4788
The value of ADC values and texture analysis in evaluating the differentiation degree of cervical squamous cell carcinoma1The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Hefei, China
Synopsis
Single ADC value can only distinguish low-differentiated CSCC from medium-well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, but it cannot distinguish medium-differentiated CSCC from highly-differentiated CSCC. ADC value combined with texture features can improve the efficacy of differentiation degree of CSCC before surgery.
INTRODUCTION
To explore the value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values and texture analysis in evaluating the differentiation degree of cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC).METHODS
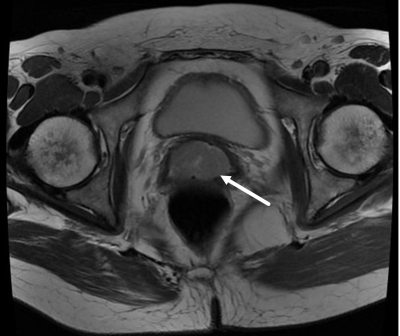
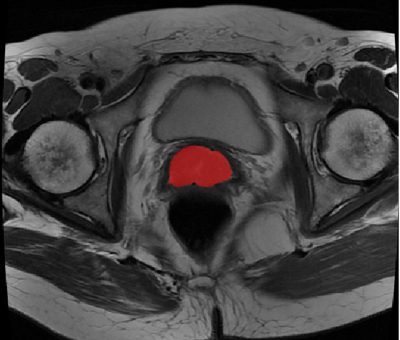
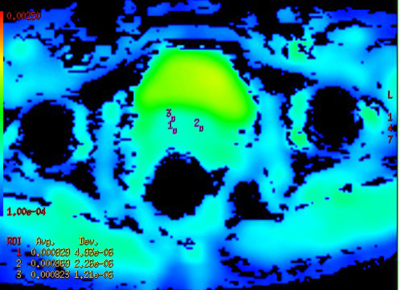
Totally 88 patients with pathologically confirmed CSCC were included. ALL the patients were performed routine MRI and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) with b=0, 1000s/mm2, and the ADC values of them were measured on postprocess workstation. Texture analysis was performed on MRI images, parts of the parameters were obtained. The results were compared by using SPSS software’s one-way ANOVA analysis and LSD, P<0.05 was statistically significant.RESULTS
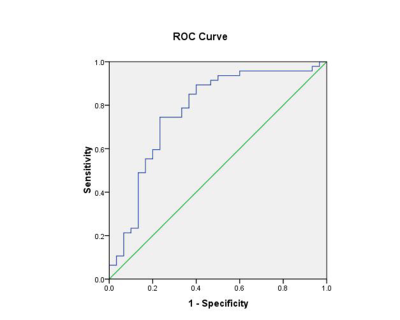
The differences between the poorly and highly differentiated groups and between poorly and moderately differentiated groups were both statistically significant (P < 0.05), while the differences between the moderately and highly differentiated groups were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). For the comparison of texture features among the three groups, there were statistically significant differences in standard deviation and entropy (P < 0.05), and there were no statistically significant differences in energy, kurtosis, mean value and skewness (P > 0.05).CONCLUSION
Single ADC value can only distinguish low-differentiated CSCC from medium-well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, but it cannot distinguish medium-differentiated CSCC from highly-differentiated CSCC. ADC value combined with texture features can improve the efficacy of differentiation degree of CSCC before surgery.KEY WORDS
cervical cancer; squamous cell carcinoma; pathological differentiation; DWI; texture analysisAcknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. SIEGEL, REBECCA L, MILLER, et al. Cancer Statistics[J]. CA: A cancer journal for clinicians, 2017, 67(1): 7-30.
2. LUCAS R, LOPES D J, CUNHA T M. Added value of diffusion-weighted MRI in detection of cervical cancer recurrence compared with morphologic and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI sequences[J]. Diagnostic and interventional radiology: official journal of the Turkish Society of Radiology, 2015, 21(5): 368-375.
3. TAKAHARA T, IMAI Y, YAMASHITA T, et al. Diffusion weighted whole body imaging with backgrond body signal suppression(DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display[J]. Radiat Med, 2004, 22(4): 275-282.
4. LE B D. Diffusion, confusion and functional MRI[J]. NeuroImage, 2012, 62(2): 1131-1136.
5. KASSNER A, THORNHILL R E. Texture analysis: a review of neurologic MR imaging applications[J]. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol, 2010, 31 (5): 809-816.
6. CASTELLANO G, BONILHA L, LI L M, et al. Texture analysis of medical images[J]. Clinical Radiology, 2004, 59(12): 1061-1069.
7. FUJIMA N, HOMMA A, HARADA T, et al. The utility of MRI histogram and texture analysis for the prediction of histological diagnosis in head and neck malignancies[J]. Cancer imaging: the official publication of the International Cancer Imaging Society, 2019, 19(1): 5.