4848
The application of APT and IVIM in predicting the recurrence of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma treated with TACE: A pilot study1The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University, Xin xiang, China, 2GE Healthcare ,MR Research China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
This work assessed the feasibility of quantitative parameters derived from APT and IVIM in the predicting the recurrence of early stage Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). We find that combined quantitative parameters of APT and IVIM can be used to predict the recurrence. Therefore, APT and IVIM can be used as imaging biomarkers to predict the recurrence of early stage of HCC after TACE treatment.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignant hepatic tumor worldwide and the third most common cause of cancer-related death. Despite the improvements in the treatment and postoperative management of HCC, the tumor recurrence rate remains high and the prognosis is still poor [1]. Therefore, it is essential to predict the recurrence of HCC after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment to avoid delayed detection and to do re-treatment timely. As cutting-edge functional imaging technologies, intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) and amide proton transfer (APT) imaging can provide biological information in terms of molecules and metabolism other than morphology [2]. In addition, these two technologies have been applied to evaluating the therapeutic efficacy and prognosis of various malignant tumors [3,4]. However, the role of APT and IVIM in predicting the recurrence of early stage HCC treated with TACE has not been reported yet. This study is aimed to investigate whether APT imaging and IVIM imaging parameters can predict the recurrence of early stage HCC treated with TACE.Methods
In this study 35 patients with HCC were recruited. All the subjects underwent abdomen MR imagine on a 3T MR scanner (Discovery MR750W, GE Healthcare, USA) with a 32-channel phased-array torso coil. MR scans included routine abdomen sequences, IVIM (b=0, 20,40,80,160,200,400,600,800,1000s/mm2), and APT (TR, 3000 ms; TE, 12.0 ms; FOV, 36×36 cm2; matrix, 128×128; layer thickness, 5 mm; RF, 2.0 μT; saturation time, 500 ms and 1 NEX resulting in 52 images). Two radiologists, who were blinded to the pathologic results, performed image analyses on GE AW4.6 Workstation. The ROIs were manually placed on the maximal section of each lesion, carefully avoiding the area of cystic degeneration, necrosis, and bleeding. At last, APT parameter MTRasym and the IVIM parameters including apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), pure molecular diffusion coefficient (D), pseudo-diffusion coefficient (D*), and perfusion fraction (f) were measured. The recurrence rate of HCC treated with TACE was recorded after a median follow-up of 6 months. The subjects were divided into the recurrence and non-recurrence groups. The parameters from those two groups were compared by using independent t-tests. Diagnostic performance was evaluated with the operating characteristic curve (ROC curve) analysis. The optimal threshold of each parameter and the corresponding sensitivity and specificity were calculated.Results and Discussion
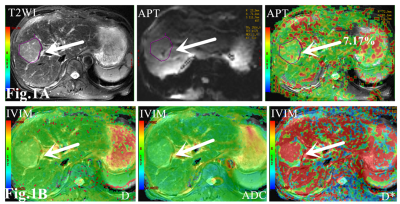
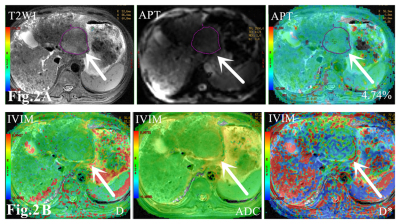
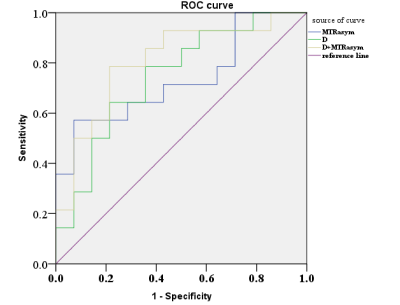
Except parameter D, there were no significant differences in ADC, D* and f values between the two groups (P > 0.05). The APT value of the recurrence group in Fig.1A (7.76 ± 2.55%) was higher than that of the non-recurrence group in Fig. 2A (5.95 ± 1.57%) with P = 0.034. D value of the recurrence group in Fig.1B (0.78± 0.17)×10−3 mm2/s was lower than that of the non-recurrence group in Fig. 2B (0.99± 0.26)×10−3 mm2/s) with P = 0.024. D value had the higher AUC than MTRasym value in predicting the recurrence of early stage HCC treated with TACE, but the combination of them had the highest AUC value (AUC=0.806) as shown in Fig.3.Conclusion
In this study, we explored the performance of APT and IVIM in predicting the recurrence of early stage HCC treated with TACE. This study showed that recurrence group of HCC treated with TACE had higher APT value and lower D value, suggesting strong protein secretion ability and strong confined diffusion [5]. APT combined with IVIM imaging may be a useful technique in predicting the recurrence of early stage HCC treated with TACE.Acknowledgements
I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose with regard to the subject matter of this presentation.References
[1]. Wang Chun-Yan, Li Sheng mian, Clinical characteristics and prognosis of 2887 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A single center 14 years experience from China.[J] .Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98(4): e14070.
[2]. Li Beibei, Sun Hongzan, Zhang Siyu et al. The utility of APT and IVIM in the diagnosis and differentiation of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix: A pilot study.[J] .Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 63: 105-113.
[3].Niu Jinliang,Li Wenjin,Wang Hongwei et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow in patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a pilot study of prognostic value.[J] .J Magn Reson Imaging, 2017, 46: 476-482.
[4].Krikken Erwin,Khlebnikov Vitaliy,Zaiss Moritz et al. Amide chemical exchange saturation transfer at 7 T: a possible biomarker for detecting early response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.[J] .Breast Cancer Res., 2018, 20: 51.
[5].Meng Nan, Wang Jing, Sun Jing et al. Using amide proton transfer to identify cervical squamous carcinoma/adenocarcinoma and evaluate its differentiation grade.[J] .Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 61: 9-15.
Figures