0494
Identifying microstructural changes in diffusion MRI models; How to break parameter degeneracies1Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging (WIN), Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences (NDCN), University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom, 2Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging (WIN), Department of Psychiatry, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Synopsis
We present a novel Bayesian framework to relate changes in data to changes in model parameters even in models that cannot be directly inverted. We do so by training probabilistic models that characterise how the measurements change as a result of a change in the parameters. While the approach is general, in this work we used the framework to study microstructural parameter changes that are associated with the appearance of areas of white matter hyperintensities. We found a dichotomy between periventricular and deep white matter hyperintensities, where the latter are associated with increased extracellular signal.
Introduction
Biophysical models that attempt to infer real-world quantities from data usually have many free parameters. This can result in degeneracies in model inversion and make parameter estimation ill-posed. However, often we are not interested in parameter estimation per se, but rather in estimating changes in parameters between experimental conditions (e.g. patients vs controls). We present a novel Bayesian framework for inference on changes in the parameters of biophysical forward models. The framework allows us to relate changes in measurements to changes in parameters even in models that cannot be directly inverted. Whilst the approach is general, in this work we apply it in the context of diffusion MRI modeling to study microstructural changes. Specifically, we used this framework to ask what microstructural parameter changes are associated with the appearance of areas of white matter hyperintensities seen in T2-FLAIR images.Bayesian Estimation of Change
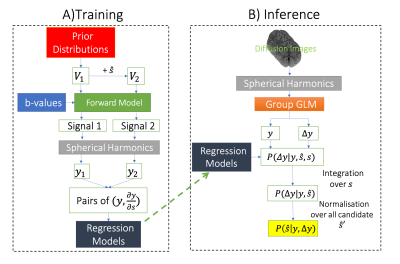
Given a measurement ($$$y$$$), an observed change in this measurement ($$$ \Delta y $$$), and a generative model ($$$M$$$), we ask what model parameters $$$ \hat{s} $$$ can best explain this change (Figure 1A). We can use Bayes rule to write the posterior probability associated with a hypothesized parameter change:$$ P( \hat{s} | y, \Delta y) = \frac{ P(\Delta y | y, \hat{s}) P(\hat{s})} {\sum_{\hat{s}'}{P(\Delta y | y, \hat{s}') P(\hat{s}')}} $$
Assuming no prior preference ($$$ P(\hat{s}|y) = P(\hat{s}) = uniform $$$), we only need to estimate $$$P(\Delta y | y, \hat{s})$$$, which represents the likelihood of a change in the data given a starting point and the underlying parameter change. $$$\hat{s}$$$ defines the direction, but not the amplitude, of the change in the model parameters. We, therefore, marginalize over the amplitude of change ($$$s$$$):
$$ P(\Delta y | y, \hat{s}) = \int{P(s) P(\Delta y| y, \hat{s}, s) ds} $$
We assume a zero-centered prior distribution for the amplitude of change ($$$P(s)= N(0, \sigma_s^2)$$$. The likelihood term inside the integral characterizes how the data changes as a result of a change in the direction of $$$\hat{s} $$$ by an amount s, which we estimate from a pre-trained machine learning model (Figure 2A) using forward simulations. Once trained, we can use the model and the above integral to compute the desired posterior probabilities for pairs of real datasets (Figure 2B).
Methods
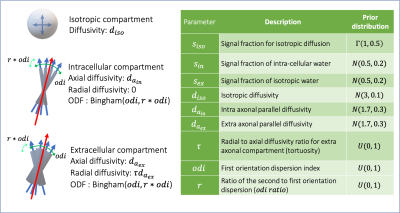
We used dMRI data from 200 subjects taken from the UK Biobank dataset (Miller et al., 2016) which had white matter hyperintensities (WMH) in their T2-FLAIR images. The data consists of 2 shells of diffusion-weighted MRI data (b = 1000, 2000 $$$\frac{s}{mm^2}) each with 50 directions along with 5 b0 images. We trained models of change for a few hypothetical patterns of change in parameters of an extended (and highly degenerate) NODDI model (Zhang et al., 2012) (Figure 3). As we are only interested in the microstructural parameters and not fiber orientations, we fitted spherical harmonics to each shell of the diffusion data and computed the power (vector norm of coefficients) in degrees 0, 2, and 4. These summary measurements are rotationally invariant (Kazhdan et al., 2003) and practically represent signal attenuation and anisotropy. We used a voxel-wise across subjects regression to estimate both the average summary measurements within the normal-appearing white matter, and the average deviation from this normal in WMHs estimated using BIANCA (Griffanti et al., 2016).Results
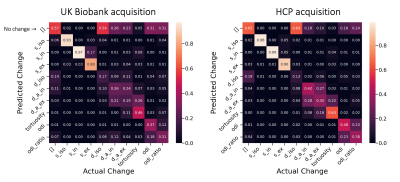
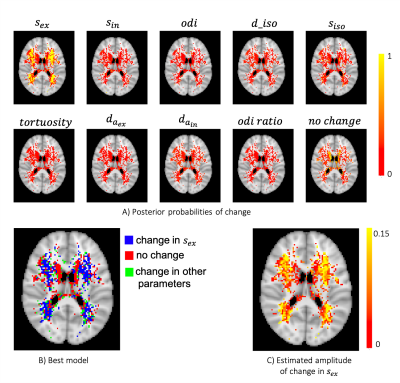
To assess the ability of the proposed approach in identifying the true underlying changes from the provided measurements, we simulated pairs of diffusion signals with known parameter changes. Although here we only considered changing a single parameter at a time, the framework allows for models of changes that affect multiple parameters. The confusion matrix (Figure 4) suggests that we are able to accurately identify changes in the signal fraction parameters. The diffusivities have a smaller effect on the signal and hence are more easily confused with each other or the “no change” model.We then applied the same trained model to the results of GLM on the WMH dataset (Figure 5). We found a dichotomy in WMHs regions, with periventricular white matter most probably associated with “no change” in model parameters, while changes in deep WMHs were best explained by an increase in $$$s_{ex}$$$. Interestingly, this result was specific to the extracellular signal. We note that in conventional NODDI, the two compartments are not independent, and therefore a change in $$$s_{ex}$$$ would coincide with an opposite change in intracellular signal. This result might reflect an increase of extra-axonal space or an increase in the extra-axonal T2 due to demyelination in the deep WMHs. The results are consistent with the traditional categorization of WMH into periventricular WMH (PWMH) and deep WMH (DWMH) (Fazekas et al., 1987), which have been associated with different clinical, histopathological, and etiological correlates (Kim et al., 2008).
