0526
Measures of bone water and porosity are associated with whole-bone stiffness and mineral density in the human femur1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 3Biomedical Science and Medical Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing, China, 4Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
Synopsis
UTE measures of cortical bone water were evaluated in 15 cadaveric proximal femora. Pore water content, total water content, and porosity index were all negatively associated with whole-bone stiffness obtained in a sideways fall loading configuration and with volumetric bone mineral density. In contrast, bound water content was not found to be related to stiffness or mineral density. This data suggest that bone water measures may provide useful information on cortical bone mechanical competence.
INTRODUCTION
Hip fracture is a devastating outcome of osteoporosis [1, 2]. Cortical bone comprises 80% of whole-body bony mass [3] and experiences considerable age-related changes including endocortical erosion, periosteal expansion, and increased intracortical porosity [4, 5]. Cortical porosity is a major determinant of bone strength [6, 7] and is related to fractures independent of bone mineral density (BMD) [8, 9]. While existing imaging methods can probe cortical thickness and BMD, no such method has been established for quantifying cortical porosity at the proximal femur in vivo. Ultrashort echo time (UTE)-based MR imaging methods can indirectly probe cortical microarchitecture by differentiating between the two MRI-detectable water pools, bound water (BW) and pore water (PW), which have T2* of ~390 µsec and 1 msec-1 sec, respectively [10, 11]. Various UTE bone water imaging methods have been proposed, including directly measuring BW and PW concentrations [10, 12-14], as signal fractions from bi- [15, 16] or tri-component analysis [17, 18], or computing the magnitude ratio of two echo times, termed the porosity index (PI) [19-21]. Cadaver studies have shown that PI and PW and BW concentrations are all correlated to µCT-derived porosity and mechanical properties [10, 12, 13, 15, 17, 19-23]. While these studies suggest potential for UTE bone water measures to assess cortical bone quality, these methods have never been investigated in the proximal femur where the most dangerous fractures occur. Therefore, the goal of this study was to perform a validation of UTE-derived quantifications of PW, BW, and PI compared to (1) whole femur stiffness obtained in sideways fall experiments and (2) CT-derived volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD) measurements.METHODS
Fifteen whole human femora (ages 72 ± 15 years) were obtained from a local biobank (National Disease Research Interchange, Philadelphia, PA) (Table 1). Bones were stored at -30°C and were thawed for a minimum of 16 hours prior to MRI data acquisition which, based on our previous work, provides best signal to noise ratio without degrading samples [21, 24]. All MR/CT scanner, sequence/protocol, and calibration phantom information is listed in Table 2.(1) PW and BW were quantified with a custom-built, transmit/receive birdcage calf coil (Rapid Biomedical, Rimpar, Germany). Two customized pulse sequences and an external reference sample for signal calibration placed adjacent to the specimen (Table 2) [14, 25] enabled quantification of absolute bone water concentrations. Briefly, a 1H dual-echo radial-UTE sequence was used to quantify total bone water (TW), and a 1H IR-prepared rapid radial-UTE (IR-rUTE) sequence was used for BW. Signal intensity normalization was performed based on relaxation constants [11, 26] before using the following equation for quantification [27]:
$$ \rho_{bone}=\rho_{ref}\frac{I_{bone}*F_{ref}}{I_{ref}*F_{bone}}*e^{-TE\left(\frac{1}{T_{2,ref}^*}-\frac{1}{T_{2,bone}^*}\right)}$$
where ρ, I, and F represent 1H density, image voxel intensity, and magnetization fraction, respectively. PW was then calculated by subtracting BW from TW.
(2) PI was quantified with an 18-element flexible RF coil and a custom dual-echo 1H radial pulse sequence (Table 2) [21, 28]. PI is defined as:
$$Porosity Index (\%) = \frac{Echo_{long}intensity}{Echo_{short}intensity}*100 \%\approx \frac{PW}{PW+BW}$$
which is based on the assumption that BW transverse magnetization has entirely decayed away while PW magnetization has decayed negligibly. The first echo time should be as short as possible to maximize signal within the cortical bone [19].
(3) vBMD was measured using a clinical CT scanner in the presence of calcium rod phantoms (Table 1).
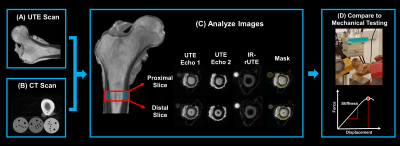
(4) Specimens were nondestructively mechanically tested in a sideways fall loading orientation as previously reported (Fig 1) [21].
A 1 cm cortical bone region just inferior to the lesser trochanter along the shaft was manually selected from each image for analysis (Fig 1). Statistical analyses were conducted using JMP Pro Discovery Software (JMP 14.0 SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC) with P < 0.05 threshold indicating statistical significance.
