bingbing gao1, Yuhan Jiang1, Nan Zhang1, Yanwei Miao1, Qingwei Song1, Ailian Liu1, and Peng Sun2
1the First Affiliated hospital of Dalian Medical university, Dalian, China, 2Philips Healthcare, BeiJing, China
Synopsis
Strategically Acquired Gradient Echo (STAGE) imaging is a
novel and useful MR sequence which can provide seven different key modalities
at the same time, T1w, PDw, SWI, T1 mapping, PD mapping, T2* mapping, and SWIM.
However, the acquisition time is relatively long (about 8 minutes). The
compressed sensing (CS) technique is now wildly applied for accelerating MR
acquisition. This study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of CS accelerated
STAGE technique, and find an optimal acceleration factor (AF). According to our
preliminary results, the AF of 4 was recommended.
Introduction
Multimodality MRI, a combination of imaging modalities may provide a better solution to improve
the diagnosis of diseases. Strategically Acquired Gradient Echo
(STAGE) imaging can provide seven different key modalities at the same time,
including T1w, PDw, SWI, T1 mapping, PD mapping, T2*mapping, and SWIM. It takes
a relatively long time to collect the data because a second echo must be
acquired to maintain flow compensation under a separate scan. CS has been
wildly applied to accelerate 3D MRI acquisitions. Here, we demonstrate the
feasibility of the CS accelerated STAGE technique, and evaluate the impact of
AF on the images by comparing the CS accelerated images with different AF and
images without CS. Methods
The study was prospective. Fifteen volunteers (25.78±7.79, range:
22-36years, 6 men) were enrolled, who underwent
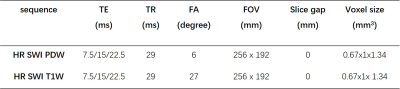
a STAGE protocol (MR parameters were shown in Table 1, scan
protocol was shown in Table 2) on a 3.0 Tesla Philips MR (Ingenia CX,
Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) using a 32-channel head coil. Three CS
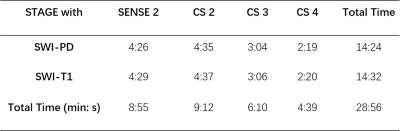
STAGE with AF of 2, 3, 4 were scanned,
and the routine STAGE accelerated 2 times by SENSE was used as a reference. All
DICOM raw data were processed by using SPIN and STAGE software by one
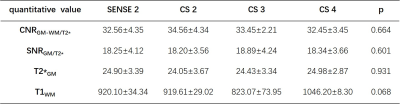
experienced neuroradiologist. Quantitative value-T1 value and T2* value,
signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were measured in
both white matter (WM)- frontal lobe and gray matter (GM)-globus pallidus. Kruskal-Wallis
test was calculated for the intermethod comparison.Results
The CS STAGE with AF of 2, 3, 4 took 9min12s, 6min10s, 4min39s respectively. The scan
time of routinely used SENSE protocol was 8min55s. The detailed quantitative
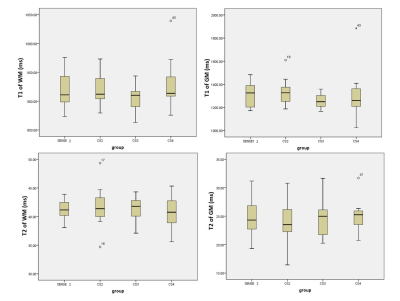
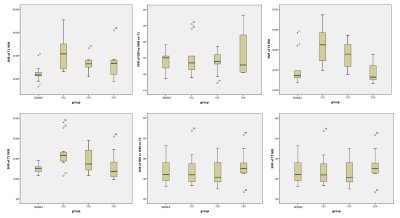
values (SNR, CNR, T1, T2) derived from STAGE with different acceleration strategies
were shown in Table 3, and no statistically significant difference was detected
(p﹥0.05;
Figure 1 and 2). Thus, by using an AF of 4, CS STAGE achieved 51.9% time
saving compared with 2 times accelerated SENSE protocol while maintaining image
qualities.Conclusion
In this study, comparing with the SENSE technique, CS was a
reliable method for fast STAGE imaging with comparable image quality. The CS-based
STAGE imaging can be easily integrated into the clinical protocols and would be
beneficial for a wide range of applications, such as cerebrovascular disease,
Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis disease. According to our results, CS
STAGE with AF of 4 was recommended. Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Department of Radiology, First
Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, for supporting this study.
The authors thank all volunteers who participated in this study.References
[1] B.M.A. Delattre, S. Boudabbous, C. Hansen, A. Neroladaki, A.L.
Hachulla, and M.I. Vargas, Compressed sensing MRI of different organs: ready
for clinical daily practice? Eur Radiol 30 (2020) 308-319.
[2] Y. Liu, J. Li, N. He, Y. Chen, Z. Jin, F. Yan, and E.M. Haacke,
Optimizing neuromelanin contrast in the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus
using a magnetization transfer contrast prepared 3D gradient recalled echo
sequence. Neuroimage 218 (2020) 116935.
[3] C.J. Park, J. Cha, S.S. Ahn, H.S. Choi, Y.D. Kim, H.S. Nam, J.H.
Heo, and S.K. Lee, Contrast-Enhanced High-Resolution Intracranial Vessel Wall
MRI with Compressed Sensing: Comparison with Conventional T1 Volumetric
Isotropic Turbo Spin Echo Acquisition Sequence. Korean J Radiol 21 (2020)
1334-1344.