4764
Rectal Carcinoma at 3T Assessed via iShim DWI: A Comparison of Image Quality with RESOLVE1Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University & Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou, China, 2Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 3MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, China, 4MR Scientific Marketing, Siemens Healthcare, Xi'an, China, 5Application Development, Siemens Healthcare GmbH, Erlangen, Germany
Synopsis
This study evaluated a new diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) technique for assessing rectal cancer. Based on a population of 12 patients diagnosed with rectal carcinoma, images were acquired using both Read-out Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging (RESOLVE) and integrated slice-specific shimming (iShim)-DWI sequences using the same field of view (FOV) at 3T in assessment of rectal carcinoma. The quality of the images was compared based on independent review by radiologists plus parameter data analysis. The results showed that the image quality and lesion conspicuity of the iShim-DWI sequence were significantly better than RESOLVE DWI sequence in assessment of rectal carcinoma at 3T.
Background and Purpose
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) plays a valuable role in assessing rectal cancer, such that the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of cancerous rectal tissue may quantitatively predict histopathological tumor (T) staging and grade in a noninvasive manner1. Read-out Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging (RESOLVE) and integrated slice-specific shimming (iShim)-DWI sequences have shown greater advantages than conventional DWI, based on previous studies.2 3 However, no previously published research was found that analyzes the image quality (IQ) of both RESOLVE and iShim-DWI sequences in rectal cancer. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare IQ between RESOLVE and iShim-DWI sequences using the same field-of-view (FOV) at 3T in assessment of rectal carcinoma.Materials and Methods
This study was approved by the Hospital Ethics Committee, and written informed consent was acquired. Participants comprised 12 patients with rectal cancer who received magnetic resonance (MR) examinations on a 3T scanner (MAGNETOM Prisma, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), including RESOLVE and a prototype iShim-DWI sequences. The detailed sequence parameters used are as follows: (1) RESOLVE-DWI: thickness =3mm, repetition time/echo time (TR/TE) =4600-5200ms/53-56ms, matrix=142X142, FOV=220mm, scanning time=204s, b=50, 1000 s/mm²; (2) iShim-DWI: thickness =3mm, TR/TE =7700ms/68ms, matrix=248X256, FOV=220mm, scanning time=78s, b=50, 1000 s/mm².The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were quantitatively evaluated using a paired t-test. Two radiologists independently assessed subjective IQ parameters based on: image sharpness, distortion, artifacts, lesion conspicuity, and overall subjective IQ of both sequences. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare subjective IQ scores and tumor ADCs between RESOLVE-DWI and iShim-DWI.Results
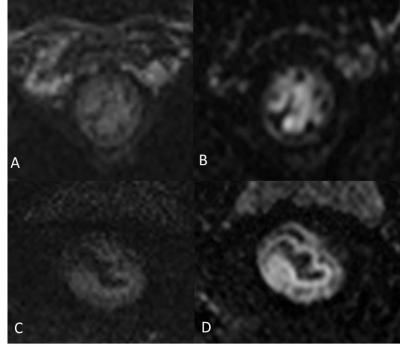
CNR was significantly greater in iShim-DWI (9.57 ± 2.49, [Figure 1; images A, C]) than that in the RESOLVE DWI (7.74 ±2.21, P < 0.001 [Figure 1, Image B]). SNR was significantly higher in iShim-DWI (130.59 ± 11.01) than that in RESOLVE DWI (37.16 ± 11.20, P < 0.001). The subjective IQ parameters of iShim-DWI sequence (Figure 1; image A) were rated superior to those of RESOLVE DWI (Figure 1; image B) sequence by both readers (P < 0.001). No significant difference was found between the mean tumor ADC values of both sequences (iShim-DWI [0.991 ± 0.121]; RESOLVE DWI [0.100 ± 0.126 x 10-3 mm2 /s, P = 0.617]).Conclusion
The iShim-DWI sequence provided significantly better IQ and lesion conspicuity than RESOLVE DWI sequence in assessment of rectal carcinoma at 3T. The number of cases is small, and larger sample size may provide more information.Acknowledgements
References
1. Peng Y, Li Z, Tang H, et al. Comparison of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and conventional DWI techniques in the assessment of rectal carcinoma at 3.0T: Image quality and histological T staging. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 2018;47(4):967-75. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25814 [published Online First: 2017/07/12]
2. Li H, Liu L, Shi Q, et al. Bladder cancer: detection and image quality compared among iShim, RESOLVE, and ss-EPI diffusion-weighted MR imaging with high b value at 3.0 T MRI. Medicine 2017;96(50):e9292. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009292 [published Online First: 2018/02/03]
3. Song C, Cheng P, Cheng J, et al. Differential diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal lymphoma based on DCE-MRI and RESOLVE-DWI. European radiology 2019 doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06343-0 [published Online First: 2019/08/03]