0895
Optimization of scan parameters to reduce acquisition time for resolve-based DKI in NPC
Yaoyao He1, Hao Chen1, Huiting Zhang2, Robert Grimm2, Cecheng Zhao3, Xiaofang Guo1, Yulin Liu1, and Zilong Yuan1
1Hubei Cancer Hospital, Wuhan, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany, 3Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
1Hubei Cancer Hospital, Wuhan, China, 2Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany, 3Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to shorten acquisition time of RESOLVE-based diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), and we explored the influence of b value combinations on the scan time and parameters from DKI. The results showed that the group with b-value (200, 400, 800, 2000) had excellent agreement with the actual acquisition with b-value (200, 400, 800, 1500, 2000) and the scan time saved 28% (3min46s vs 5min13s), and was recommended in the clinical DKI research in NPC.
Introduction
Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), a non-invasive diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) technique, can detect the non-Gaussian diffusion of water molecules in different tissues [1], and is helpful for the early detection, diagnosis, and treatment evaluation of patients with Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Previous literature has shown that the choice of b-value combination, number of direction, and diffusion time can generate variability in DKI research, because they reflect the degree of diffusion weight [2,3]. Different b-value combinations will produce different estimates of DKI-derived parameters [4]. Choosing a suitable b-value combination is very crucial, which can further reduce time. Hence, this study will further explore the appropriate b-value combination for NPC.Materials and Methods
This prospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and the requirement for formal informed consent was acquired from all patients. 38 patients were enrolled between March 2018 and December 2019. MRI examinations were performed on a 3.0T MRI scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with 24-channel head and neck coil. A DKI with 5b-values was obtained using RESOLVE sequence, and the sequence parameters were as follows: 5b-values, including 200, 400, 800, 1500, 2000 s/mm2, TR = 3960 ms, TE1/TE2 = 68/98 ms, thickness/intersection gap = 4/0.4 mm, matrix size = 134 × 134; FOV = 258× 258 mm, readout segments = 5, Readout Partial Fourier (RPF) = 5/8, three orthogonal directions, scan time = 5min 13s. The different b-value combinations and corresponding simulated acquisition time used are shown in Table 1. All images with different b-value combinations were imported to a protype MR diffusion toolbox (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) for analysis, and the software fits the DKI model through equations (1)$$ Sb/S0=exp(-b*D+1/6 b2*MD*MK (1)
Where, MD is the apparent diffusion coefficient, and MK is the apparent diffusion kurtosis. Differences in RESOLVE based DKI sequences between different b-value combinations with RPF were compared using the Kruskal-Wallis H test. P < 0.001 was considered significantly difference by Bonferroni correction.
Result
Through the comparison of the ICC and P values of 9 groups of different b-value combinations in RESOLVE-based DKI, group 2 (200, 800, 2000), group 6 (200, 400, 800, 2000) and group 7 (200, 800, 1500, 2000) simultaneously satisfy the conditions of no significant difference (P > 0.001) and excellent agreement (0.81-1.00) with group 9 (200, 400, 800, 1500, 2000) (Figure 1), as shown in Table 2. The ICC of MK and MD in the group 6 were the largest (0.9897 and 0.9804, respectively) compared to the group 6 and group 7. Combining b-value optimization and RPF technology, the group 6 (200, 400, 800, 2000) can save about 28% of the time (3min46s vs 5min13s).Discussion
Some studies suggested that DKI should be added to routine clinical applications, which is helpful for cancer screening [5], and can also provide more accurate information about diffusion [6]. DKI may be helpful in predicting the radiotherapy response in NPC[8]. Therefore, the standardization of DKI imaging protocol is very essential, and the b-value optimization is one of the key factors. Both RPF and b-value combination can affect the scan time. In our study, when the RPF and the optimal b-value combination were used at the same time, that is, the group (200, 400, 800, 2000) with RPF can save up to 28% of time compared to the RESOLVE with RPF (200, 400, 800, 1500, 2000) and 56% without RPF (8min 31s)[7].Conclusions
The combination of RPF and b-value optimization can ensure the stability of DKI parameters and reduce the scanning time. With the advantages of stable image quality and time saving, we recommended that the DKI imaging of (200, 400, 800, 2000) with 5/8 RPF can be applied to the clinical DKI research in NPC.Acknowledgements
The author(s) disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This study was supported by the Hubei Key Laboratory of Medical Information Analysis & Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment (Grant No. PJS140012005).References
1. Rosenkrantz AB, Padhani AR, Chenevert TL, et al. Body diffusion kurtosis imaging: Basic principles, applications, and considerations for clinical practice. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;42(5):1190-202. 2. Veraart J, Poot DHJ, Van Hecke W, et al. More accurate estimation of diffusion tensor parameters using diffusion kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65(1):138-45. 3. Bihan DL. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Beyond: What Diffusion MR Imaging Can Tell Us about Tissue Structure. Radiology. 2013;268(2):318-22. 4. Poot D, Den Dekker AJ, Achten E, et al. Optimal Experimental Design for Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29(3):819-29. 5. Wang W, Yang L, Hu Z, et al. Assessment of Microvascular Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging. Radiology. 2018. 6. Huang Li, Li X,, Huang S, et al. Diffusion kurtosis MRI versus conventional diffusion-weighted imaging for evaluating inflammatory activity in Crohn's disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017. 7. Yuan Z, Chen H, He Y, et al. Partial Fourier Readout in Readout Segmentation of Long Variable Echo Trains-Based Imaging In Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Intl Soc Mag Reson Med, 2020.Figures
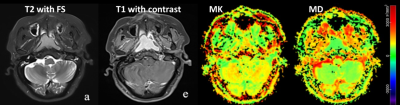
Figure
1. Representative images from a patient, including T2w with fat suppression
(FS), T1w with contrast, MK and MD based on DKI with 5b-values (200, 400, 800,
1500, 2000).
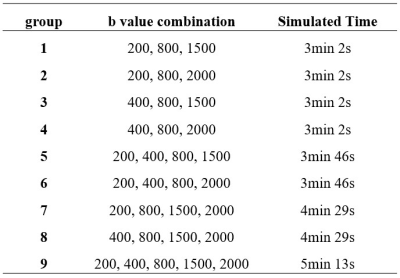
Table 1. The
b-value combinations and simulated acquisition time used in this study.
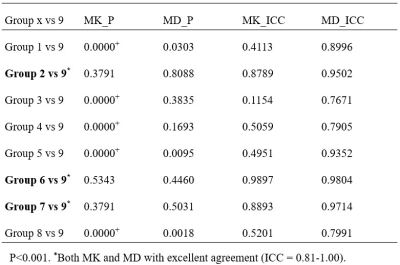
Table 2. Influence of different b-value
combinations in RESOLVE based DKI