S101
A comparison of 2D High resolution PROPELLER with 3D Fast spin echo imaging on multi-planar reconstruction1Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2Wonkwang Health Science University, Iksan, Republic of Korea
Synopsis
2D High resolution PROPELLER technique was compared to 3D Fast spin echo imaging on axial and reformatted (sag and cor) images.
Background or Purpose
The motion insensitive PROPELLER (Periodically Rotated Overlapping Parallel Lines with Enhanced Reconstruction) have been improved enabling high resolution images even with excellent contrast along the slice selection direction and other directions which can obtain similar quality to 3D sequences. Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare high resolution (HR) 2D PROPELLER and 3D CUBE T2-weighted sequence for image quality of general brain imaging.Methods
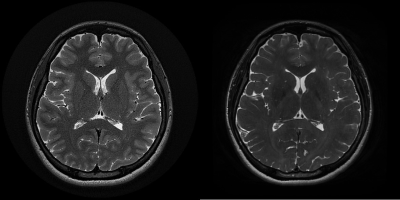
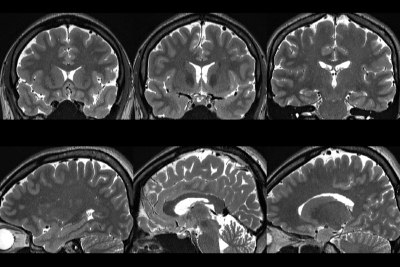
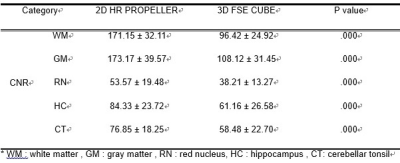
13 healthy volunteers underwent cine MRI at 3.0 T (Signa Architect, GE Healthcare, USA) using 48-channel head coil. The axial data sets were reconstructed on a free-standing workstation to generate 1mm reformatted images in the sagittal and coronal, and sagittal planes. Contrast-to-noise ratios (CNR)s were calculated and measured in five regions of interest (ROIs). ROI were selected on frontal white matter, occipital gray matter and red nucleus, hippocampus, cerebellar tonsils (Fig.1). Overall image quality was graded on a scale of 1–5 (1, excellent, 2, good, probably no artifact; 3, fair, no sure on artifact; for each sequence, 4, poor, probable artifact; definitely no artifact 5, unacceptable, definite artifact; Statistical significance was verified using paired t-test on quantitative analysis and Wilcoxon-signed rank test was performed on qualitative analysis. Parameters of the two sequences were maintained similar: TRs= [HR PROPELLER 4000msec, 3D CUBE; 2000msec], FOV=220*220 mm2, effective TE= [94msec, 96msec], voxel size=[0.6* 0.6 * 1, 1*1*1], acquisition time=[ 5min 17sec, 5min 43sec], acceleration factor=[3, 2*1.5].Results
As a result, in the slice selection direction (AX), 2D HR had high CNRs in all 5 ROIs (p<0.01) (Table 1). In particular, the difference in contrast between WM and GM was even stronger. In the reconstructed images(COR and SAG), although the difference was smaller than those of the slice selection images the 2D HR PROPELLER had higher CNRs. Qualitative evaluation of the reconstructed images showed no significant differences between the two groups. In addition, artifacts were rather reduced in the 2D HR PROPELLER images in slice selection (Table 2).Conclusions
In conclusion, HR PROPELLER has excellent contrast and motion compensation, and also maintains the same image quality as the slice selection surface in MPR reconstruction.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Lavdas, Eleftherios, et al. "Elimination of motion and pulsation artifacts using BLADE sequences in knee MR imaging." Magnetic resonance imaging 30.8 (2012): 1099-1110.
2. Lavdas, Eleftherios, et al. "Improvement of image quality using BLADE sequences in brain MR imaging." Magnetic resonance imaging 31.2 (2013): 189-200.
3. Attenberger, Ulrike I., et al. "T1-weighted brain imaging with a 32-channel coil at 3T using TurboFLASH BLADE compared with standard cartesian k-space sampling." Investigative radiology 44.3 (2009): 177-183.
4. Froehlich, Johannes M., et al. "Should less motion sensitive T2-weighted BLADE TSE replace Cartesian TSE for female pelvic MRI?." Insights into imaging 3.6 (2012): 611-618.
5. Pipe, James G., and Nicholas Zwart. "Turboprop: improved PROPELLER imaging." Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 55.2 (2006): 380-385.