0897
Optimization of Compressed Sensing Acceleration Factors for Lumbosacral Plexus 3D MRI
Renwang PU1, Qingwei SONG2, Ailian LIU1, Hao nan ZHANG1, Nan ZHANG1, and Jiazheng WANG3
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, DALIAN, China, 3Philips Healthcare, BEIJING, China
1the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, DALIAN, China, 3Philips Healthcare, BEIJING, China
Synopsis
MRI, particularly the 3D-T2*-FFE sequence is widely used imaging tool for evaluating lumbosacral plexus because of its multiplanar capabilities and excellent soft-tissue contrast. However, conventional 3D-T2*-FFE scan time is long, despite the SENSE acceleration, which may cause spontaneous or involuntary movement due to the patient's discomfort and which may ultimately lead to imaging artifacts. Compressed Sensing (CS) is able to further reduce the imaging time by pseudo-random under-sample through the acquisition , but the image quality may be degraded when the acceleration factor (AF) is over-stretched. In this study we explored the optimal CS acceleration factor for lumbosacral plexus 3D-T2*-FFE imaging.
Synopsis
Lumbosacral plexus MRI with 3D-T2*-FFE enables high-resolution periphery nerve images, but the scanning time is long, leading to potential motion artifacts especially in patients with poor coordination. Compressed sensing(CS)is a novel imaging technology reported reduce imaging time while retaining image quality. We compared a series of compressed sensing acceleration factors to 2-fold SENSE acceleration and identified 3-fold acceleration with compressed sensing optimal for brachial plexus images.Introduction
MRI, particularly the 3D-T2*-FFE (fast field echo) sequence is a widely used imaging tool for evaluating the lumbosacral plexus because of its multiplanar capabilities and excellent soft-tissue contrast. However, the conventional 3D-T2*-FFE scan time is long, despite the SENSE acceleration, which may cause spontaneous or involuntary movement due to the patient's discomfort and which may ultimately lead to imaging artifacts. Compressed Sensing (CS) is able to further reduce the imaging time by pseudo-random under-sample through the acquisition [1-4], but the image quality may be degraded when the acceleration factor (AF) is over-stretched. In this study we explored the optimal CS acceleration factor for lumbosacral plexus 3D-T2*-FFE imaging.Materials and Methods
This study has been approved by the institutional IRB. 11 healthy volunteers (7 males and 4 females, age 24-62, 41.82±11.66) were recruited and underwent the 3D-T2*-FFE scan of lumbosacral plexus on a 3.0 T MR scanner (Ingenia CX, Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands). For each patient, the 3D-T2*-FFE scan was repeated 6 times (hence 6 groups) with different acceleration schemes: SENSE2 (conventional), CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6(Table1). Mean signal and the standard deviation (SD) was measured with ROIs (~8 mm2) placed in on both the lumbosacral plexus and muscles in the coronal images (Figure 1), and the SNR and CNR were calculated as: SNR=SI lumbosacral plexus/SDmuscle;CNR=(SI lumbosacral plexus- SI muscle)/SD muscle. The overall image quality of each group was also scored subjectively by two radiologists (10 years of radiology experiences) on a four-point scoring criterion. The Wilcoxon test (SPSS 24.0) was used to compare the lumbosacral plexus SNR and CNR between the SENSE2 group and the CS groups. The interobserver reliability on qualitative evaluation was assessed via Cohen’s kappa test (excellent agreement if k > 0.9; good agreement if k > 0.6). The Friedman test was used to compare the subjective scores of the images.Result
The subjective scores reached good agreement between the two observers (k=0.647, p<0.05). The average scores between the two observers were then taken for the subsequent analysis. No statistical difference in quantitative and subjective evaluations was found between SENSE2, CS2, and CS3 groups (p>0.05). Image quality (SNR, CNR, and subjective scores) were significantly lower in the CS4~6 groups than in SENSE2 group (p<0.05). As the AF increased, lumbosacral plexus SNR, CNR and subjective scores decreased (Table2-3). The scanning time for the SENSE2, CS2, CS3, CS4, CS5, CS6 groups was 225s, 190s, 128s,96s,78s and 66s, respectively.Discussion and Conclusion
Three-fold acceleration rate with compressed sensing reached an acceptable balance between imaging time and image quality for lumbosacral plexus 3D-T2*-FFE imaging, taking the traditional 2-fold SENSE acceleration as a gold standard, with the scan time cut by 43% from the baseline.Acknowledgements
Thank you, Dr. Wang Jiazheng from Philips HealthcareReferences
[1] Bratke G, Rau R, Weiss K, et al. Accelerated MRI of the Lumbar Spine Using Compressed Sensing: Quality and Efficiency[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2019,49(7):e164-e175. [2] Lee S H, Lee Y H, Suh J S. Accelerating knee MR imaging: Compressed sensing in isotropic three-dimensional fast spin-echo sequence[J]. Magn Reson Imaging,2018,46:90-97. Bratke G, Rau R, Weiss K, et al. Accelerated MRI of the Lumbar Spine Using Compressed Sensing: Quality and Efficiency[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging,2019,49(7):e164-e175. [3] Yoneyama M, Takahara T, Kwee TC, Nakamura M, Tabuchi T. Rapid high resolution MR neurography with a diffusion-weighted pre-pulse. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2013;12(2):111-119. [4] Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly J M. Sparse MRI: The application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med,2007,58(6):1182-1195.Figures
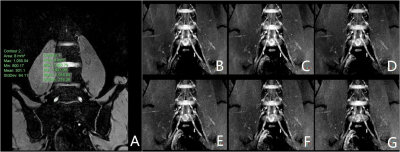
one-slice
images of the 3D-T2*-FFE.A:Coronal image of lumbosacral plexus.The areaof
interest in the nerve and muscle. B: Conventional 3D-T2*-FFE with SENSE factor
of 2.C-G: 3D-T2*-FFE with CS factors of 2, 3, 4,5 and 6, respectively. Data
were collected from a healthy volunteer (male, 24 years old).
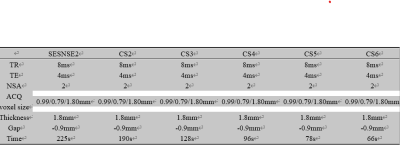
The scan parameters of 3D-T2*-FFE with SENSE
factor of 2, 3D-T2*-FFE with CS factors of 2, 3, 4,5 and 6, respectively.
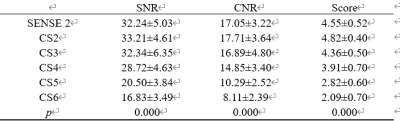
Measurements of SNR,CNR and subjective scores for
3D-T2*-FFE images with different acceleration factors.
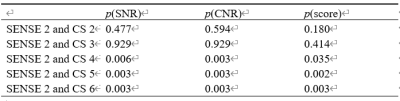
The measurements/scores from 3D-T2*-FFE with CS
factors of 2 to 3D-T2*-FFE with CS factors of 6 were compared to those from 3D-T2*-FFE
with SENSE factor of 2 (P values shown in the Table).