4877
Characterization of Sub-centimeter Enhancing Breast Masses on MRI with Radiomics and Machine Learning in BRCA Mutation Carriers1Radiology, Breast imaging, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States, 3medical physics, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
The purpose of our study was to investigate whether radiomics features
extracted from MRI of BRCA-positive patients with breast masses smaller than 1
cm coupled with machine learning can differentiate benign from malignant lesions using
model-free parameter maps. We included 96 patients with 116 lesions assessed by two readers according to the BI-RADS lexicon. Radiomics features were calculated and included in a machine learning model, along with clinical factors, to
discriminate between malignant and benign lesions. The machine learning model, combining two clinical and three radiomics features, achieved higher diagnostic accuracy (81.5%) compared to morphological assessment alone (53.4%)
Introduction
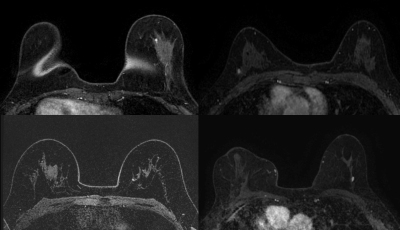
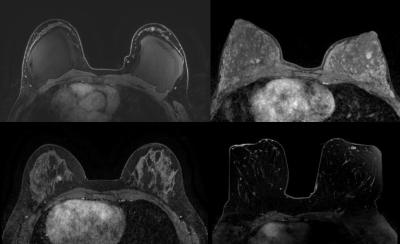
Women who inherit BRCA mutations are more prone to developing tumors of the breast, resulting in numerous often benign breast biopsies during their life. The purpose of this study is to investigate whether radiomics features extracted from MRI of BRCA-positive patients with breast masses smaller than 1 cm can be coupled with machine learning to differentiate benign from malignant lesions using model-free parameter maps.Materials and Methods
In this retrospective study, 96 BRCA mutation carriers (mean age at the time of biopsy = 45.5±13.5 years) who had an MRI from November 2013–February 2019 that led to a biopsy (BI-RADS 4) or imaging follow-up (BI-RADS 3) were included. Two radiologists assessed all lesions independently and in consensus according to the BI-RADS lexicon. Radiomics features, based on first-order statistics, the gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), run length matrix (RLM), size zone matrix (SZM), neighborhood gray level dependence matrix, and neighborhood gray tone difference matrix were calculated. Univariate analysis and multivariate modeling were performed to identify significant radiomic features and clinical factors to be included in a machine learning model to discriminate between malignant and benign lesions.Results
Consensus BI-RADS classification assessment achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 53.4%, sensitivity of 73.1%, specificity of 42.1%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 40.5%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of 76.2%. The machine learning model combining five parameters (age, lesion location, GLCM-based correlation from the pre-contrast phase, first-order coefficient of variation from the 1st post-contrast phase, and SZM-based gray level variance from the 1st post-contrast phase) achieved a diagnostic accuracy of 81.5%, sensitivity of 63.2% (24/38), specificity of 91.4% (64/70), PPV of 80.0% (24/30), and NPV of 82.1% (64/78).Conclusion
Radiomics analysis coupled with machine learning improves the diagnostic accuracy in small breast masses compared to the qualitative morphological assessment with BI-RADS classification alone in BRCA mutation carriers.Acknowledgements
This study received funding from the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA008748), the Breast Cancer Research Foundation, Susan G. Komen, Spanish Foundation Alfonso Martin Escudero, and the European School of Radiology.References
1. Lakhani SR, Jacquemier J, Sloane JP et al. Multifactorial analysis of differences between sporadic breast cancers and cancers involving BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998 Aug 5;90(15):1138-45.
2. Julia Krammer, Katja Pinker-Domenig, Mark E. Robson et al. Breast cancer detection and tumor characteristics in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Jun;163(3):565-571. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4198-4. Epub 2017 Mar 25.
3. Matthias Meissnitzer, David Dershaw, Kimberly Feigin et al. MRI appearance of invasive subcentimetre breast carcinoma: benign characteristics are common. Br J Radiol. 2017 Jun;90(1074):20170102. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20170102. Epub 2017 May 25.
Figures