0578
Inhibitory Thalamic Reticular Nucleus Drives Frequency Specific Brain-wide Responses1Laboratory of Biomedical Imaging and Signal Processing, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, 2Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, 3Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China, 4School of Biomedical Sciences, Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
Synopsis
Thalamic inhibition from thalamic reticular nucleus has been shown to provide critical gating upon thalamo-cortical interactions and exert selective modulation on information processing according to behavioral demands. However, where and how thalamic reticular nucleus exerts control of brain-wide neural activities over different spatial and temporal scales remained unclear. In this study, we demonstrate for the first time the frequency specific brain-wide responses driven by inhibitory somatosensory thalamic reticular nucleus using optogenetic fMRI. Such frequency specific engagements of brain-wide neural activities could underlie selective modulation of local circuits versus global networks in different brain functions.
Purpose
Thalamo-cortical networks rely on the requisite cooperation of excitatory and inhibitory neurons to control selective processing of information1,2. In particular, thalamic inhibition exerts dynamical control upon thalamo-cortical interactions according to behavioral demands2. The thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) consists of a shell of inhibitory neurons that provide the major inhibitory control to excitatory thalamo-cortical neurons of dorsal thalamic nuclei during sensory processing, arousal/sleep regulation and cognition/memory functions3-7. Converging evidence has demonstrated that TRN subdivisions exhibit distinct connections with dorsal thalamic nuclei3,5,6, and modulate neural activities at corresponding local cortical regions3,7-9. However, where and how TRN exerts specific inhibitory control of brain-wide neural activities over different spatiotemporal scales remained poorly understood. In this study, we employ optogenetic fMRI to interrogate the brain-wide spatiotemporal responses driven by cell-type-specific and spatiotemporal precise excitation of inhibitory somatosensory TRN (ssTRN) neurons. Additionally, we also examine the brain-wide fMRI responses to optogenetic stimulation of limbic TRN (lTRN).Method
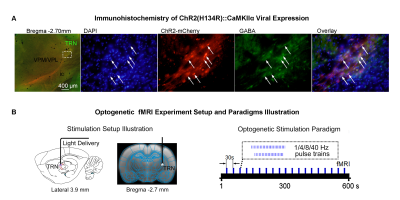
Animal preparation and MRI experimental setup: 3μl rAAV5-hsyn-hChR2(H134R)-mcherry-WPRE-PA was injected to ssTRN or lTRN in adult SD rats. After 4 weeks (Figure 1A), opaque optical fiber cannulas were implanted at the injection sites. All fMRI experiments were performed under 1.0% isoflurane. MRI data was acquired at 7T using GE-EPI.Optogenetic fMRI experiments: 12 pulses 1Hz 100ms pulse width, 48 pulses 4Hz 125ms pulse width, 96 pulses 8Hz 63 or 10ms pulse width, 400 pulses 40Hz 10ms pulse width and 24 pulses 8Hz 63ms pulse width of blue (473nm) light optogenetic stimulations were presented at ssTRN every 30s (40mW/mm2; Figure 1B). The 96 pulses 8Hz 63ms pulse width stimulation was also presented to lTRN. Coherence analysis10 was applied to identify significant BOLD responses. BOLD signal profiles were extracted from atlas-based ROIs.
