0042
MRI-based assessment of regional patterns of cortical strain in the human brain resulting from non-impact dynamic mechanical loading1Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States, 2Physiology and Biomedical Engineering, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
Synopsis
There is growing recognition of morbidity resulting from subconcussive repetitive head impact (RHI). Mechanical interactions between the skull-brain interface (e.g., transmission and tethering) contribute significantly to the response of the brain to head impact. Local cortical strain concentrations would likely reflect the nearby tethering interactions at the skull-brain interface. In this study, we have developed MR elastography (MRE)-based methods that enable in vivo visualization and quantification of 3D full-volume cortical strain in response to non-impact dynamic loading. We have found that the distribution of the cortical strain is region-dependent, constituting a possible mechanism for RHI vulnerability among individuals.
Introduction
The negative effects of exposure to sub-concussive, repetitive head impact (RHI) are increasingly recognized as a public health issue.1-3 There is an unmet need for better tools to evaluate the effect of RHI exposures. A previous study used MR elastography (MRE) to measure the skull-brain motion transfer and showed that RHI induced by hockey-playing can degrade the damping capabilities of the skull-brain interface, suggesting MRE-assessed skull-brain coupling metrics may be highly sensitive to early RHI deficits.4,5 To further understand the mechanisms of head force transfer, in this study, we developed an MRE-based method to investigate the heterogeneity of the skull-brain interface by quantifying cortical strain distributions under non-impact dynamic loading. Local cortical strain concentrations would likely reflect the nearby tethering interactions between the brain and the connective tissue that anchors it inside the skull.Method
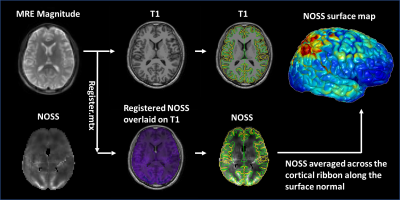
After IRB approval and written informed consent, 27 volunteers (age 39.74±14.13yrs, 11F/16M) were imaged with brain MRE and T1 MR-RAGE on a compact 3T MR scanner.6,7 Low amplitude 60-Hz vertical vibration was introduced from the skull into the brain via a soft pillow-like driver placed under the head.4 To evaluate the effect of vibration direction on the distribution of cortical strain, 3 volunteers were also scanned with a multi-excitation driver with both vertical and horizontal vibrations.8 The 3D full-volume head displacement was imaged by the dual-sensitivity and dual-motion encoding (DSDM) MRE sequence.4 Octahedral shear strain (OSS) was computed using a neural network trained algorithm to perform numerical differentiation.9 Normalized OSS (NOSS) was calculated to reduce the amplitude variations by normalizing OSS to the wave displacement amplitude at each voxel.10 Cortical surface reconstructions of T1-weighted scans and standard-space co-registrations of the individual anatomical data were conducted using FreeSurfer (Fig.1). Individual MRE data were rigidly aligned with MP-RAGE data from which the averaged NOSS across the cortical ribbon was calculated. The cortical NOSS was then averaged for different brain lobes to evaluate its regional variations. A one-way ANOVA with post hoc Steel-Dwass multiple comparisons was performed to identify differences between different lobes. P-value<0.05 was significant.Results
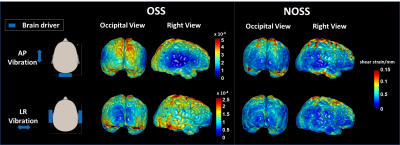
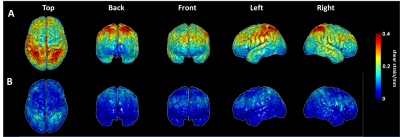
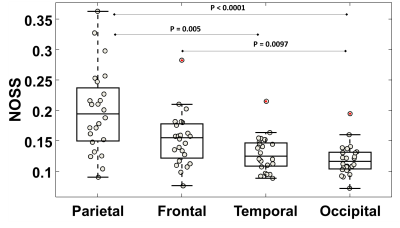
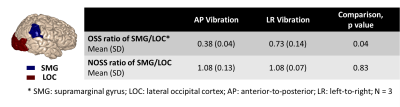
As seen by Fig.2, the distribution of cortical OSS is dominated by the vibration mode: high occipital OSS with AP vibration and high lateral OSS with LR vibration, corresponding to the MRE driver locations. However, the regional variations of NOSS are similar across the brain surface between two vibrations, indicating that normalization reduces the bias induced by the driving pattern. Strain ratios between two subcortical regions that are close to the driver locations were calculated and compared (Table 1). The difference of strain distributions caused by vibration was normalized by NOSS. The averaged NOSS map across all subjects in a common surface-based coordinate system is shown in Fig.3. There were no significant differences in NOSS between hemispheres. Regional trends were identified (Fig.4), where NOSS in superior regions was significantly higher than NOSS in inferior regions. NOSS was also significantly greater in the parietal lobe compared to the occipital lobe.Discussion
Mechanical interactions between the skull-brain interface (e.g., transmission and tethering) contribute significantly to the brain’s response to head impacts. Post-mortem human and ex vivo animal studies have shown that the arachnoid trabeculae (AT) in the subarachnoid space significantly influence the magnitude and distribution of brain deformation during impact.11-15 Such unique patterns of cortical strain may be due to the regional variations in the skull-brain coupling system. Our findings of significantly higher NOSS near the superior regions suggest an increased tethering of the arachnoid membrane to the falx. This is consistent with in situ experiments, where the density of arachnoid is significantly greater by 12% near the superior regions of the brain.11 However, the largest NOSS was found in the parietal regions, whereas the density of AT is suggested to be greatest in the frontal lobes. This inconsistency may due to the different methods utilized to segment brain lobes and different sample sizes.Conclusion
We have developed a MRE-based methods that enable in vivo visualization and quantification of 3D full-volume cortical strain in response to non-impact dynamic loading. Patterns of increasing cortical strain from inferior to superior and occipital/frontal to parietal were identified. These findings constitute a possible mechanism for RHI vulnerability among individuals and reveal that the specific status of skull-brain mechanical coupling has the potential to affect an individual’s response to both subsequent sub-concussive and concussive trauma.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the NIH (R01 EB001981, R01 NS113760, and U01EB02445).References
1. Mainwaring L, Ferdinand Pennock KM, Mylabathula S, Alavie BZ. Subconcussive head impacts in sport: A systematic review of the evidence. International journal of psychophysiology : official journal of the International Organization of Psychophysiology 2018.
