S111
Accuracy of Non-Contrast MRI Biopsy in Diagnosing a Breast Cancer Pathologic Complete Response Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy1Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
Non-contrast MRI-guided biopsy is a promising minimally-invasive approach with high accuracy in diagnosing a breast cancer pathologic complete response post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy which could potentially obviate surgery in this subset of patients.
PURPOSE
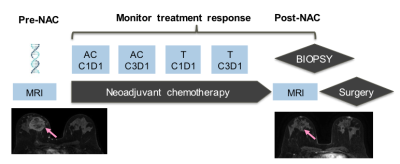
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has changed the management of breast cancer. The best outcome post-NAC is a pathologic complete response (pCR). There remains no minimally-invasive approach with sufficient accuracy to diagnose a pCR so surgery remains the standard of care (1)(2). Others have reported the potential utility of image-guided biopsies in diagnosing a pCR with variable accuracy but none used MRI or MRI-biopsy, the most sensitive test (3). The purpose of this proof-of-concept clinical trial is to evaluate the accuracy of a non-contrast MRI-biopsy in diagnosing a pCR post NAC compared to reference-standard breast surgery specimen.METHODS
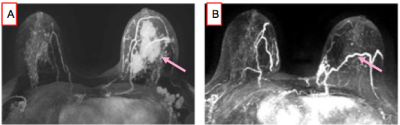
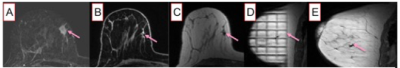
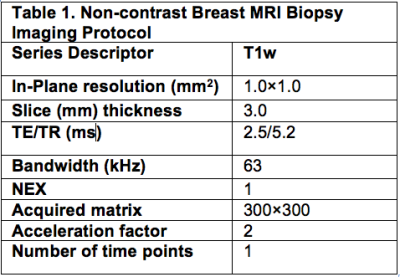
Between 2017-2019, our institutional review board approved this pilot study that required informed consent and accrued 15 women with biopsy-proven operable invasive breast cancer who met the following inclusion criteria: (a) standard-of-care NAC, (b) pre- and post-NAC MRI, (c) imaging complete response defined as no residual enhancement on post-NAC MRI and (d) planned definitive surgery at our institution. Eligibility for MRI-guided biopsy was determined by a breast-imaging radiologist and included an assessment of the treated tumor bed and its location. Exclusion criteria were: (a) tumor locations that precluded safe MRI-biopsy which included if the treated tumor bed is: (i) <1 cm from the pectoralis muscle; (ii) in the axillary tail and/or (iii) breast implant; (b) medical reason that precludes study participation and (c) prior history of breast cancer surgery and/or breast radiation therapy. The non-contrast MRI biopsies were scheduled within 0–60 days after completing NAC and before surgery. All MRI-guided biopsies were performed with either a 1. 5 or 3.0-Tesla GE Signa whole-body MRI unit (GE Medical Systems, Waukesha, WI) equipped with a dedicated 16-channel surface breast coil. This biopsy protocol was standard of care with the exception of no intravenous gadolinium because per protocol inclusion there is no residual enhancing tumor. A T1- weighted sagittal acquisition (Table 1) was used for biopsy planning. Biopsy target will be the treated tumor bed defined by the accurately positioned pre-NAC marker at site of biopsy proven cancer (per standard of care biopsy), treated tumor bed and/or anatomic landmarks. A 9-guage vacuum-assisted MRI compatible biopsy system (ATEC Breast Biopsy System, Suros Surgical Systems, Indianapolis, IN) will be used. Through a single incision site, 7–12 samples will be taken and sent to pathology for analysis. A titanium marker will be placed post-biopsy under MRI guidance, which is the standard practice and a post-biopsy mammogram will be performed to document adequate positioning of the biopsy marker and representative sampling of the treated tumor bed. The research biopsy specimen was interpreted by one of the breast pathologists on the clinical trial IRB. The percutaneous biopsy pathology was evaluated for chemotherapeutic response. A pCR is defined as absence of invasive and in situ breast cancer cells. The primary endpoint was to estimate the negative predictive value (NPV) of non-contrast MRI biopsy to reference-standard breast surgery specimen. In this context, NPV is defined as the number of true pCR (biopsy negative, i.e. no disease found on the percutaneous biopsy and pCR at surgery) divided by the number of all biopsy negatives. The positive predictive value (PPV), sensitivity, and specificity of the biopsy were also calculated.RESULTS
15 patients with an MR imaging complete response post-NAC underwent MRI biopsy. Reference standard surgical pathology demonstrated a pCR in 10/15 (67%) and no-pCR in 5/15 (33%). The accuracy of MRI biopsy was 14/15 (93%). MRI biopsy was false in 1/15 (7%). In this false negative case surgical pathology identified 0.2mm of invasive disease, a true positive (no-pCR). All no-pCR tumor beds demonstrated very small volume residual disease with the largest invasive cancer measuring 3mm. The statistical measurements of non-contrast MRI-guided biopsy in diagnosing a pCR compared with the reference standard surgical pathology are: NPV 91%, PPV 100%, Sensitivity 80% and Specificity 100%.CONCLUSIONS
The accuracy of non-contrast MRI-guided biopsy in diagnosing a pCR post-NAC in this pilot study is very high when compared to reference standard surgical pathology, which supports the need for a larger study.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Dialani V, Chadashvili T, Slanetz PJ. Role of imaging in neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Annals of surgical oncology. 2015;22(5):1416-24. Epub 2015/03/03. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4403-9. PubMed PMID: 25727555.
2. Mamounas EP. Impact of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on locoregional surgical treatment of breast cancer. Annals of surgical oncology. 2015;22(5):1425-33. Epub 2015/03/03. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4406-6. PubMed PMID: 25727558.
3. Kuerer HM, Rauch GM, Krishnamurthy S, Adrada BE, Caudle AS, DeSnyder SM, Black DM, Santiago L, Hobbs BP, Lucci A, Jr., Gilcrease M, Hwang RF, Candelaria RP, Chavez-MacGregor M, Smith BD, Arribas E, Moseley T, Teshome M, Miggins MV, Valero V, Hunt KK, Yang WT. A Clinical Feasibility Trial for Identification of Exceptional Responders in Whom Breast Cancer Surgery Can Be Eliminated Following Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy. Annals of surgery. 2018;267(5):946-51. Epub 2017/05/27. doi: 10.1097/sla.0000000000002313. PubMed PMID: 28549010.
Figures