4829
Study on Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy Plan Design of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma based on MR Images1Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Jinan, China
Synopsis
To study the feasibility of intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) plan which designed for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) based on MRI-only comparing the dosimetric difference of different CT value assignment methods on dose calculation. Pseudo CT were generated by different assignment methods based on simulation CT. The areas with a difference of more than 1% were mainly distributed in the air cavity, bone periphery and the skin. The assignment method of each tissue and organs were set to Populate CT value compared with other methods has the least influence on the dose calculation of NPC-IMRT plan, which could meet the clinical requirements.
Introduction
Radiotherapy plan based on MRI-only can eliminate registration error. (1) It will become a trend to make radiotherapy plan by using MRI alone. However, MRI does not have electron density information and cannot be used for dose calculation, so it cannot be used in radiotherapy plan design alone. To study the feasibility of intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) plan which designed for nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) based on MRI-only comparing the dosimetric difference of different CT value assignment methods on dose calculation.Materials and Methods
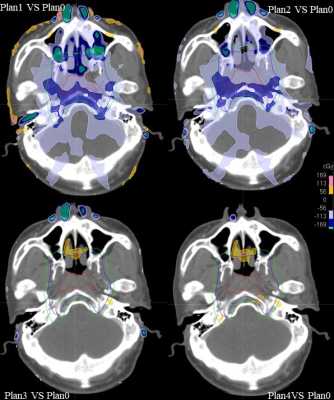
Simulation CT and MR image of thirty-two NPC patients were selected for this study. Populate CT values were obtained by contouring and analyzing tissue of patients including Body, bone, air, brain, eyeball, optic-nerve, lens, parotid, masseter, skin, on their simulation CT. Pseudo CT were generated by different assignment methods based on simulation CT: ①CT1: CT value of all tissues was set to 0HU; CT2: CT value of air cavity was set to Populate CT value based on CT1; CT3: CT value of Bone was set to Populate CT value based on CT2; CT4: CT value of each soft tissue were set to Populate CT value based on CT3. The IMRT plan as Plan0 was designed base on simulation CT. Then Plan0 was transplanted to four pseudo CT to recalculate the dose, and Plan1, Plan2, Plan3 and Plan4, were obtained and difference of dosimetric parameters were compared with Plan0. NPC-IMRT plan was designed base on MRI-only by using the assignment method with CT value of each tissue were set to Populate CT value.Results
The difference of dosimetric indexes of Plan1, Plan2, Plan3, Plan4 decreased in turn compare to Plan0. The differences of V30 in bilateral parotid and Dmax in right optic-nerve between Plan1 and Plan0 were more than 3%, which were 3.13%, 3.08% and 3.07% respectively. The differences of D99 and D95 of PTV, Dmax and D5 of brainstem, Dmax of eyeball, lens and optic nerve, Dmean, V20, D50 of bilateral parotid and Dmax of spinal cord between Plan4 and Plan0 were all less than 1%. The differences of V30 in bilateral parotid between Plan4 and Plan0 were all less than 1.5%. At the pixel point dose distribution comparison, the areas with a difference of more than 1% were mainly distributed in the air cavity, bone periphery and the skin.Discussion
The radiation therapy planning system performs dose calculations by electron density information provided in the patient's CT to obtain an accurate dose distribution. In the present study, the dose was calculated on the assigned image, and the areas with larger dose differences compared with the original plan were mainly concentrated in the cavity gap and bone periphery and skin. This is because the human tissue is uneven, and the head and neck contain many bone and sinus cavities. When high-energy photons enter the cavity, electron imbalance occurs, resulting in a large gap between the cavity and the tissue. (2) Dose transitions, and the absorption of high-density skeletal contrast rays in the head and neck are large, resulting in unevenness and fluctuations in the dose distribution, affecting the results of the final dose calculation. (3) Accurate and more refined divisional regions respectively give grouped CT values, which can be closer to the true electron density of human tissue, have the least impact on NPC-IMRT plan dose calculation, and the dose distribution is closer to the actual situation. (4)Conclusion
The assignment method of each tissue and organs were set to Populate CT value compared with other methods has the least influence on the dose calculation of NPC-IMRT plan, which could meet the clinical requirements. So it should be the first choice of assignment method when designing NPC-IMRT plan based on MR image.Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Guangxi Province (No. AB17195005) and the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (No. 2018GSF118006)References
1. Karlsson M, Karlsson M G, Nyholm T, et al. Dedicated Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Radiotherapy Clinic. Int J Radiat Oncol, 2009, 74(2):644-651.
2. Seif F, Bayatiani MR, Hamidi S, et al. Investigating the Effect of Air Cavities of Sinuses on the Radiotherapy Dose Distribution Using Monte Carlo Method. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2019, 9(1):121-126.
3. Baines J, Zawlodzka S, Markwell T, et al. Measured and Monte Carlo simulated surface dose reduction for superficial X-rays incident on tissue with underlying air or bone. Med Phys. 2018,45(2):926-933.
4. Usui K , Sasai K , Ogawa K . Effect of region extraction and assigned mass-density values on the accuracy of dose calculation with magnetic resonance-based volumetric arc therapy planning. Radiological Physics and Technology, 2018.