4875
Prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer using deep learning method
Yuhong Qu1, Haitao Zhu1, Kun Cao1, Xiaoting Li1, and Ying-shi Sun1
1Beijing cancer hospital, Beijing, China
1Beijing cancer hospital, Beijing, China
Synopsis
This study established a deep learning model to predict PCR status after neoadjuvant therapy by combining pre-NAC and post-NAC MRI data.The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) of the models are 0.968 for post-NAC and 0.970 for the combined data.
Purpose: To develop a deep learning (DL) algorithm to evaluate pathological complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC)in breast cancer.Materials and Methods:In this retrospective study,302 eligible breast cancer patients were enrolled and randomly divided into a training set (n=244) and a validation set (n=58). Tumor regions were manually delineated on each slice by two expert radiologists, containing the surrounding chords and burrs as visualized by the second phase of T1-weighted images(T1WI)with Gadolinium enhancement. Pathological results were used as ground truth. Deep learning network (Tensorflow) contains 5 repetition of convolution and max-pooling layers and ends with 3 dense layers. Pre-NAC model and post-NAC model inputs 6 phases of enhancement from pre-NAC and post-NAC images respectively. Combined model uses 12 channels from 6 phases of pre-NAC and 6 phases of post-NAC images.Results: The training set contains 137 non-pCR participants and 107 pCR participants. The validation set contains 33 non-pCR participants and 25 pCR participants. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) of three models are 0.553 for pre-NAC, 0.968 for post-NAC and 0.970 for the combined data, respectively. Significant difference can be found in AUC between using pre-NAC data alone and using combined data (Z=5.297, P<0.0001). The positive predictive value of the combined model (PPV=100%) is greater than that of post-NAC model (PPV=82.8) (χ2=4.569, P=0.033). Conclusion:This study established a deep learning model to predict PCR status after neoadjuvant therapy by combining pre-NAC and post-NAC MRI data. The model showed significantly larger AUC than using pre-NAC data only, and also showed significantly larger positive predictive value than using post-NAC data only.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
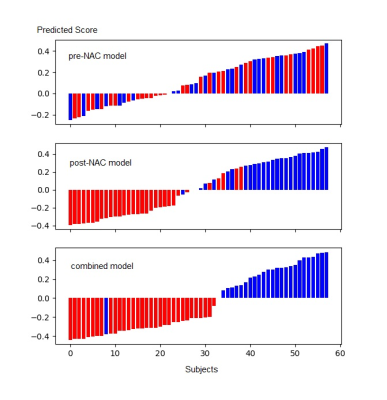
Predicted scores of 58 participants withlocally advanced breast cancerin the test set. Blue color indicates pCR proven by pathological analysis. Red color indicates non-pCR proven by pathological analysis.Bars above 0 are pCR predicted by DL models. Bars below 0 are non-pCR predicted by DL models.
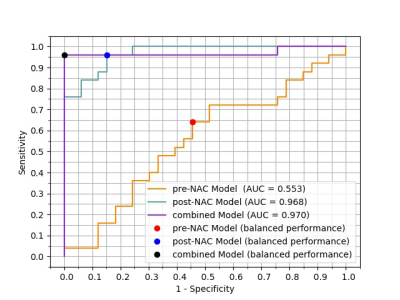
Receiver operating characteristic curves of pre-NAC, post-NAC and combined model. The area under curve (AUC) is 0.553(0.416-0.683) for pre-NAC model, 0.968(0.885-0.997) for post-NAC model and 0.970(0.887-0.997) for the combined model. The largest Youden index was used to set the cutoff value.
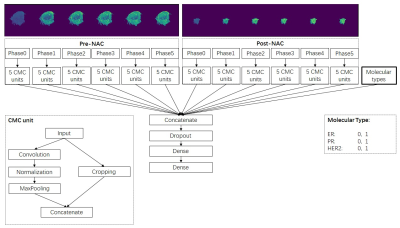
A multi-path deep convolutional neural network architecture