0541
Progressive microstructural alterations in subcortical nuclei in Parkinson's disease: a diffusion magnetic resonance imaging study1The second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
Synopsis
In this study, we employed diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to measure the microstructural alterations in subcortical nuclei across PD patients at different disease stages. Individual diagnostic model was constructed to test the performance of diffusion metrics in identifying PD patients at different stages. We found that PD patients at different stages have progressive microstructural alterations in the main nuclei of widely acknowledged nigral-pallidal and thalamo-cortical pathways. DKI is sensitive to detect microstructural changes in GP and thalamus between early stage PD and moderate-late stage PD patients. The combination of kurtosis and tensor metrics can achieve a good performance in diagnosing PD.
Abstract
Background:In clinical practice, Parkinson's disease (PD) patients at different disease stages may present differential manifestations and may show different progressive rates. The heterogeneous clinical symptoms in PD indicate that the degenerative patterns of the nigrostrital-nigropallidal and thalamo-cortical pathways may be different during PD progression, which have yet to be elucidated.Objectives: In the present study, we aim to explore the microstructural alterations in subcortical nuclei across Parkinson's disease (PD) patients at different stages with diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) techniques and to test the performance of diffusion metrics in identifying PD patients at different stages.
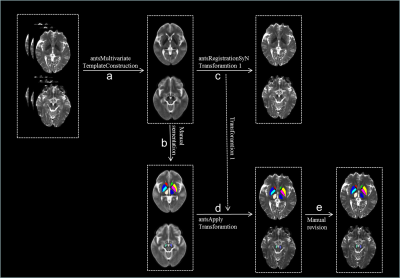
Methods: 110 PD patients and 64 healthy controls (HC) were recruited. According to the Hoehn-Yahr stage, 65 patients with Hoehn–Yahr stage ≤ 2 were grouped into the early-stage PD (EPD) group, and 45 patients with Hoehn–Yahr stage ≥ 2.5 were grouped into the moderate-late-stage PD (MLPD) group. All subjects were scanned on a 3.0 Tesla MR imaging system (Discovery MR750, GE Healthcare). Two-shell diffusion images were acquired using spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence with 60 gradient directions for non-zero b values (b value = 1000 s/mm2, 30 directions; b value = 2000 s/mm2, 30 directions); Diffusion images were preprocessed using FMRIB Software Library (FSL, https://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/), including the brain extraction and the correction of eddy current distortion and inter-volume head motion. After the data preprocessing, tensor and kurtosis metrics, including fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD), radial diffusivity (RD), mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (AK), and radial kurtosis (RK) were estimated using a constrained weighted linear least squares approach by Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Matlab Toolbox (https://cai2r.net/resources/software/diffusion-kurtosis-imaging-matlab-toolbox). Regions of interest (ROI) include bilateral substantia nigra (SN), caudate head, putamen, globus pallidus (GP) and thalamus (Fig. 1). FA, MD, AD, RD, MK, AK, RK in the subcortical nuclei were compared among the three groups. Partial correlation was used to correlate the diffusion metrics and Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale part-III (UPDRS-III) score. Logistic regression and receiving operator characteristic analayses were applied to test the diagnostic performance of the diffusion metrics.