RESULTS
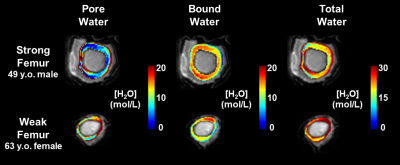
Stiffness was negatively correlated with PW, TW, and PI (r = -0.73, -0.69, -0.82; P = 0.01, 0.02, 0.01, respectively) (Fig 2). Similarly, vBMD was negatively correlated with PW, TW, and PI (r = -0.70, -0.62, -0.64; P = 0.01, 0.03, 0.02). PW and PI were positively associated (r = 0.85; P = 0.01). PW and BW were associated with TW (r = 0.96, 0.62; P = 0.01, 0.03) (Fig 3). BW was not associated with either stiffness or vBMD (P = 0.87, 0.85). Bone water colormaps are compared between a strong and a weak specimen in Fig 2.DISCUSSION
The data suggest that UTE measures of pore water and porosity are predictive of whole-bone stiffness the proximal femur, indicating that they may be useful measures of cortical bone health. As expected, we found that PW content and PI, both surrogates of cortical porosity, were strongly correlated with each other. Even though no association between stiffness and BW content was found, since bending strength [10, 17, 22] and ultimate stress [23] are both related to BW content, it is possible that BW contributes more to bone’s post-yield than to its linear properties.CONCLUSION
This study suggests that cortical UTE biomarkers could provide useful information about femoral bone quality in clinically practical acquisition times. Ongoing work will investigate the feasibility and reproducibility of acquiring these biomarkers in vivo.Acknowledgements
NIH R01 AR068382, R01 AR076392, R01 AR050068, T32 EB020087, P30 AR069619References
1. Cummings, S.R. and L.J. Melton, Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet, 2002. 359(9319): p. 1761-7.
2. Leibson, C.L., A.N. Tosteson, S.E. Gabriel, J.E. Ransom, and L.J. Melton, Mortality, disability, and nursing home use for persons with and without hip fracture: a population-based study. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2002. 50(10): p. 1644-50.
3. Seeman, E., Age- and menopause-related bone loss compromise cortical and trabecular microstructure. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2013. 68(10): p. 1218-25.
4. Seeman, E. and P.D. Delmas, Bone quality--the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. N Engl J Med, 2006. 354(21): p. 2250-61.
5. Allen, M.R., J.M. Hock, and D.B. Burr, Periosteum: biology, regulation, and response to osteoporosis therapies. Bone, 2004. 35(5): p. 1003-12.
6. Iori, G., J. Schneider, A. Reisinger, F. Heyer, L. Peralta, C. Wyers, M. Gräsel, R. Barkmann, C.C. Glüer, J.P. van den Bergh, D. Pahr, and K. Raum, Large cortical bone pores in the tibia are associated with proximal femur strength. PLOS ONE, 2019. 14(4): p. e0215405.
7. Mirzaali, M.J., J.J. Schwiedrzik, S. Thaiwichai, J.P. Best, J. Michler, P.K. Zysset, and U. Wolfram, Mechanical properties of cortical bone and their relationships with age, gender, composition and microindentation properties in the elderly. Bone, 2016. 93: p. 196-211.
8. Kral, R., M. Osima, R. Vestgaard, E. Richardsen, and Å. Bjørnerem, Women with fracture, unidentified by FRAX, but identified by cortical porosity, have a set of characteristics that contribute to their increased fracture risk beyond high FRAX score and high cortical porosity. Bone, 2018. 116: p. 259-265.
9. Samelson, E.J., K.E. Broe, H. Xu, L. Yang, S. Boyd, E. Biver, P. Szulc, J. Adachi, S. Amin, E. Atkinson, C. Berger, L. Burt, R. Chapurlat, T. Chevalley, S. Ferrari, D. Goltzman, D.A. Hanley, M.T. Hannan, S. Khosla, C.T. Liu, M. Lorentzon, D. Mellstrom, B. Merle, M. Nethander, R. Rizzoli, E. Sornay-Rendu, B. Van Rietbergen, D. Sundh, A.K.O. Wong, C. Ohlsson, S. Demissie, D.P. Kiel, and M.L. Bouxsein, Cortical and trabecular bone microarchitecture as an independent predictor of incident fracture risk in older women and men in the Bone Microarchitecture International Consortium (BoMIC): a prospective study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2019. 7(1): p. 34-43.
10. Horch, R.A., D.F. Gochberg, J.S. Nyman, and M.D. Does, Non-invasive Predictors of Human Cortical Bone Mechanical Properties: T2-Discriminated 1H NMR Compared with High Resolution X-ray. PLOS ONE, 2011. 6(1): p. e16359.
11. Seifert, A.C., S.L. Wehrli, and F.W. Wehrli, Bi-component T2 * analysis of bound and pore bone water fractions fails at high field strengths. NMR Biomed, 2015. 28(7): p. 861-72.
