4879
Radiomics analysis on magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imagefor prediction of Ki-67 expression in breast cancer1Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai, China, 2Huiying Medical Technology Co., Beijing, China
Synopsis
The expression level of Ki-67 has an important reference value for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis evaluation of breast cancer. To explore the feasibility of diffusion-weighted imaging for prediction of Ki-67 expression. In this study, the expression of Ki-67 in breast cancer was differentiated by semi-automatic extraction of the image parameters of diffusion-weighted(DWI) before treatment. The results of this study show that Ki-67-negative and Ki-67-positive breast cancer have different imaging characterization values in DWI images. The imaging of DWI is feasible in identifying the two, which is helpful to predict the expression level of Ki-67 in breast cancer before operation.
Introduction
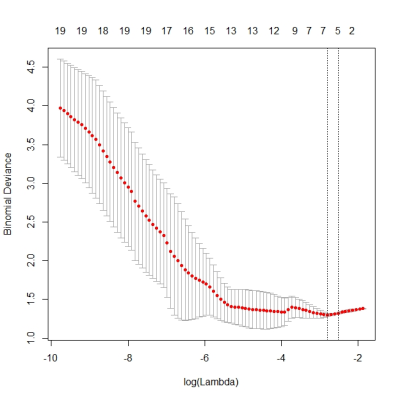
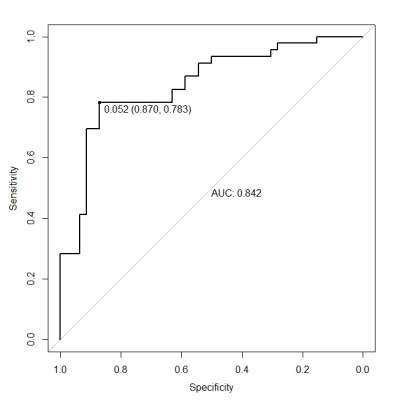
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in women. As an independent prognostic factor, Ki-67 has an important reference value for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis evaluation of breast cancer. Therefore, early and accurate prediction of Ki-67 expression level is of great significance for the prognosis judgment and clinical guidance of breast cancer. In recent years, there have been studies on the prediction of Ki-67 expression based on T2WI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, but it is fresh See the study of diffusion-weighted imaging in predicting Ki-67 expression. This study intends to explore the feasibility of preoperative prediction of Ki-67 expression in breast cancer using DWI.Materials and Methods. A total of 114 patients who underwent preoperative MRI scan and postoperative expression of Ki-67 in pathological tissues were obtained, of which 38 were negative for Ki-67 and 76 were positive for Ki-67. Two radiologists manually outlined the lessions extracted 1409 radiomics features. First the data were randomly divided into training set and verification set as a ratio of 8:2 and the training set analyzed the features and built model of machine learning, and the test set evaluated the performance of the model. The LASSO method was used to select the features more relevant to the expression on Ki-67 and construct the image-signature.The prediction model for assessing the expression level of Ki-67 in breast cancer was established by combining the image-signature with the indicators of pathologic analyses. The area under the ROC curve was used to evaluat the performance of the training set and test set.Results Statistical results showed that 25 of the 76 radiomics features, such as entropy,energy and contrast, had statistical significance in the two groups of data (P < 0.05).Further, LASSO method selected 4 features from 67 image radiomics features, and combined with pathological results for two-class modeling. Among them, AUC in training concentration reached 0.83, and AUC in verification concentration reached 0.76. Conclusion Ki-67-negative and Ki-67-positive breast cancer have different imaging characterization values in DWI images. The imaging of DWI is feasible in identifying the two, which is helpful to predict the expression level of Ki-67 in breast cancer before operation.Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671654, 81401385) and National Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2017PH043) for the financial support.References
[1]Denkert C, von Minckwitz G. Reply to Ki67 in breast cancer: a useful prognostic marker! [J].Ann Oncol, 2014, 25(2):542-3.
[2]Juan MW, Yu J, Peng GX, et al. Correlation between DCE-MRI radiomics features and Ki-67 expression in invasive breast cancer[J]. Oncol Lett. 2018, 16(4):5084-5090.
[3]Liang C, Cheng Z,Huang Y, et al. An MRI-based Radiomics Classifier for Preoperative Prediction of Ki-67 Status in Breast Cancer[J]. Acad Radiol. 2018,25(9):1111-1117.
[4]Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensuson the Primary Therapy of Ealy Breast Cancer 2013[J]. Ann Oncol, 2013,24(9):2206-2223.
[5]Mao N, Wang Q, Liu M, et al. Computerized Image Analysis to Differentiate Benign and Malignant Breast Tumors on Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Weighted Image: A Preliminary Study[J]. J ComputAssist Tomogr. 2019 43(1):93-97.
[6]Wang S, Li W, Liu N, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis for molecular subtypes in low-grade breast carcinoma: comparison with grade one invasive ductal carcinoma-not otherwise specified[J]. Med Oncol, 2012,29(4):2556-64.
[7]Brown JR, DiGiovanna MP, Killelea B, et al. Quantitative assessment Ki-67 score for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer[J]. LabInvest, 2014, 94: 98-106.
[8]Song Y, Liu X, Zhang G, et al. Unique clinico pathological features of metaplastic breast carcinoma compared with invasive ductal carcinoma and poor prognostic indicators[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2013, 11(1):129.
[9]Boros M, Moncea D, Moldovan C, et al. Intratumoral heterogeneity for Ki-67 index in invasive breast carcinoma: a study on 131 consecutive cases[J]. ApplImmunohistochem Mol Morphol, 2017, 25:338–340.[10]Moy L, Elias K, Patel V, et al. Is breast MRI helpful in the evaluation of inconclusive mammographic findings[J].Am J Roentgenol, 2009, 193(4):986-993.
[11]Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, et al. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011[J]. Ann Oncol, 2011,22(8):1736-1747.
[12]Chen H, Liu N, Li Y, et al. The role of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR in evaluating level III collateral circulation in a rat model of acute ischemic stroke[J].Mol Neurobiol, 2017, 54(4):2731-2738.
[13]Yuan M, Zhang YD, Zhu C, et al. Comparison of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for differentiating lung cancer from benign solitary pulmonary lesions[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2016, 43(3):669-679.
[14]Choi Y, Kim SH, Youn IK, et al. Rim sign and histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient values on diffusion-weighted MRI in triple-negative breast cancer: Comparison with ER-positive subtype[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5):e0177903.
[15]Waugh SA, Purdie CA, Jordan LB, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging texture analysis classification of primary breast cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2016, 26(2):322-330.
Figures