Multi-Nuclear Coils
1NYU Langone Medical Center, United States
Synopsis
· Dual-tuned coils provide metabolic information (x-nuclei module) and co-registered anatomical images and B0 shim settings (1H module) without repositioning the subject or coil
· X-nuclei signal strength is typically less than 1/1,000× that of 1H (1). Therefore it is important to maximize x-nuclei receive sensitivity while simultaneously providing adequate 1H sensitivity
· We will discuss prevalent dual-tuning techniques and considerations for performance characterization and interfacing dual-tuned coils
Highlights
· Dual-tuned coils provide metabolic information (x-nuclei module) and co-registered anatomical images and B0 shim settings (1H module) without repositioning the subject or coil· X-nuclei signal strength is typically less than 1/1,000× that of 1H (1). Therefore it is important to maximize x-nuclei receive sensitivity while simultaneously providing adequate 1H sensitivity
· We will discuss prevalent dual-tuning techniques and considerations for performance characterization and interfacing dual-tuned coils
Background
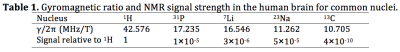
Multi-nuclear MRI and MRS are of great interest to the scientific community because of the ability to probe functional metabolites such as 23Na, 31P, 19F, 7Li, 13C, 129Xe, etc., which are collectively referred to as “x-nuclei” (2-5). For example, quantitative 23Na MRI has been shown to be highly specific to the glycosaminoglycan content in cartilage and could therefore be used as a means to detect biochemical degradation in the early stages of osteoarthritis (5). Meanwhile, 31P MRS and 17O can quantify metabolites that play important roles in energy consumption and delivery, thus providing a means to probe oxidative phosphorylation and the metabolic rate of oxygen (3). A dual-nuclei RF coil is preferred for x-nuclei applications; the 1H module provides anatomical reference images and phase images to determine B0 shim settings, while the x-nuclei module provides metabolic information without repositioning the subject. Given that standard RF coils are narrowband devices tuned only to the 1H frequency, specialized techniques must be used to simultaneously detect 1H and x-nuclei signals. Popular techniques for achieving dual resonance will be reviewed in the following section.It is important to keep in mind that the main difficulty with x-nuclei MRI is its fundamentally low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) due primarily to the low concentration of x-nuclei in the body and low gyromagnetic ratio (Table 1). These characteristics imply undesirably long acquisition times and large voxel volumes to sufficiently average signals in time and space. Over the past several years, the SNR deficit has been somewhat alleviated by efficient pulse sequences (6) and reconstruction techniques along with the proliferation of high field scanners (≥ 3 Tesla) that boost the baseline SNR. Coil hardware also has a significant influence on SNR, which will be the focus of this text.
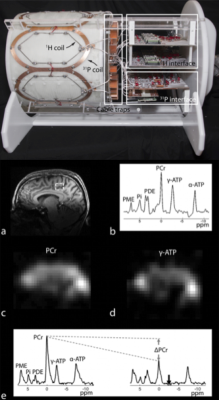
Dual-nuclei RF coil designs have recently transitioned from single channel and volume coils to multi-element phased arrays. Multi-element phased arrays are advantageous because they combine the large field-of-view of a volume coil with the improved sensitivity of a surface coil (7,8). An example of a 7 Tesla multi-element 31P/1H brain coil is shown in Figure 1 (9). The coil enables 31P spectroscopy, a saturation transfer technique to calculate the global creatine kinase forward reaction rate, and single-metabolite whole-brain imaging with 1.4 cm nominal isotropic resolution in 15 min, as well as 1 mm isotropic 1H imaging.
Methods
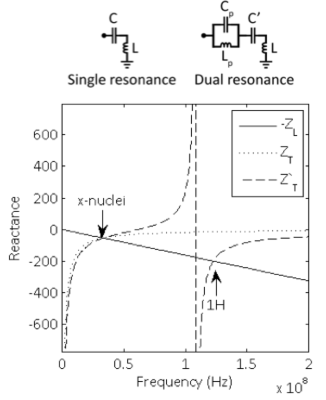
Single tuned coilA coil’s inherent inductive impedance is given by ZL=jwL. A single resonance is achieved by canceling the inductance with a tuning capacitor ZT=(jwC)-1 such that Z=jwL+(jwC)-1=0. Plots of the coil’s negative inductive reactance and tuning network reactance curves show that resonance occurs at their intersection at the x-nuclei frequency (Figure 2).
