4789
Differentiation of Liver Abscess and Liver Metastatic Tumor: Diffusion Weighted Images Texture Analysis1The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China, 2Translational Medicine Team, GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 3GE Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Liver abscess is a serious abdominal infection that may be caused by bacteria, fungi, or parasites. The typical imaging findings of liver abscess on multiphase contrast-enhanced CT are well known, such as the “double target sign” in liver abscess, multilocular appearance, small bubbles or gas-liquid plane in the cavity. liver metastasis that develop central necrosis or cyst may mimic the appearance of liver abscess.
Purpose
To determine feasibility of texture analysis of diffusion weighted imaging for differential diagnosis of liver abscess and liver metastatic tumor.Introduction
MRI has the characteristics of multi-azimuth, multi-direction and multi-parameter, which plays an important role in the diagnosis of liver abscess and liver metastasis[1,2]. The role of MRI in the diagnosis of liver abscess has been discussed in previous studies. Texture analysis (TA) is an emerging imaging application that allows for quantification of the heterogeneity in an organ or focal lesion by analyzing the distribution and/or relation-ship of pixel gray levels of intensity within a region of interest(ROI)[3].Methods
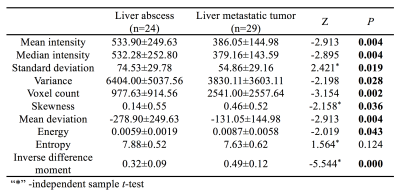
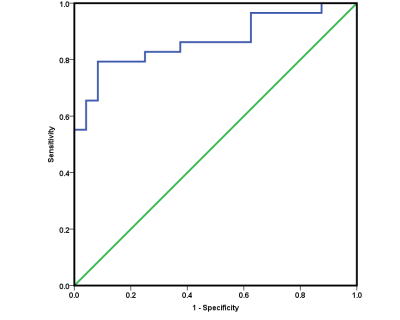
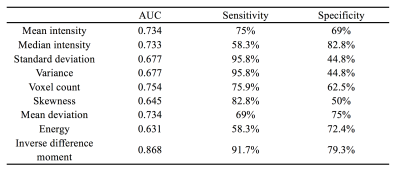
From June 2015 to Dec 2018, 43 patients with 66 liver lesions(24 liver abscess by percutaneous drainage or combining with clinical symptom and imaging after follow-up, and 29 liver metastatic tumor by medical history and follow-up) underwent 1.5T MRI scans. The images of DWI were derived for texture analysis on AW4.5 workstation. The ROI was placed at the maximum level of high signal region, 2mm inside along the medial margin of the lesion. Texture features derived from the gray-level histogram, co-occurrence were calculated, including mean intensity, median intensity, standard deviation, variance, voxel count, skewness, mean deviation, energy, entropy, inverse difference moment. These parameters of liver abscess and liver metastatic tumor were compared by independent sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U. The operating characteristic curve of subjects was drawn, and the area under the curve was obtained. Sensitivity and specificity in calculating the optimal threshold.Results
The mean intensity, median intensity, standard deviation and variance of liver abscesses were significantly higher than that of liver metastatic tumors(P<0.05). The voxel count, skewness, mean deviation and inverse difference moment of liver metastatic tumors were significantly higher than that of liver abscesses(P<0.05). The entropy of liver abscesses were higher than that of liver metastatic tumors(P>0.05). The energy of liver metastatic tumors were higher than that of liver abscesses(P>0.05) (Table 1). Inverse difference moment is the best parameters for differential diagnosis. The area under curve(AUC) was 0.868. The sensitivity and specificity of liver metastatic tumors except liver abscesses were 91.7% and 79.3% (Table 2, Figure 1).Conclution
Texture analysis of DWI images is an effective methods in differential diagnosis of liver abscess and liver metastatic tumor. Inverse difference moment is the best texture parameters.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgements found.References
1. Giambelluca D, Panzuto F, Giambellluca E, et al. The “double target sign” in liver abscess. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018. 43(10): 2885-2886.
2. Alsaif HS, Venkatesh SK, Chan DS, et al. CT appearance of pyogenic liver abscesses caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Radiology. 2011, 260(1): 129-138.
3. Stocker D, Marquez HP, Wagner MW, et al. MRI texture analysis for differentiation of malignant and benign hepatocellular tumors in the noncirrhotic liver. Heliyon. 2018, 4(11): e00987.