S65
High spatial and temporal resolution dynamic contrast enhanced MRI of the breast for improved breast cancer detection: Differential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO) Versus LAVA VIBRANT-Flex Breast MRI
Larowin Toni1, Olga Smelianskaia1, Sunitha Thakur1, and Katja Pinker-Domenig1
1Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
1Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
MRI of the breast is the most sensitive test for breast lesion
detection. The backbone of any breast
MRI protocol is a high-resolution T1-weighted contrast enhanced sequence, which
allows the assessment of high-resolution breast tumor and enhancement kinetics
to depict angiogenesis as a tumor-specific feature. DISCO and LAVA VIBRANT-Flex
MRI provide similar excellent image quality while allowing faster acquisition
time and high spatial and temporal resolution. In comparison DISCO provides
excellent fat suppression at 3T where conventional fat saturation techniques
are often suboptimal, reduces motion artifacts and it provides better and
higher spatial resolution.
Background
MRI of the breast is the most sensitive test for breast cancer detection and outperforms conventional imaging with mammography, digital breast tomosynthesis or ultrasound. Indications include pre-operative staging, monitoring of neoadjuvant chemotherapy, differentiation between scar and recurrence, evaluation of breast implants, evaluation of patients with cancer of unknown primary, and annual screening of high-risk patients. The backbone of any breast MRI protocol is a high-resolution T1-weighted dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE-MRI) sequence, which is acquired before and at several time points after intravenous application of a Gadolinium-based contrast agent (1). DCE-MRI allows the assessment of high-resolution breast tumor morphology and enhancement kinetics to depict angiogenesis as a tumor-specific feature. High spatial resolution images must be acquired within a short time-span to enable an optimal contrast in the arterial phase between the enhancing lesion and the adjacent breast parenchyma (2). However, due to reasons related to the signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR), the maximum achievable spatial resolution at 1.5T is limited. The use of parallel imaging techniques (8, 16 channel dedicated breast coils) and high-field scanners operating at 3T offer the advantage of a higher SNR, which allows a simultaneous higher spatial and temporal resolution DCE-MR image acquisition, thus resolving the “temporal versus spatial dilemma” that breast MR imaging protocols face with 1.5 T.Methods and Teaching Points
All patients underwent DCE-MRI of the breast at 3T (3 Tesla GE Discovery MRI equipped with DV 26 software) in the prone position using a dedicated 16- channel breast coil (Sentinelle, Invivo).3D LAVA VIBRANT-Flex sequence: is based on a 3-dimensional spoiled gradient echo pulse sequence, which provides enhanced image contrast and uniform fat suppression. The application of Array Spatial Sensitivity Encoding Technique (ASSET) with partial data filling, shorter TE and TR allows for less scan time (1:32min). The sequence allows the user to prescribe thinner slices and high spatial resolution imaging.
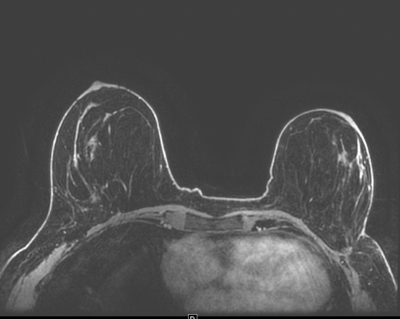
The 3D LAVA VIBRANT-Flex protocol: The sequence uses ARC with acceleration factor of 1.5, TR of 7.8ms, TE of 4.3ms, matrix size 300 x 300, field of view (FOV) 32-36m, spatial resolution of 1x1 mm2, slice thickness of 1.1mm, temporal resolution 90sec, bandwidth of 200KHz (Figure 1).
Differential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO) sequence: The DISCO sequence is acquired by combining a dual-echo SPGR sequence with variable density k-space segmentation (2). The combination achieves a two-pint Dixon fat-water reconstruction algorithm resulting in a clear delineation of fat suppression emphasizing the breast anatomy. Furthermore, this fast sequence results in 12 phases of post contrast enhance series to be acquire in less than 5 min.
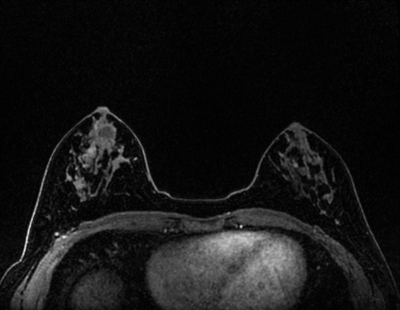
DISCO breast MRI protocol: Acceleration factor of 3, using ARC, TR 3.9mm, TE 1.7mm, flip angel of 12, matrix size 320x320, FOV 32-36, spatial resolution 1.1 x 1.1 mm2, slice thickness of 1.1mm, temporal resolution 10sec, bandwidth of 166.7 (Figure 2).
Summary
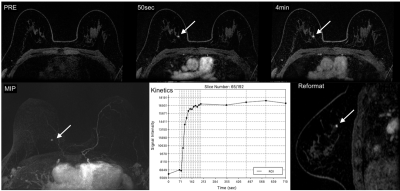
Differential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO) and LAVA VIBRANT-Flex provide similar excellent image quality while allowing faster acquisition time and high spatial and temporal resolution. In addition, DISCO provides excellent fat suppression at 3T where conventional fat saturation techniques are often suboptimal, reduce motion artifacts in breast and it delivers better and higher isotropic spatial resolution (1.1mm). These results enable better image qualities in the coronal and sagittal planes reformatting. Furthermore, a significant advantage of DISCO compared to LAVA VIBRANT-Flex (90sec temporal resolution) is that while it achieves the same high spatial resolution, a higher temporal resolution of 10sec is feasible. The simultaneous high spatial and temporal resolution improves diagnostic accuracy particularly in patients with marked background parenchymal enhancement, non-mass enhancing and small lesions.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
References1. Morrison CK, Henze Bancroft LC, DeMartini WB, et al. Novel High Spatiotemporal Resolution Versus Standard-of-Care Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Breast MRI: Comparison of Image Quality. Invest Radiol. 2017;52(4):198–205. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000329
2. Saranathan, Manojkumar et al. “DIfferential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO): a high spatio-temporal resolution Dixon imaging sequence for multiphasic contrast enhanced abdominal imaging.” Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI vol. 35,6 (2012): 1484-92. doi:10.1002/jmri.23602