Pole insertion
One way to achieve dual resonance is by inserting a parallel inductor/capacitor pair (i.e. a pole or “trap” circuit) in series with the coil (10-12). In this case, the tuning network impedance is ZT'=(jwC')-1+[jwLp(jwCp)-1]/[jwLp+(jwCp)-1]. Inspection of the reactance plot shows two intersections between the coil’s negative inductive reactance and tuning network reactance, which give rise to resonances at both 1H and x frequencies. The low resonance frequency can be modified primarily by the main capacitance C’, while the high resonance frequency can be modified primarily by the pole capacitance Cp.
In general, dual-nuclei coil techniques involve tradeoffs. In the pole insertion method, flux generated in the trap inductor Lp is not coupled to the sample and therefore generates loss associated with its resistance. The efficiency of the low frequency channel approaches unity (where unity is the baseline efficiency of a single tuned coil) when the value of Lp approaches zero. Of course, the dual resonance property vanishes when Lp is zero rendering it irrelevant. In practice, the ratio of Lp :L is chosen to be ~1:4-5, yielding ~90% efficiency on the low frequency channel and ~45% efficiency on the high frequency channel (10).
Other methods – nested, transformer coupled, etc.
Another method to achieve dual resonance is to use two separate “nested” or explicitly coupled transformer coils, whose individual structures can be semi-independently tuned to the low and high frequencies of interest (13-27). In this case, it is instructive to model the coils as a mutually coupled system (16,25,26). The resonant frequencies of the coupled coils can be written as: , where k is the coupling coefficient, and the resonance frequencies of each coil in isolation, and the resonance frequency of the coupled system (25). In the coupled system, two modes are formed: high-frequency mode is created at a frequency while the low-frequency mode is created at a frequency . The high-frequency mode is “counter-rotating” because the current induced in the x-nuclei coil flows 180° out-of-phase with that in the 1H coil. This out-of-phase current shields the 1H coil by compressing its flux pattern and reducing its effective inductance, which can reduce B1 sensitivity, increase resistive loss, and potentially reduce radiation loss. In contrast, the low-frequency co-rotating mode is generally unperturbed by the presence of the 1H coil.
This combination of behaviors can be leveraged in a concentric nested dual nuclei strategy; 1) the low frequency coil is not significantly affected by the high frequency coil, while 2) the low frequency coil shields the high frequency coil to reduce its radiation loss and neighbor coupling (28), albeit at the expense of coverage and penetration due to counter-rotating current induced in the low frequency coil shield. If radiation loss is not significant, it may be desirable to install filters in the x-nuclei coils that are tuned to block counter-rotating 1H currents. Note that the filters come with a small x-nuclei SNR penalty (25,26,29). Another method to reduce counter-rotating currents is with a 1H butterfly/x-nuclei loop pair, which generate orthogonal fields and hence experience very little coupling (23,24). This approach can be desirable in proton decoupling applications, where a so-called B2 field is generated to saturate 1H spins concurrent to the x-nuclei MRS experiment to augment the x-nuclei signal. Still other dual-nuclei coil techniques have included modified volume coils with alternating 1H/x legs (30-32) and additional endrings (33-35). Volume coils generally provide a uniform transmit field (B1+), which can simplify x-nuclei quantification methods that may be undesirably sensitive to a spatially varying flip angle.