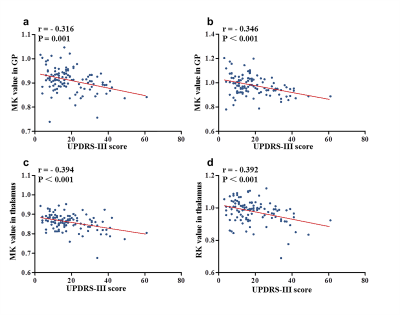
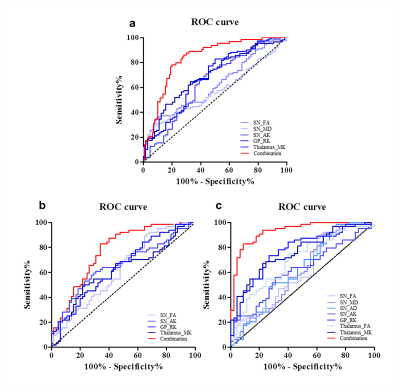
Results: Compared with HC, both EPD and MLPD patients showed higher FA and AD, lower MK and AK in substantia nigra, lower MK and RK in GP and thalamus (all p < 0.05) (Fig. 2). Higher MD in SN and lower FA in thalamus were only detected in MLPD (both p < 0.05). Compared with EPD patients, MLPD showed lower MK, RK in GP and thalamus (all p < 0.05), while no significant diffusion metrics difference in SN was observed. No significant diffusion difference in other nuclei (e.g., caudate nucleus and putamen) was observed among the three groups. MK and RK in GP and thalamus were negatively correlated with UPDRS-III score ((MK in the GP: r = - 0.316, p = 0.001; RK in the GP: r = - 0.346, p < 0.001; MK in the thalamus: r = - 0.394, p < 0.001; RK in the thalamus: r = - 0.392, p < 0.001) (Fig. 3). Before binary logistic regression analysis, no significant multi-colliearity among the diffusional metrics was observed. In detail, the metrics comprising the discriminating combination from the regression model for PD were: FA, MD, and AK in SN, RK in GP, and MK in thalamus. The ROC curves of the altered diffusion metrics with statistical significance in logistic regression model and their combinations from the model for discriminating PD patients from HC or between EPD (and MLPD) and HC are presented in Fig. 4. The combination of kurtosis and tensor metrics from different nuclei contributed to a better diagnostic performance than that from derived from each metric (all p < 0.05). The AUC of combined metrics to diagnose PD, EPD, MLPD were 0.833 (95% CI: 0.692-0.854), 0.773 (95% CI: 0.772-0.894), and 0.931 (95% CI: 0.884-0.978), respectively(Fig. 4).
Conclusions: PD patients at different stages have progressive microstructural alterations in the main nuclei of widely acknowledged nigral-pallidal and thalamo-cortical pathways. DKI is sensitive to detect microstructural changes in GP and thalamus between EPD and MLPD and the combination of kurtosis and tensor metrics can achieve a good performance in diagnosing PD.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all our subjects for participating this research. This study was supported by the 13th Five-year Plan for National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2016YFC1306600), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81971577, 81571654, 81701647 and 81771820).References
1. Braak H, Tredici K D, Rüb U, de Vos R A I, Jansen Steur E N H, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. DOI: 10.1016/s0197-4580(02)00065-9
2. Cheng H, Ulane C, Burke R (2010) Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Annals of neurology 6:715-725
3. Andica C, Kamagata K, Hatano T et al (2018) Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the nigrostriatal pathway in Parkinson's disease: Retrograde degeneration observed by tract-profile analysis. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.02.046
4. Kalia L V, Lang A E (2015) Parkinson's disease. The Lancet 9996:896-912
5. Latt M D, Lord S R, Morris J G, Fung V S (2009) Clinical and physiological assessments for elucidating falls risk in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 9:1280-1289
6. Zhao Y J, Wee H L, Chan Y-H et al (2010) Progression of Parkinson's disease as evaluated by Hoehn and Yahr stage transition times. Movement Disorders 6:710-716
7. Selikhova M, Williams D R, Kempster P A, Holton J L, Revesz T, Lees A J (2009) A clinico-pathological study of subtypes in Parkinson's disease. Brain 11:2947-2957
8. Boska M D, Hasan K M, Kibuule D et al (2007) Quantitative diffusion tensor imaging detects dopaminergic neuronal degeneration in a murine model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 3:590-596 9. Mori S, Zhang J (2006) Principles of diffusion tensor imaging and its applications to basic neuroscience research. Neuron 5:527-539
