cancer cells with good affinity (Fig. 1). Sensitive detection of liver lesions in several animal models can be achieved using multiple imaging methodologies taken advantage of dual relaxation property of ProCA32.collagen1 and ProCA32.CXCR4. ProCA32.collagen1 enables sensitive and early stage detection of hepatic micrometastasis as small as 0.144 mm2 using dual imaging and inversion recovery (Fig 2). To demonstrate the CXCR4 targeting capability in tumor, we have carried out an additional receptor blocking experiment to demonstrate specific CXCR4 receptor binding in vivo. In the mice with the CXCR4 targeted contrast agent ProCA32.CXCR4 administration, UM tumors exhibited significant SNR increase at 24 hours post administration (Fig.3). In contrast, tumors from mice that first received the blocking reagent did not exhibit SNR enhancement at 24 hours post administration of ProCA32.CXCR4. Injection of non-targeted contrast agent ProCA32 only resulted in initial SNR enhancement 3 hours post administration due to blood pool effect. This enhancement returned to baseline at 24 hours. In contrast, injection of ProCA32.CXCR4 resulted in maximum SNR enhancement at 24 hours post injection and returned to the baseline at 48 hours. Prior injection of the CXCR4 receptor blocking reagent specifically eliminated the enhancement at 24 hours by ProCA32.CXCR4 but retained the 3 hours initial enhancement due to blood pool effect. Taken together, ProCA32.CXCR4 is able to specifically bind to the over-expressed CXCR4 receptors at the tumors and enable molecular targeting MR imaging of liver metastasis. Fig 4 shows that small liver metastasis of three UM murine models generated by OCM1, OMM2.3, and M20-09-196 UM cell lines with low, medium, and high in vitro CXCR4 expression levels can be detected using ProCA32.CXCR4 by MRI at 7T. In contrast, no hepatic metastases were visible in the pre-injection MR images and cannot be detected using clinical contrast agent Eovist nor the non-targeted MRI contrast agent ProCA32. These detected liver metastases and burden were verified by histological analysis (Fig 5). Conclusion: The discovery of upregulated CXCR4 and collagen as imaging biomarkers of hepatic metastasis and our development of novel imaging methodology enabled by CXCR4 and collagen targeted protein MRI contrast agents are expected to fill the major gap in non-invasive precise early detection of cancer metastasis, monitoring progression, devising targeted therapy, and understanding hepatic metastasis biology.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH research grants(UT2AA028659, AA112713 and CA183376) to J. Y. of InLighta Biosciences and Georgia State University. This work was supported by NIH research grants R33CA235319 to J. Y. of Georgia State University. Dr. Jenny Yang is founder and president of InLighta Biosciences LLC.References
(1) Salarian M, Turaga RC, Xue S, Nezafati M, Hekmatyar K, Qiao J, Zhang Y, Tan S, Ibhagui OY, Hai Y, Li J, Mukkavilli R, Sharma M, Mittal P, Min X, Keilholz S, Yu L, Qin G, Farris AB, Liu ZR, Yang JJ. Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4777. Epub 2019/10/31. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11984-2. PMID: 31664017; PMCID: PMC6820552.
(2) Tan S, Yang H, Xue S, Qiao J, Salarian M, Hekmatyar K, Meng Y, Mukkavilli R, Pu F, Odubade OY, Harris W, Hai Y, Yushak ML, Morales-Tirado VM, Mittal P, Sun PZ, Lawson D, Grossniklaus HE, Yang JJ. Chemokine receptor 4 targeted protein MRI contrast agent for early detection of liver metastases. Sci Adv. 2020;6(6):eaav7504. Epub 2020/02/23. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav7504. PMID: 32083172; PMCID: PMC7007242.
(3) Salarian M, Yang H, Turaga RC, Tan S, Qiao J, Xue S, Gui Z, Peng G, Han H, Mittal P, Grossniklaus HE, Yang JJ. Precision detection of liver metastasis by collagen-targeted protein MRI contrast agent. Biomaterials. 2019;224:119478. Epub 2019/09/23. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119478. PMID: 31542517.
(4) Xue S, Yang H, Qiao J, Pu F, Jiang J, Hubbard K, Hekmatyar K, Langley J, Salarian M, Long RC, Bryant RG, Hu XP, Grossniklaus HE, Liu ZR, Yang JJ. Protein MRI contrast agent with unprecedented metal selectivity and sensitivity for liver cancer imaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2015;112(21):6607-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423021112. PMID: 25971726; PMCID: 4450423.
(5) Turaga RC, Yin L, Yang JJ, Lee H, Ivanov I, Yan C, Yang H, Grossniklaus HE, Wang S, Ma C, Sun L, Liu ZR. Rational design of a protein that binds integrin alphavbeta3 outside the ligand binding site. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11675. Epub 2016/06/01. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11675. PMID: 27241473; PMCID: PMC4895024.
Figures