Accessible and Affordable MRI to make world healthier : An Indian Initiative
1SAMEER, India
Synopsis
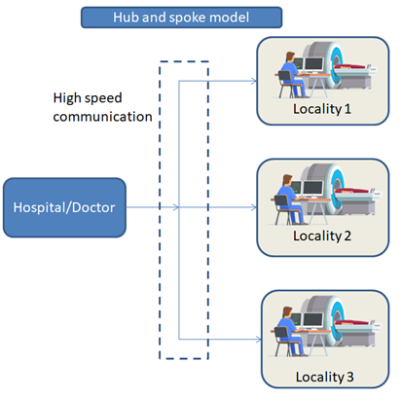
Affordability of the MRI system, its complex design requirements such as power, technology, availability of experts at remote locations, socio-technical concerns have restricted the penetration of MRI technology in India. Solving these issues and bringing MRI to the underdeveloped & developing countries require indigenization of the system and innovations in its operation. Along with cutting edge research for bringing the cost down, innovative strategies such as better patient management system, optimum usage of MRI, hub and spoke operation model and use of renewable energy play an important role.
Purpose
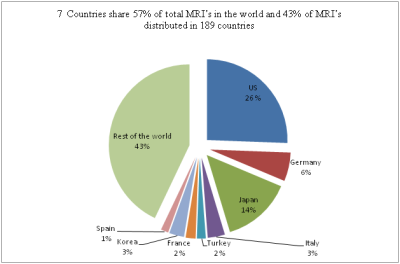
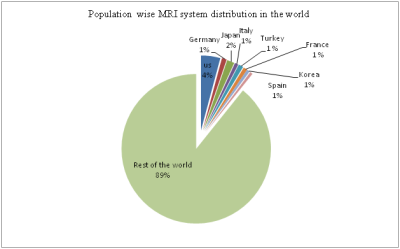
Magnetic Imaging resonance has become integral part of imaging domain in health care. Every needy person of the world has right to access cutting end medical technologies. 11% of the world’s population has access to 57% of total worldwide MRI leaving the other 89% with just 43% of the MRI machines, as per OECD and WHO data.It is estimated that India has less than 1 MRI per million people. The primary reasons behind this huge deficit are the high cost of the system and its maintenance, absence of ingenious research and development programs,dearth of open source knowledge. Proper Lack of feedback and collaboration between the research organizations and industries has further aggravated this situation. To solve this problem and make MRI more accessible, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Govt of India has commenced the development of Indigenous 1.5T MRI system project with SAMEER as nodal agency.
Method
SAMEERs approach in making 1.5T MRI system more accessible includes reduction of hardware cost, efficient patient management system, adoption of hub and spoke model, creation of ecosystem for setting up manufacturing and testing facility for MRI, adopting cutting edge technologies such as conduction cooled magnets, on chip imaging for reduction in the scan time, solar powered MRI. All subsystems of MRI have been developed ingeniously. Module based amplifier system is developed which is expected to make service and maintenance easier. Low cost RF coils and front end system have been developed in house. Spectrometer system has been developed using FPGA and NI hardware. Partial Fourier technique for fast imaging is developed in FPGA. It takes 60% of k-space data to construct full image. Reconstruction is done on the FPGA itself which reduces transmission time. Image reconstruction and image visualization module are also developed in house. These modules are tested and validated using data obtained from different hospitals in India. Integration of Image reconstruction module with newly developed spectrometer is under process. 25 pulse sequences including the calibration sequences are completed. Scientists have indigenously designed actively-shielded whole-body 1.5T superconducting MRI magnet system with cryocooler based latest technology of Zero-Boil-Off (ZBO). Scientists are also working on conduction cooled magnet and low field Halbach array as part of this development. Along with hardware cost reduction, exploration is also in progress to shed the cost from system operation point of view. In this direction it is proposed to develop hub and spoke model for efficient resource management.Acknowledgements
1. Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology, Govt of India
2. SAMEER and Collaborating partners of Indian MRI programme ie CDAC-T, CDAC-K, IUAC, DSIR
3. Prof Larry Wald, MGH, Prof J.T. Vaughan, Columbia University, Prof Steen Moiller, University of Minnesota
4. Members of National Steering Committee and Technical Advisory Committee
References
- OECD Health Statistics: Health care resources (https://data.oecd.org/healtheqt/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri-units.htm)
- Social Adoption of a technology: Magnetic Resonance Imaging in India by Amit Prasad, Georgia Institute of Technology
- Geethanath, S. and Vaughan, J.T., Jr. (2019), Accessible magnetic resonance imaging: A review. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, 49: e65-e77. doi:10.1002/jmri.26638