2. Bailes JE, Petraglia AL, Omalu BI, Nauman E, Talavage T. Role of subconcussion in repetitive mild traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 2013;119(5):1235-1245.
3. Montenigro PH, Alosco ML, Martin BM, Daneshvar DH, Mez J, Chaisson CE, Nowinski CJ, Au R, McKee AC, Cantu RC, McClean MD, Stern RA, Tripodis Y. Cumulative Head Impact Exposure Predicts Later-Life Depression, Apathy, Executive Dysfunction, and Cognitive Impairment in Former High School and College Football Players. Journal of neurotrauma 2017;34(2):328-340.
4. Yin Z, Sui Y, Trzasko Joshua D, Rossman Phillip J, Manduca A, Ehman Richard L, Huston J. In vivo characterization of 3D skull and brain motion during dynamic head vibration using magnetic resonance elastography. Magn Reson Med 2018;0(0).
5. Yin Z, Sui Y, Manduca A, Romano AJ, Ehman RL, III JH. MR Elastography (MRE)-assessed Skull-brain Coupling is Affected by Sports-related Repetitive Head Impacts (RHI). 2019; Montréal, Canada.
6. Weavers PT, Shu Y, Tao S, Huston J, Lee S-K, Graziani D, Mathieu J-B, Trzasko JD, Foo TKF, Bernstein MA. Technical Note: Compact three-tesla magnetic resonance imager with high-performance gradients passes ACR image quality and acoustic noise tests. Med Phys 2016;43(3):1259-1264.
7. Foo TKF, Laskaris E, Vermilyea M, Xu M, Thompson P, Conte G, Van Epps C, Immer C, Lee S-K, Tan ET, Graziani D, Mathieu J-B, Hardy CJ, Schenck JF, Fiveland E, Stautner W, Ricci J, Piel J, Park K, Hua Y, Bai Y, Kagan A, Stanley D, Weavers PT, Gray E, Shu Y, Frick MA, Campeau NG, Trzasko J, Huston III J, Bernstein MA. Lightweight, compact, and high-performance 3T MR system for imaging the brain and extremities. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2018;80(5):2232-2245.
8. Yin Z, Sui Y, Trzasko JD, Rossman PJ, Manduca A, Ehman RL, Huston J. In Vivo Characterization of 3D Skull and Brain Motion using MR Elastography with Multi-Excitation Head Driver. 2018; Paris, France.
9. Murphy M, Trzasko J, Scott J, Manduca A, Huston I, John , Ehman R. Artificial neural networks for numerical differentiation with application to magnetic resonance elastography. 2020; Virtual Conference.
10. Yin Z, Hughes JD, Trzasko JD, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Van Gompel J, Link MJ, Romano A, Ehman RL, Huston J. Slip interface imaging based on MR-elastography preoperatively predicts meningioma–brain adhesion. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017;46(4):1007-1016.
11. Benko N, Luke E, Alsanea Y, Coats B. Spatial distribution of human arachnoid trabeculae. Journal of Anatomy 2020;237(2):275-284.
12. Scott G, Coats B. Microstructural characterization of the pia-arachnoid complex using optical coherence tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2015. doi: 10.1109/tmi.2015.2396527.
13. Saboori P, Sadegh A. Histology and morphology of the brain subarachnoid trabeculae. Anatomy Research International 2015;2015:9.
14. Mortazavi MM, Quadri SA, Khan MA, Gustin A, Suriya SS, Hassanzadeh T, Fahimdanesh KM, Adl FH, Fard SA, Taqi MA, Armstrong I, Martin BA, Tubbs RS. Subarachnoid Trabeculae: A Comprehensive Review of Their Embryology, Histology, Morphology, and Surgical Significance. World Neurosurg 2018;111:279-290.
15. Scott GG, Margulies SS, Coats B. Utilizing multiple scale models to improve predictions of extra-axial hemorrhage in the immature piglet. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2016;15(5):1101-1119.
Figures