12. Seifert, A.C., C. Li, C.S. Rajapakse, M. Bashoor-Zadeh, Y.A. Bhagat, A.C. Wright, B.S. Zemel, A. Zavaliangos, and F.W. Wehrli, Bone mineral (31)P and matrix-bound water densities measured by solid-state (31)P and (1)H MRI. NMR in biomedicine, 2014. 27(7): p. 739-748.
13. Seifert, A.C., C. Li, S.L. Wehrli, and F.W. Wehrli, A Surrogate Measure of Cortical Bone Matrix Density by Long T2 -Suppressed MRI. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research, 2015. 30(12): p. 2229-2238.
14. Zhao, X., H.K. Song, A.C. Seifert, C. Li, and F.W. Wehrli, Feasibility of assessing bone matrix and mineral properties in vivo by combined solid-state 1H and 31P MRI. PLOS ONE, 2017. 12(3): p. e0173995.
15. Chen, J., S.P. Grogan, H. Shao, D. D'Lima, G.M. Bydder, Z. Wu, and J. Du, Evaluation of bound and pore water in cortical bone using ultrashort-TE MRI. NMR in biomedicine, 2015. 28(12): p. 1754-1762.
16. Du, J., E. Diaz, M. Carl, W. Bae, C.B. Chung, and G.M. Bydder, Ultrashort echo time imaging with bicomponent analysis. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2012. 67(3): p. 645-649.
17. Jerban, S., X. Lu, E.W. Dorthe, S. Alenezi, Y. Ma, L. Kakos, H. Jang, R.L. Sah, E.Y. Chang, D. D'Lima, and J. Du, Correlations of cortical bone microstructural and mechanical properties with water proton fractions obtained from ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI tricomponent T2* model. NMR Biomed, 2020. 33(3): p. e4233.
18. Lu, X., S. Jerban, L. Wan, Y. Ma, H. Jang, N. Le, W. Yang, E.Y. Chang, and J. Du, Three-dimensional ultrashort echo time imaging with tricomponent analysis for human cortical bone. Magn Reson Med, 2019. 82(1): p. 348-355.
19. Rajapakse, C.S., M. Bashoor-Zadeh, C. Li, W. Sun, A.C. Wright, and F.W. Wehrli, Volumetric Cortical Bone Porosity Assessment with MR Imaging: Validation and Clinical Feasibility. Radiology, 2015. 276(2): p. 526-35.
20. Hong, A.L., M. Ispiryan, M.V. Padalkar, B.C. Jones, A.S. Batzdorf, S.S. Shetye, N. Pleshko, and C.S. Rajapakse, MRI-derived bone porosity index correlates to bone composition and mechanical stiffness. Bone Rep, 2019. 11: p. 100213.
21. Jones, B.C., S. Jia, H. Lee, A. Feng, S.S. Shetye, A. Batzdorf, N. Shapira, P.B. Noël, N. Pleshko, and C.S. Rajapakse, MRI-derived porosity index is associated with whole-bone stiffness and mineral density in human cadaveric femora. Bone, 2020: p. 115774.
22. Manhard, M.K., S. Uppuganti, M. Granke, D.F. Gochberg, J.S. Nyman, and M.D. Does, MRI-derived bound and pore water concentrations as predictors of fracture resistance. Bone, 2016. 87: p. 1-10.
23. Bae, W.C., P.C. Chen, C.B. Chung, K. Masuda, D. D'Lima, and J. Du, Quantitative ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI of human cortical bone: correlation with porosity and biomechanical properties. J Bone Miner Res, 2012. 27(4): p. 848-57.
24. Rajapakse, C.S., A.R. Farid, D.C. Kargilis, B.C. Jones, J.S. Lee, A.J. Johncola, A.S. Batzdorf, S.S. Shetye, M.W. Hast, and G. Chang, MRI-based assessment of proximal femur strength compared to mechanical testing. Bone, 2020. 133: p. 115227.
25. Li, C., J.F. Magland, X. Zhao, A.C. Seifert, and F.W. Wehrli, Selective in vivo bone imaging with long-T(2) suppressed PETRA MRI. Magn Reson Med, 2017. 77(3): p. 989-997.
26. Rad, H.S., S.C. Lam, J.F. Magland, H. Ong, C. Li, H.K. Song, J. Love, and F.W. Wehrli, Quantifying cortical bone water in vivo by three-dimensional ultra-short echo-time MRI. NMR Biomed, 2011. 24(7): p. 855-64.
27. Techawiboonwong, A., H.K. Song, M.B. Leonard, and F.W. Wehrli, Cortical bone water: in vivo quantification with ultrashort echo-time MR imaging. Radiology, 2008. 248(3): p. 824-833. 28. Zhao, X., H. Lee, H.K. Song, C.C. Cheng, and F.W. Wehrli, Impact of gradient imperfections on bone water quantification with UTE MRI. Magn Reson Med, 2020. 84(4): p. 2034-2047.
Figures