Results
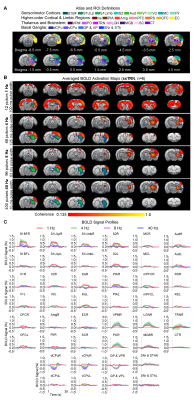
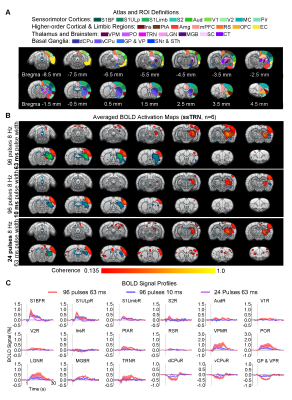
Frequency specific brain-wide responses driven by inhibitory somatosensory TRN neurons: Optogenetic stimulation of ssTRN at 1, 4, 8, and 40Hz commonly evoked robust positive BOLD responses in numerous sensorimotor cortical and thalamic regions (Figure 2), including ipsilateral somatosensory (primary: -barrel field, S1BF; -limb region, S1Limb; -upper lip region, S1ULp; secondary: S2), visual (primary and secondary, V1 & V2), and auditory (Aud) cortices, somatosensory (ventral posteromedial, VPM; posterior nuclei, PO), visual (LGN) and auditory (MGB) thalamus. Negative BOLD responses were commonly evoked at the posterior part of ipsilateral dorsal caudate putamen (dCPu). Notably, 1Hz stimulation evoked broad positive BOLD responses beyond the commonly activated regions, including the contralateral somatosensory, visual, auditory cortices and dCPu, bilateral ventral caudate putamen (vCPu), motor (MC), insular (Ins), parietal (PtA), medial prefrontal (mPFC), retrosplenial (RS), and orbitofrontal (OFC) cortices, ipsilateral amygdala (Amg), piriform cortex (Pir), entorhinal area (EC), substantia nigra and subthalamus (SNr & STh). Interestingly, 4, 8 and 40 Hz stimulations evoked strong negative BOLD responses at the ipsilateral ventral striatum including vCPu and pallidum (GP & VP).Brain-wide fMRI responses to reduced pulse width or number of pulses of 8 Hz stimulation: 96 pulses 10ms pulse width or 24 pulses 63ms pulse width optogenetic stimulation of ssTRN evoked localized positive sensory thalamic and cortical responses and negative vCPu and GPVP responses (Figure 3), resembling those evoked by the 96 pulses 63ms pulse width stimulation.
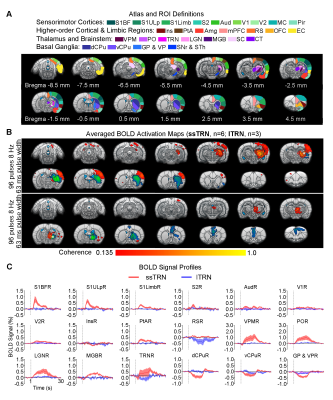
Distinct brain-wide responses to optogenetic stimulation of lTRN versus ssTRN: In contrast to ssTRN stimulation, lTRN stimulation evoked positive BOLD responses at central thalamic nuclei (CT) and negative BOLD responses at mPFC but no responses in the sensory thalamus and cortices (Figure 4). We detected negative BOLD responses at vCPu and GPVP for both ssTRN and lTRN stimulations.
Discussion
Our results demonstrated that the optogenetic stimulation of ssTRN evoked robust brain-wide BOLD responses within and beyond its primary projection targets. In particular, low frequency stimulation (1Hz) elicited brain-wide positive responses across bilateral cortex and vCPu beyond sensorimotor. Increasing stimulation frequency (i.e., from 1 to 4, 8 and 40Hz) resulted in positive responses being confined within sensory thalamo-cortical circuits while the negative ipsilateral dCPu response being extended to vCPu. Reducing pulse width or the number of pulses did not affect the confined response patterns at high stimulation frequency (8Hz). Similar to thalamo-cortical neurons, TRN neurons mainly fire in bursting mode during quiescence and sleep periods2,13,14. Optogenetic stimulation of sensory TRN can induce thalamo-cortical oscillations in corresponding circuits by bursting activity8,9,11,12. Stronger TRN bursting induce more robust and synchronized oscillation-related bursting in thalamo-cortical neurons, thus could consequently engage more thalamo-cortical circuits2. Indeed, our previous study revealed brain-wide bilateral cortical activations associated with sustained bursting activity upon 1 Hz, but not 5-40Hz, stimulation of VPM15. Our results here indicated that 1Hz, not 4-40Hz, stimulation elicited strong bursting activity at the sensory TRN and dorsal thalamic nuclei, consequently led to brain-wide bilateral cortical regions being recruited. We postulate that lTRN exhibit distinct brain-wide modulation targets but similar spatiotemporal specific control of brain-wide neural activities as ssTRN. In addition, our observed transition of positive bilateral responses into negative ipsilateral responses at vCPu suggests a frequency specific response property of the recently found TRN-striatal projection which can exert net excitation or inhibition upon different striatal neurons16. Together, our study reveals frequency specific brain-wide responses driven by TRN, which can contribute to selective local versus global control of information processing over thalamo-cortical networks.Acknowledgements
This study is supported in part by Hong Kong Research Grant Council (R7003-19, C7048-16G, HKU17112120, HKU17103819 and HKU17104020), Guangdong Key Technologies for Treatment of Brain Disorders (2018B030332001) and Guangdong Key Technologies for Alzheimer’ Disease Diagnosis and Treatment (2018B030336001).References
1. Isaacson, J.S. & Scanziani, M. How inhibition shapes cortical activity. Neuron 72, 231-243 (2011).
2. Halassa, M.M. & Acsady, L. Thalamic Inhibition: Diverse Sources, Diverse Scales. Trends Neurosci 39, 680-693 (2016).
3. Halassa, M.M., Chen, Z., Wimmer, R.D., Brunetti, P.M., Zhao, S., Zikopoulos, B., Wang, F., Brown, E.N. & Wilson, M.A. State-dependent architecture of thalamic reticular subnetworks. Cell 158, 808-821 (2014).