Dual-tuned phased arrays
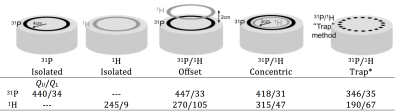
While early dual-tuned coils primarily consisted of single channel surface or volume coils, recent literature shows a dramatic increase in dual-tuned phased arrays (14,17,18,20,21,27,36-43). This can be traced to a general revitalization of x-nuclei research resulting from the new prevalence of high-field scanners (which inherently improve the x-nuclei SNR), as well as improved pulse sequences and sampling strategies. Ideally, many-element arrays outperform single channel coils in both the periphery as well as in the center of the object (8). However, transitioning from a single channel x-nuclei coil to a many-element array implies a diminishing quality factor (Q=f0/BW=wL/R) ratio that coincides with smaller coils and is accentuated at low frequencies. A good rule-of-thumb is to design an array such that the quantity and size of the individual coils provide the required coverage and a Q ratio ≥ ~3, which is considered to be on the edge of the sample noise dominated regime. Note that an array with a smaller coils and therefore lower Q ratio is unlikely to provide SNR benefit at the center of the object compared to a simpler array with fewer, larger coils. Further, higher channel counts necessitate additional opportunities for unwanted stray currents and noise coupling (i.e. through coaxial cables, interface components, and preamplifiers). Subtle enhancements such as presenting the preamplifier with an impedance mismatch can reduce noise coupling between coils, which can be particularly beneficial in x-nuclei arrays where the loaded Q is high due to low coil-tissue coupling (27,44,45). Performance characterization It is important to quantify dual-tuned coil performance as a function of its environment. The quality factor is a straightforward way to measure coil efficiency; the unloaded QU is an indication of losses associated with the coil itself (namely conductor resistance and radiation) and the loaded QL is an indication of losses in the coil plus those induced from the sample. Here, coil Q was measured on 31P/1H coils tuned for operation at 7 Tesla as a means to compare several dual-nuclei strategies in Figure 3.
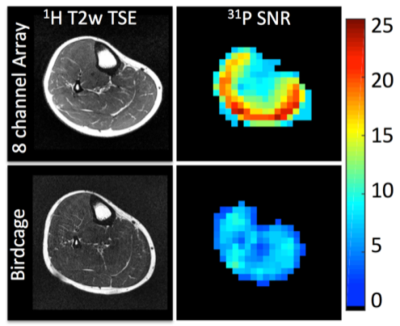
Several interesting conclusions can be drawn from the Q measurements. Importantly, the Q of the 31P coil is practically unaffected by the presence of the 1H coil in the offset and concentric arrangements. Conversely, the offset 31P coil shields the 1H coil, resulting in an increased unloaded Q value (due to reduced radiation loss) but also increased loaded Q due to shielding of the coil from the sample and thus a significantly reduced Q ratio and B1 sensitivity. The concentric arrangement partially restores the Q ratio of the 1H coil, while the trap method results in loss of performance at both frequencies. The key performance metric in a dual-tuned coil is the SNR of the x-nuclei module. It can be insightful to compare the SNR of a coil developed in-house to that attained with a commercially available coil that serves as a reference standard. When a reference coil is not available, it can be problematic to engage in inter-site SNR comparison owing to the wide variety of specialized pulse sequences and acquisition parameters and the arbitrary nature of SNR units. For this reason, it is preferred to publish SNR measurements acquired with standard gradient echo Cartesian sequences and a well-described tissue-equivalent phantom (46,47) along with the processing method such that the measurements can be easily replicated at other institutions. Figure 4 (39) illustrates the SNR advantage of an eight-channel 31P/1H array over a birdcage coil processed using the algorithm described by Kellman and McVeigh (48). SNR was measured from data acquired with a 2D gradient echo sequence with the following parameters: voxel size = 8×8×50mm3, TE = 6.5 ms, TR = 10s, FA = 76°, receiver bandwidth = 100 Hz/pixel, and acquisition time = 640s.
A performance metric that is somewhat easier to quantify is transmit efficiency. This quantity stipulates the amount of power or voltage required to generate a given . The high 1H signal level allows for a variety of 1H flip angle-mapping methods (49-54) that are difficult to translate to x-nuclei (55). One approach, though time-consuming, is to acquire fully relaxed gradient echo images (TR>>T1) over a range of transmit pulse amplitudes V with known duration τ. The signal intensities can then be fit to a sine curve to determine the pulse amplitude required to generate a flip angle α. This value can finally be translated into transmit efficiency: η=B1+/V=[(360γτ/α)-1/V, which is a convenient metric for coil comparisons due to its relative insensitivity to imaging parameters.