In summary, we have developed a general Bayesian framework for inference on parameter changes from changes in the data. We showed how this approach can be used to alleviate the need for injecting strong priors to constrain model parameters and avoid degeneracies in fitting (e.g. Kunz et al., 2014; Schneider et al., 2017). Future work will apply this same framework to other types of biophysical models and data, e.g., dynamic causal modeling.
Acknowledgements
This research has been conducted in part using the UK Biobank Resource under Application Number 8107. We are grateful to UK Biobank for making the data available, and to all UK Biobank study participants, who generously donated their time to make this resource possible. This research is supported by a Wellcome Trust Collaborative Award 215573/Z/19/Z. Compute resources were provided by the Oxford Biomedical Research Computing (BMRC) facility (a joint development between Oxford’s Wellcome Centre for Human Genetics and Big Data Institute, supported by Health Data Research UK and the NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre) and The Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging (WIN FMRIB), which is supported by centre funding from the Wellcome Trust (203139/Z/16/Z).References
Fazekas, F., Chawluk, J., Alavi, A., Hurtig, H., & Zimmerman, R. (1987). MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. American Journal of Roentgenology, 149(2), 351–356. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.149.2.351
Griffanti, L., Zamboni, G., Khan, A., Li, L., Bonifacio, G., Sundaresan, V., Schulz, U. G., Kuker, W., Battaglini, M., Rothwell, P. M., & Jenkinson, M. (2016). BIANCA (Brain Intensity AbNormality Classification Algorithm): A new tool for automated segmentation of white matter hyperintensities. NeuroImage, 141, 191–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.018
Howard, A. FD., Mollink, J., Kleinnijenhuis, M., Pallebage-Gamarallage, M., Bastiani, M., Cottaar, M., Miller, K. L., & Jbabdi, S. (2019). Joint modelling of diffusion MRI and microscopy. NeuroImage, 201, 116014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116014
Kazhdan, M., Funkhouser, T., & Rusinkiewicz, S. (2003). Rotation invariant spherical harmonic representation of 3 d shape descriptors. Symposium on Geometry Processing, 6, 156–164.Kim, K. W., MacFall, J. R., & Payne, M. E. (2008). Classification of White Matter Lesions on Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Elderly Persons. Biological Psychiatry, 64(4), 273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.03.024
Kunz, N., Zhang, H., Vasung, L., O’Brien, K. R., Assaf, Y., Lazeyras, F., Alexander, D. C., & Hüppi, P. S. (2014). Assessing white matter microstructure of the newborn with multi-shell diffusion MRI and biophysical compartment models. NeuroImage, 96, 288–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.057
Miller, K. L., Alfaro-Almagro, F., Bangerter, N. K., Thomas, D. L., Yacoub, E., Xu, J., Bartsch, A. J., Jbabdi, S., Sotiropoulos, S. N., Andersson, J. L. R., Griffanti, L., Douaud, G., Okell, T. W., Weale, P., Dragonu, I., Garratt, S., Hudson, S., Collins, R., Jenkinson, M., … Smith, S. M. (2016).Multimodal population brain imaging in the UK Biobank prospective epidemiological study. Nature Neuroscience, 19(11), 1523–1536. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4393Schneider,
T., Brownlee, W., Zhang, H., Ciccarelli, O., Miller, D. H., & Wheeler-Kingshott, C. G. (2017). Sensitivity of multi-shell NODDI to multiple sclerosis white matter changes: A pilot study. Functional Neurology, 32(2), 97–101. https://doi.org/10.11138/FNeur/2017.32.2.097
Sotiropoulos, S. N., Jbabdi, S., Xu, J., Andersson, J. L., Moeller, S., Auerbach, E. J., Glasser, M. F., Hernandez, M., Sapiro, G., Jenkinson, M., Feinberg, D. A., Yacoub, E., Lenglet, C., Van Essen, D. C., Ugurbil, K., & Behrens, T. E. J. (2013). Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage, 80, 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.057
Zhang, H., Schneider, T., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., & Alexander, D. C. (2012). NODDI: Practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage, 61(4), 1000–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.072
Figures