4825
Application Value of Radiomics Approach in Predicting Chromosomal Arms 1p/19q in Low-Grade Gliomas1Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, XianYang, China
Synopsis
Genes play a crucial role in the development, progression and therapeutic outcome of tumors. Several studies have linked codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p/19q in LGG with positive response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy and longer progression-free survival, so 1p/19q status of LGG can impact optimal therapy options. Unfortunately, determining 1p/19q status requires surgical biopsy to identify chromosomal deletion. Radiomics, which extracts high-throughput features from medical images, showing great advantages in tumor phenotype classification, treatment options and prognosis analysis.
Objective
To evluate the value of radiomics in predicting the 1p/19q status of Low-Grade Gliomas (LGG) based on T2-weighted MR images.Materials and Methods
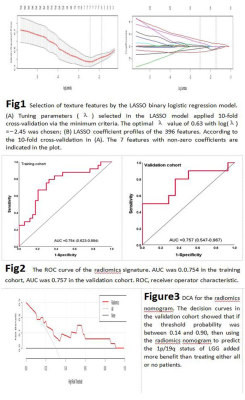
All study patients (n=159) from the Cancer Genome Atla (TCGA) data portal who had pre-operative MRI images and biopsy proven 1p/19q status consisting either no deletion (n=85) or co-deletion (n=74) were included. Patients were divided into training (n=111) and validation cohorts (n=48) in a ratio of 7:3. T2-weighted images were imported into the ITK-SNAP to manually delineate volume of interest (VOI) of the entire-tumor. Each VOI produced 396 radiomics features including Histogram, GLCM, GLSZM, RLM, Form Factor and Haralick. LASSO regression was used for feature screening. A formula was generated using a linear combination of selected features that were weighted by their respective LASSO coefficients. A radiomics score was calculated for each patient by the formula to reflect the 1p/19q status. The predictive accuracy of radiomics was quantified by the area under curve (AUC) of a ROC curve in both cohorts. The calibration degree (CD) of the radiomics was evaluated by Hosmer-Lemeshow test. The clinical usefulness of the radiomics signatures was assessed by decision curve analysis (DCA).Results
Seven radiomics features with non-zero coefficients were chosen to build a radiomics label that that significantly correlated with the 1p/19q status with an AUC, sensitivity, specificity and CD of 0.754, 79%, 74% and 0.647 in the training cohort; and 0.757, 80%, 71% and 0.731 in the validation cohort. DCA for the radiomics label showed that if the threshold probability was between 0.14 and 0.90, using the radiomics label to predict 1p/19q status added more benefit than treating either all or no patients.Conclusion
The radiomics label can be used as a noninvasive method to predict the 1p/19q status of LGG for clinical decision optimal therapy options.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Clark K , Vendt B , Smith K , et al. The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): Maintaining and Operating a Public Information Repository[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2013, 26(6):1045-1057.
2.Erickson, Bradley; Akkus, Zeynettin; Sedlar, Jiri; Korfiatis, Panagiotis. (2017). Data From LGG-1p19qDeletion. The Cancer Imaging Archive.
3.Yushkevich P A , Piven J , Hazlett H C , et al. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability[J]. NeuroImage, 2006, 31(3):1116-1128.
4.Wang Q, et al. Radiomics nomogram building from multiparametric MRI to predict grade in patients with glioma: a cohort study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;49(3):825–833.