Interface
Due to the lack of a system integrated x-nuclei transmit coil (the body coil in clinical systems operates only at the 1H frequency, while high field 7 Tesla systems do not include a body coil for any nucleus), dual-nuclei coils are typically operated in transmit/receive mode or transmit only/receive only (ToRo) mode, both of which necessitate custom transmit/receive switches and other interface hardware (56). Additionally, coils designed with proton decoupling applications in mind require a low-loss low-pass or band-pass filter at the input of the x-nuclei preamplifier to prevent damage from power leaked from the large concurrent 1H B2 pulses (57). Finally, a diplexer circuit may be required for true multi-tuned coils (where both frequencies are available at the same coil port). A diplexer is a passive three-port device with high-pass, low-pass, and combined ports in order to allow frequency multiplexing. This is required to separate signals prior to narrowband amplification. Cable traps are essential components that reduce common mode currents on the coaxial cable shields in any RF coil (58). In particular, electric fields generated on coaxial cables in close proximity to the subject can pose a safety hazard, while their existence generally deteriorates coil performance through parasitic current pathways. In dual-tuned coils, cable traps are typically required to suppress both 1H and x-nuclei current, regardless of the resonant frequency of the coil connected to a given cable. Dual-tuned cable traps can be formed in a similar manner (i.e. using trap circuits) as a dual-tuned coil is formed; an excellent example of a dual-tuned tri-axial cable trap is detailed in Ref. (17). Interface – back end Most clinical systems are designed only for 1H-MRI and require modifications to the RF architecture in order to process or generate signals at heteronuclear frequencies (56,59). In the receive chain, signals are sampled at a predetermined “intermediate frequency (IF)” that is set by the manufacturer and created by down-converting the 1H signal via frequency mixing with a local oscillator signal (LO). In order to process heteronuclear receive signals, one can pre-mix the x-signal with an auxiliary LO set to the difference between the 1H and x frequencies. In this way, the x-signal is disguised as 1H, allowing the system to process the signal as usual. On the transmit side, one needs a dedicated broadband amplifier that is fed by a pre-modified waveform generated originally at the 1H frequency by the system (to synchronize timing) and down-converted to the desired x frequency (56,60).Power Limits
Dual-nuclei transmit coils must be carefully regulated in order to restrict tissue heating caused by their electric field in accordance with limits set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC 60601-2-33 2010). The merits of various approaches for determining safe power limits for RF coils are a topic of vigorous discussion in the field. A comprehensive review on procedures for self-developed coils with respect to mechanical and electrical safety is given in Ref. (61). Computer-based specific absorption rate (SAR) prediction models provide excellent insight on the coil’s behavior, though extreme care must be taken to accurately represent the coil, relevant interface components, and subject in the computer model and finally confirm their equivalence in situ (62,63). In the case of dual-nuclei coils, it is important to model and simulate both 1H and x-nuclei coil structures to account for their interaction and to determine power limits for both operating frequencies. An accompanying approach is to measure heating in situ through MR thermometry (64) and/or fluoroptic probes. The main benefit of this approach is that all components of the RF chain are inherently accounted for, although it is critical to recognize experimental subtleties such as the heat diffusivity of the phantom, phase SNR, and B0 drift that can reduce accuracy. Given the uncertainties associated with both simulation and thermometry methods, it is generally prudent to install a safety margin beyond the IEC limits.Summary
Dual-nuclei coils are valuable tools for x-nuclei studies, as their performance plays a critical role in image quality and minimizing acquisition time and spatial resolution. Many of the sound engineering guidelines for single-tuned coils such as minimizing coil loss, improving sensitivity through multi-channel receive arrays, and eliminating coaxial cable shield currents can be extended to dual-nuclei coils. Dual-resonance can be achieved in a variety of manners, all of which are intended to maximize receive sensitivity on the x-nuclei module while simultaneously providing adequate 1H sensitivity. The popular techniques mentioned above can be considered a starting point for those interested in designing multi-tuned coils.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Haacke EM, Brown RW, Thompson MR, Venkatesan R. Magnetic Resonance Imaging - physical principles and sequence design. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1999.
2. Hu R, Kleimaier D, Malzacher M, Hoesl MAU, Paschke NK, Schad LR. X-nuclei imaging: Current state, technical challenges, and future directions. J Magn Reson Imaging 2020;51(2):355-376.
3. Zhu XH, Du F, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Lei H, Zhang X, Qiao H, Ugurbil K, Chen W. Advanced In Vivo Heteronuclear MRS Approaches for Studying Brain Bioenergetics Driven by Mitochondria. Methods in molecular biology 2009;489:317-357.
4. Zhu XH, Lu M, Chen W. Quantitative imaging of brain energy metabolisms and neuroenergetics using in vivo X-nuclear (2)H, (17)O and (31)P MRS at ultra-high field. J Magn Reson 2018;292:155-170.