10. Andica C, Kamagata K, Hatano T et al (2019) MR biomarkers of degenerative brain disorders derived from diffusion imaging. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. DOI: 10.1002/jmri.27019
11. Jensen J H, Helpern J A, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 6:1432-1440
12. Paydar A, Fieremans E, Nwankwo J I et al (2014) Diffusional kurtosis imaging of the developing brain. Am J Neuroradiol 4:808-814
13. Gong N J, Wong C S, Chan C C, Leung L M, Chu Y C (2014) Aging in deep gray matter and white matter revealed by diffusional kurtosis imaging. Neurobiol Aging 10:2203-2216
14. NJ G, CC C, LM L, CS W, R D, C L (2017) Differential microstructural and morphological abnormalities in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: Evidence from cortical and deep gray matter. Hum Brain Mapp 5:2495-2508
15. Wang J J, Lin W Y, Lu C S et al (2011) Parkinson disease: diagnostic utility of diffusion kurtosis imaging. Radiology 1:210-217
16. AJ H, SE D, L K, AJ L (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson's disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry 3:181-184
17. Huang W-S, Lin S-Z, Lin J-C, Wey S-P, Ting G, Liu R-S (2001) Evaluation of Early-Stage Parkinson's Disease with 99mTc-TRODAT-1 Imaging. The Journal of Nuclear Medicine 9:1303
18. Guo T, Wu J, Zhou C et al (2020) Aberrant Fiber Coherence of Amygdala−Accumbens−Pallidum Pathway Is Associated With Disorganized Nigrostriatal−Nigropallidal Pathway in Parkinson's Disease. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging. DOI: 10.1002/jmri.27273
19. Dostrovsky J O, Hutchison W D, Lozano A M (2002) The Globus Pallidus, Deep Brain Stimulation, and Parkinson's Disease. The Neuroscientist 3:284-290
20. Pifl C, Schingnitz G, Hornykiewicz O (1992) Striatal and non-striatal neurotransmitter changes in MPTP-parkinsonism in rhesus monkey: the symptomatic versus the asymptomatic condition. Neurochemistry international. DOI: 10.1016/0197-0186(92)90255-p
21. Van Camp N, Blockx I, Verhoye M et al (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging in a rat model of Parkinson's disease after lesioning of the nigrostriatal tract. NMR in Biomedicine 7:697-706
22. Lenfeldt N, Larsson A, Nyberg L, Birgander R, Forsgren L (2015) Fractional anisotropy in the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease: a complex picture. Eur J Neurol 10:1408-1414
23. Kamagata K, Zalesky A, Hatano T et al (2017) Gray Matter Abnormalities in Idiopathic Parkinson's Disease: Evaluation by Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging and Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging. Hum Brain Mapp 7:3704-3722
24. Khairnar A, Ruda-Kucerova J, Szabó N et al (2017) Early and progressive microstructural brain changes in mice overexpressing human α-Synuclein detected by diffusion kurtosis imaging. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.11.027
25. Fearnley J M, Lees A J (1991) Ageing and Parkinson's disease: substantia nigra regional selectivity. Brain 5:2283-2301
26. Monje M, Blesa J, Garcia-Cabezas M A, Obeso J A, Cavada C (2020) Changes in thalamic dopamine innervation in a progressive Parkinson's disease model in monkeys. Mov Disord 3:419-430
27. Bingbing G, Yujing Z, Yanwei M et al (2020) Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of Microstructural Changes in Gray Matter Nucleus in Parkinson Disease. Frontiers in Neurology. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00252
28. Hirata F C C, Sato J R, Vieira G et al (2017) Substantia nigra fractional anisotropy is not a diagnostic biomarker of Parkinson's disease: A diagnostic performance study and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 6:2640-2648
29. Péran P, Cherubini A, Assogna F et al (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging markers of Parkinson’s disease nigrostriatal signature. Brain 11:3423-3433
Figures