4. Wimmer, R.D., Schmitt, L.I., Davidson, T.J., Nakajima, M., Deisseroth, K. & Halassa, M.M. Thalamic control of sensory selection in divided attention. Nature 526, 705-709 (2015).
5. Li, Y., Lopez-Huerta, V.G., Adiconis, X., Levandowski, K., Choi, S., Simmons, S.K., Arias-Garcia, M.A., Guo, B., Yao, A.Y., Blosser, T.R., Wimmer, R.D., Aida, T., Atamian, A., Naik, T., Sun, X., Bi, D., Malhotra, D., Hession, C.C., Shema, R., Gomes, M., Li, T., Hwang, E., Krol, A., Kowalczyk, M., Peca, J., Pan, G., Halassa, M.M., Levin, J.Z., Fu, Z. & Feng, G. Distinct subnetworks of the thalamic reticular nucleus. Nature 583, 819-824 (2020).
6. Martinez-Garcia, R.I., Voelcker, B., Zaltsman, J.B., Patrick, S.L., Stevens, T.R., Connors, B.W. & Cruikshank, S.J. Two dynamically distinct circuits drive inhibition in the sensory thalamus. Nature 583, 813-818 (2020).
7. Latchoumane, C.-F., Ngo, H.-V., Born, J. & Shin, H.-S. Thalamic spindles promote memory formation during sleep through triple phase-locking of cortical, thalamic, and hippocampal rhythms. Neuron 95, 424-435 (2017).
8. Lewis, L.D., Voigts, J., Flores, F.J., Schmitt, L.I., Wilson, M.A., Halassa, M.M. & Brown, E.N. Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state. Elife 4, e08760 (2015).
9. Fernandez, L.M., Vantomme, G., Osorio-Forero, A., Cardis, R., Beard, E. & Luthi, A. Thalamic reticular control of local sleep in mouse sensory cortex. Elife 7(2018).
10. Lee, J.H., Durand, R., Gradinaru, V., Zhang, F., Goshen, I., Kim, D.S., Fenno, L.E., Ramakrishnan, C. & Deisseroth, K. Global and local fMRI signals driven by neurons defined optogenetically by type and wiring. Nature 465, 788-792 (2010).
11. Clemente-Perez, A., Makinson, S.R., Higashikubo, B., Brovarney, S., Cho, F.S., Urry, A., Holden, S.S., Wimer, M., David, C., Fenno, L.E., Acsady, L., Deisseroth, K. & Paz, J.T. Distinct Thalamic Reticular Cell Types Differentially Modulate Normal and Pathological Cortical Rhythms. Cell Rep 19, 2130-2142 (2017).
12. Bartho, P., Slezia, A., Matyas, F., Faradzs-Zade, L., Ulbert, I., Harris, K.D. & Acsady, L. Ongoing network state controls the length of sleep spindles via inhibitory activity. Neuron 82, 1367-1379 (2014).
13. Crunelli, V., Lorincz, M.L., Connelly, W.M., David, F., Hughes, S.W., Lambert, R.C., Leresche, N. & Errington, A.C. Dual function of thalamic low-vigilance state oscillations: rhythm-regulation and plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 19, 107-118 (2018).
14. Steriade, M. Reticularis thalami neurons revisited- Activity changes during shifts in states of vigilance. J Neurosci (1986).
15. Leong, A.T., Chan, R.W., Gao, P.P., Chan, Y.-S., Tsia, K.K., Yung, W.-H. & Wu, E.X. Long-range projections coordinate distributed brain-wide neural activity with a specific spatiotemporal profile. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 113, E8306-E8315 (2016).
16. Klug, J.R., Engelhardt, M.D., Cadman, C.N., Li, H., Smith, J.B., Ayala, S., Williams, E.W., Hoffman, H. & Jin, X. Differential inputs to striatal cholinergic and parvalbumin interneurons imply functional distinctions. Elife 7(2018).
Figures