5. Madelin G, Lee JS, Regatte RR, Jerschow A. Sodium MRI: methods and applications. Progress in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy 2014;79:14-47.
6. Pipe JG, Zwart NR, Aboussouan EA, Robison RK, Devaraj A, Johnson KO. A new design and rationale for 3D orthogonally oversampled k-space trajectories. Magn Reson Med 2011;66(5):1303-1311.
7. Roemer PB, Edelstein WA, Hayes CE, Souza SP, Mueller OM. The NMR phased array. Magn Reson Med 1990;16(2):192-225.
8. Wright SM, Wald LL. Theory and application of array coils in MR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 1997;10(8):394-410.
9. Brown R, Lakshmanan K, Madelin G, Parasoglou P. A nested phosphorus and proton coil array for brain magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Neuroimage 2016;124(Pt A):602-611.
10. Schnall MD, Subramanian VH, Leigh JS, Chance B. A new double-tuned probe for concurrent 1H and 31P NMR. J Magn Reson 1985;65:122-129.
11. Shen GX, Boada FE, Thulborn KR. Dual-frequency, dual-quadrature, birdcage RF coil design with identical B1 pattern for sodium and proton imaging of the human brain at 1.5 T. Magn Reson Med 1997;38(5):717-725.
12. Shen GX, Wu JF, Boada FE, Thulborn KR. Experimentally verified, theoretical design of dual-tuned, low-pass birdcage radiofrequency resonators for magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain at 3.0 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 1999;41(2):268-275.
13. Fitzsimmons JR, Brooker HR, Beck B. A transformer-coupled double-resonant probe for NMR imaging and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 1987;5(5):471-477.
14. Brown R, Madelin G, Lattanzi R, Chang G, Regatte RR, Sodickson DK, Wiggins GC. Design of a nested eight-channel sodium and four-channel proton coil for 7T knee imaging. Magn Reson Med 2013;70(1):259-268.
15. Fleysher L, Oesingmann N, Brown R, Sodickson DK, Wiggins GC, Inglese M. Noninvasive quantification of intracellular sodium in human brain using ultrahigh-field MRI. NMR Biomed 2013;26(1):9-19.
16. Fitzsimmons JR, Beck BL, Brooker HR. Double resonant quadrature birdcage. Magn Reson Med 1993;30(1):107-114.
17. Avdievich NI, Hetherington HP. 4 T Actively detuneable double-tuned 1H/31P head volume coil and four-channel 31P phased array for human brain spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 2007;186(2):341-346.
18. Moon CH, Kim JH, Zhao T, Bae KT. Quantitative (23) Na MRI of human knee cartilage using dual-tuned (1) H/(23) Na transceiver array radiofrequency coil at 7 tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013;38(5):1063-1072.
19. Klomp DW, van de Bank BL, Raaijmakers A, Korteweg MA, Possanzini C, Boer VO, van de Berg CA, van de Bosch MA, Luijten PR. 31P MRSI and 1H MRS at 7 T: initial results in human breast cancer. NMR Biomed 2011;24(10):1337-1342.
20. van der Velden TA, Italiaander M, van der Kemp WJ, Raaijmakers AJ, Schmitz AM, Luijten PR, Boer VO, Klomp DW. Radiofrequency configuration to facilitate bilateral breast 31P MR spectroscopic imaging and high-resolution MRI at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 2014.
21. Kaggie JD, Hadley JR, Badal J, Campbell JR, Park DJ, Parker DL, Morrell G, Newbould RD, Wood AF, Bangerter NK. A 3 T sodium and proton composite array breast coil. Magn Reson Med 2014;71(6):2231-2242.
22. Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ, Roemer PB. Phosphate metabolite imaging and concentration measurements in human heart by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 1990;14(3):425-434.
23. Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ, Roemer PB, Mueller OM. Proton-decoupled, Overhauser-enhanced, spatially localized carbon-13 spectroscopy in humans. Magn Reson Med 1989;12(3):348-363.
24. Adriany G, Gruetter R. A half-volume coil for efficient proton decoupling in humans at 4 tesla. J Magn Reson 1997;125(1):178-184.
25. Dabirzadeh A, McDougall MP. Trap Design for Insertable Second-Nuclei Radiofrequency Coils for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy. Concepts in Magnetic Resonance Part B (Magnetic Resonance Engineering), 2009;35B(3):121-132.
26. Alecci M, Romanzetti S, Kaffanke J, Celik A, Wegener HP, Shah NJ. Practical design of a 4 Tesla double-tuned RF surface coil for interleaved 1H and 23Na MRI of rat brain. J Magn Reson 2006;181(2):203-211.
27. Brown R, Lakshmanan K, Madelin G, Alon L, Chang G, Sodickson DK, Regatte RR, Wiggins GC. A flexible nested sodium and proton coil array with wideband matching for knee cartilage MRI at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2015.
28. Lanz T, Griswold M. Concentrically Shielded Surface Coils - A New Method for Decoupling Phased Array Elements. ISMRM2006. p 217.
29. Meyerspeer M, Roig ES, Gruetter R, Magill AW. An improved trap design for decoupling multinuclear RF coils. Magn Reson Med 2014;72(2):584-590.
30. Xie Z, Xu D, Kelley DA, Vigneron DB, Zhang X. Dual-frequency Volume Microstrip Coil with Quadrature Capability for 13C/1H MRI/MRS at 7T. ISMRM Workshop on Advances in High Field MR. Pacific Grove, California, USA2007. p Poster 41.
31. Vaughan JT, Hetherington HP, Otu JO, Pan JW, Pohost GM. High frequency volume coils for clinical NMR imaging and spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 1994;32(2):206-218.
32. Amari S, Ulug AM, Bornemann J, van Zijl PC, Barker PB. Multiple tuning of birdcage resonators. Magn Reson Med 1997;37(2):243-251.
33. Murphy-Boesch J, Srinivasan R, Carvajal L, Brown TR. Two configurations of the four-ring birdcage coil for 1H imaging and 1H-decoupled 31P spectroscopy of the human head. Journal of magnetic resonance Series B 1994;103(2):103-114.
34. Lanz T, von Kienlin M, Behr W, Haase A. Double-tuned four-ring birdcage resonators for in vivo 31P-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 11.75 T. Magma 1997;5(3):243-246.
35. Derby K, Tropp J, Hawryszko C. Design and evaluation of a novel dual-tuned resonator for spectroscopic imaging. J Magn Reson 1990;86:645-651.
36. Yang X, Handa S, Zheng T, Lawrie C, Finnerty M, Herczak J, Fujita H, Bogner W, Zaric O, Zbyn S, Trattnig S. A Dual-Tune Sodium/Proton Tx/Rx 14-channel Sodium and 2-channel Proton Array Breast Coil at 7T. ISMRM. Salt Lake City, UT2013. p 2785.
37. Shajan G, Mirkes C, Buckenmaier K, Hoffmann J, Pohmann R, Scheffler K. Three-layered radio frequency coil arrangement for sodium MRI of the human brain at 9.4 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 2015.
38. Mirkes C, Shajan G, Chadzynski G, Buckenmaier K, Bender B, Scheffler K. P CSI of the human brain in healthy subjects and tumor patients at 9.4 T with a three-layered multi-nuclear coil: initial results. Magma 2016.
39. Brown R, Khegai O, Parasoglou P. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Phosphocreatine and Determination of BOLD Kinetics in Lower Extremity Muscles using a Dual-Frequency Coil Array. Sci Rep 2016;6:30568.
40. Lakshmanan K, Brown R, Madelin G, Qian Y, Boada F, Wiggins GC. An eight-channel sodium/proton coil for brain MRI at 3 T. NMR Biomed 2018;31(2).
41. Ianniello C, Madelin G, Moy L, Brown R. A dual-tuned multichannel bilateral RF coil for (1) H/(23) Na breast MRI at 7 T. Magn Reson Med 2019;82(4):1566-1575.
42. Avdievich NI, Ruhm L, Dorst J, Scheffler K, Korzowski A, Henning A. Double-tuned (31) P/(1) H human head array with high performance at both frequencies for spectroscopic imaging at 9.4T. Magn Reson Med 2020.
43. van Uden MJ, Peeters TH, Rijpma A, Rodgers CT, Heerschap A, Scheenen TWJ. An 8-channel receive array for improved (31) P MRSI of the whole brain at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2019;82(2):825-832.
44. Vester M, Biber S, Rehner R, Wiggins G, Brown R, Sodickson D. Mitigation of Inductive Coupling in Array Coils by Wideband Port Matching. ISMRM. Melbourne, Australia2012. p 2690.
45. Wiggins GC, Brown R, Zhang B, Vester M, Popescu S, Rehner R, Sodickson D. SNR Degradation in Receive Arrays Due to Preamplifier Noise Coupling and a Method for Mitigation. ISMRM. Melbourne, Australia2012. p 2689.
46. Duan Q, Duyn JH, Gudino N, de Zwart JA, van Gelderen P, Sodickson DK, Brown R. Characterization of a Dielectric Phantom for High-Field MRI Applications. ISMRM. Milan, Italy2014. p 4816.
47. Ianniello C, de Zwart JA, Duan Q, Deniz CM, Alon L, Lee JS, Lattanzi R, Brown R. Synthesized tissue-equivalent dielectric phantoms using salt and polyvinylpyrrolidone solutions. Magn Reson Med 2018;80(1):413-419.
48. Kellman P, McVeigh ER. Image reconstruction in SNR units: a general method for SNR measurement. Magn Reson Med 2005;54(6):1439-1447.
49. Helms G, Finsterbusch J, Weiskopf N, Dechent P. Rapid radiofrequency field mapping in vivo using single-shot STEAM MRI. Magn Reson Med 2008;60(3):739-743.
50. Jiru F, Klose U. Fast 3D radiofrequency field mapping using echo-planar imaging. Magn Reson Med 2006;56(6):1375-1379.
51. Lutti A, Hutton C, Finsterbusch J, Helms G, Weiskopf N. Optimization and validation of methods for mapping of the radiofrequency transmit field at 3T. Magn Reson Med 2010;64(1):229-238.
52. Yarnykh VL. Actual flip-angle imaging in the pulsed steady state: a method for rapid three-dimensional mapping of the transmitted radiofrequency field. Magn Reson Med 2007;57(1):192-200.
53. Fautz HP, Vogel M, Gross P, Kerr A, Zhu Y. B1 mapping of coil arrays for parallel transmission ISMRM. Toronto, Ontario2008. p 1247.
54. Breton E, McGorty K, Wiggins GC, Axel L, Kim D. Image-guided radio-frequency gain calibration for high-field MRI. NMR Biomed 2010;23(4):368-374.
55. Allen SP, Morrell GR, Peterson B, Park D, Gold GE, Kaggie JD, Bangerter NK. Phase-sensitive sodium B1 mapping. Magn Reson Med 2011;65(4):1125-1130.
56. Lee RF, Giaquinto R, Constantinides C, Souza S, Weiss RG, Bottomley PA. A broadband phased-array system for direct phosphorus and sodium metabolic MRI on a clinical scanner. Magn Reson Med 2000;43(2):269-277.
57. Bottomley PA, Hardy CJ. Proton Overhauser enhancements in human cardiac phosphorus NMR spectroscopy at 1.5 T. Magn Reson Med 1992;24(2):384-390.
58. Schaller BM, Magill AW, Gruetter R. Common modes and cable traps. ISMRM2011. p 4660.
59. Meyerspeer M, Magill AW, Kuehne A, Gruetter R, Moser E, Schmid AI. Simultaneous and interleaved acquisition of NMR signals from different nuclei with a clinical MRI scanner. Magn Reson Med 2015.
60. Yu Z, Madelin G, Sodickson DK, Cloos MA. Simultaneous proton magnetic resonance fingerprinting and sodium MRI. Magn Reson Med 2019.
61. Hoffmann J, Henning A, Giapitzakisa IA, Scheffler K, Shajana G, Pohmanna R, Avdievicha NI. Safety testing and operational procedures for self-developed radiofrequency coils. NMR Biomed 2015.
62. Kozlov M, Turner R. Effects of head size and position on SAR. ISMRM. Stockholm, Sweeden2010. p 3875.
63. Wolf S, Diehl D, Gebhardt M, Mallow J, Speck O. SAR simulations for high-field MRI: how much detail, effort, and accuracy is needed? Magn Reson Med 2013;69(4):1157-1168.
64. Ishihara Y, Calderon A, Watanabe H, Okamoto K, Suzuki Y, Kuroda K. A precise and fast temperature mapping using water proton chemical shift. Magn Reson Med 1995;34(6):814-823.
Figures